Class 4 Exam > Class 4 Notes > Chapter Notes: Evolution of Computer
Evolution of Computer Chapter Notes - Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Early Calculating Machines |

|
| Different Generations of Computers |

|
| Classification Based on Purpose of Computers |

|
Introduction
Charles Babbage, a Math Professor at Cambridge University, dreamed of creating a machine with input, processing, output, and storage capabilities, which later evolved into modern computers. He's known as the 'Father of Computers,' with the term 'computer' originating from 'compute,' meaning to calculate.
 Charles Babbage
Charles Babbage
Early Calculating Machines
Napier’s Bones
Sir John Napier's invention, Napier’s Bones, simplified arithmetic operations. It featured strips of wood or bones inscribed with multiplication tables, enabling users to perform calculations more efficiently.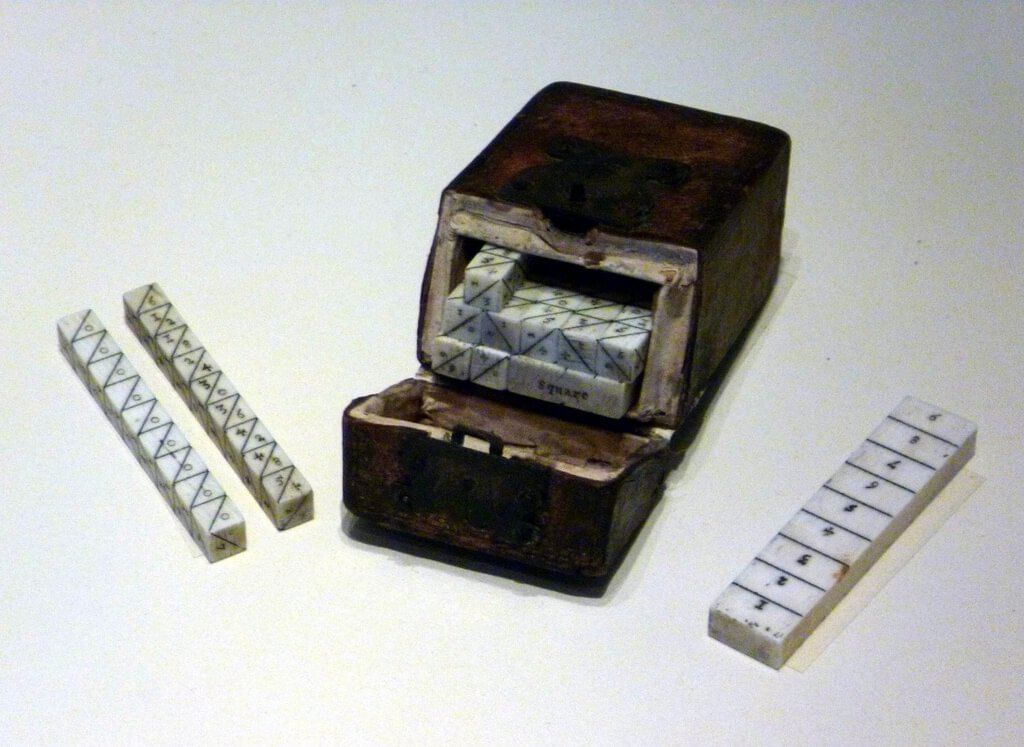
Pascaline
Blaise Pascal's Pascaline was among the earliest mechanical calculators. It facilitated addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, streamlining complex arithmetic tasks.
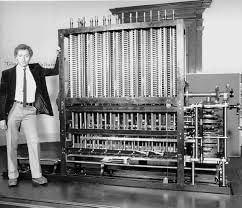
Charles Babbage's Difference Engine was designed to generate accurate mathematical tables. This precursor to modern computers automated the production of these tables, reducing errors and improving efficiency. Babbage's subsequent concept, the Analytical Engine, laid the groundwork for programmable computers.
Different Generations of Computers
First Generation Computers (Vacuum Tubes) (1942-1954)
- These were the earliest computers that used vacuum tubes as their main components. They were massive machines, such as the MARK-I, EDVAC, and UNIVAC I.
- For example, MARK-I was about 15 meters long with wires spanning around 800 kilometers. Despite their size, they were fully automatic, a significant advancement at the time.
- However, they had limitations like slow processing speeds, high power consumption, and requiring substantial space for installation.
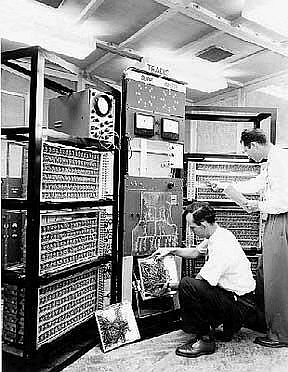
Second Generation Computers (Transistor) (1954-1959)
- The second generation saw the introduction of transistors, which replaced vacuum tubes. This transition led to computers like IBM 140, IBM 700, MARK III, and UNIVAC LEO.
- Transistors made computers smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient. Additionally, high-level programming languages like BASIC and Pascal were developed during this period, further improving usability.
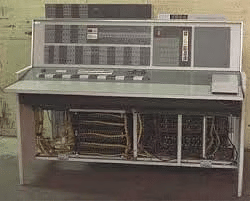
Third Generation Computers (1959-1971)
- The third generation introduced integrated circuits (ICs), which contained multiple transistors and resistors on a single chip. This innovation significantly reduced the size of computers while increasing processing speed and memory capacity.
- Computers like CDC, PDP, IBM-360, Honeywell-200, and ICL-1900 emerged during this period. High-level languages such as RPG and ALGOL facilitated easier programming.

Fourth Generation Computers (1971-present)
- The fourth generation is characterized by the invention of the microprocessor, a single chip containing the central processing unit (CPU).
- This breakthrough led to the development of microcomputers or desktop computers like Intel-4004, Apple, IBM-370, and Honeywell-6080.
- Fourth-generation computers became faster, cheaper, more reliable, and accessible to the general public.
- Programming languages like Pascal, LISP, ADA, and SQL further diversified software capabilities.

Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Future)
- Fifth-generation computers are characterized by their focus on Artificial Intelligence (AI). These computers aim to replicate human-like thinking and decision-making processes.
- While still in development, they hold the potential to outperform humans in certain tasks, marking a significant leap in computing capabilities.

Classification Based on Purpose of Computers
Digital Computers
Digital computers process data using discrete, numerical values represented in binary code (0s and 1s). They operate based on electronic circuits that perform logical operations, arithmetic calculations, and data storage using binary digits (bits). Digital computers are highly accurate and versatile, capable of executing complex algorithms and handling vast amounts of data.Digital Computer
Analog Computers
Analog computers, on the other hand, process data using continuous physical quantities, such as voltage, current, or rotation. They represent and manipulate data using analog signals that vary smoothly over time. Analog computers are particularly suited for tasks involving continuous physical phenomena, such as electrical circuits, fluid dynamics, and control systems. Analog Computer
Analog Computer
FAQs on Evolution of Computer Chapter Notes - Class 4
| 1. What are early calculating machines mentioned in the article? |  |
Ans. Early calculating machines mentioned in the article include the abacus, the slide rule, and mechanical calculators.
| 2. How are different generations of computers classified in the article? |  |
Ans. Different generations of computers are classified based on their technological advancements and major developments in hardware and software components.
| 3. What is the classification of computers based on their purpose mentioned in the article? |  |
Ans. The classification of computers based on their purpose includes mainframe computers, personal computers, and supercomputers, each serving specific functions.
| 4. What are some examples of early calculating machines discussed in the article? |  |
Ans. Some examples of early calculating machines discussed in the article are the Pascaline, the Jacquard Loom, and the Analytical Engine.
| 5. How did the evolution of computers impact society, as mentioned in the article? |  |
Ans. The evolution of computers has revolutionized various aspects of society, including communication, education, research, and business operations.
Related Searches














