Interpersonal Skills Including Communication Skills-2 | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Emotional Intelligence |

|
| Key Skills of Emotional Intelligence |

|
| Advantages of Emotional Intelligence |

|
| Stress Management |

|
| Leadership Styles |

|
| Conflict Management |

|
Emotional Intelligence
- Emotional Intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, manage, and assess emotions, both in oneself and in others.
- Some researchers suggest that emotional intelligence can be learned and strengthened, while others claim it to be an inborn characteristic.
- Since 1990, Peter Salovey and John D Mayer have been the leading researchers on emotional intelligence.
- In their influential article ‘Emotional Intelligence’ in 1990, they defined emotional intelligence as, “the subset of social intelligence that involves the ability to monitor one’s own and others’ feelings and emotions, to discriminate among them and to use this information to guide one’s thinking and action”.
Key Skills of Emotional Intelligence
- Select socially appropriate responses to situations and others emotions.
- Self-regulate ones own emotional state.
- Arouse or affect emotions of others.
- Use emotional knowledge to solve problems.
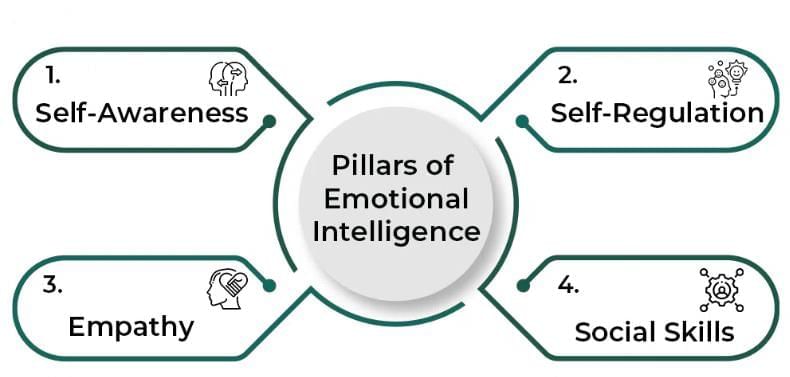 Key Skills of Emotional Intelligence
Key Skills of Emotional Intelligence
Advantages of Emotional Intelligence
(i) Advantages to the individual:
- Improved self-confidence: Individuals with high emotional intelligence often experience a boost in their self-confidence.
- Willingness to express thoughts: They are more open and willing to express their thoughts and opinions.
- Advocacy for values: Such individuals are better at advocating for their personal values and beliefs.
- Enhanced resilience: Emotional intelligence helps individuals become more resilient in the face of challenges and changes, both in their personal and professional lives.
(ii) Advantages to organisations:
- Increased confidence: Employees with high emotional intelligence contribute to a higher level of confidence within the organization.
- Boosted motivation and commitment: Emotional intelligence leads to increased motivation and commitment among employees towards the organization’s goals.
- Better application of skills: Employees are better able to apply their unique skills to tasks when they possess emotional intelligence.
- Willingness to share ideas: There is a greater willingness to share creative and innovative ideas within the organization.
- Improved relationships: Emotional intelligence fosters better relationships among colleagues and with clients.
Factors of Emotional Intelligence
EI has four important factors that help to become an expert in EI. These factors are:
(i) Perceiving emotions: The first step in understanding emotions is to perceive them accurately. In many cases, this might involve understanding non-verbal signals, such as body language and facial expressions.
(ii) Reasoning with emotions: The next step involves using emotions to promote thinking and cognitive activity. Emotions help to prioritise what we pay attention to and react to, we respond emotionally to the things that garner our attention.
(iii) Understanding emotions: The emotions that we perceive can carry a wide variety of meanings. If someone is expressing angry emotions, the observer must interpret the cause of their anger and what it might mean. To illustrate, if your boss is acting angrily, it might mean that he/she is dissatisfied with your work; or it could be because he/she had some bitter experience from you etc.
(iv) Managing emotions: The ability to manage emotions effectively is a key part of emotional intelligence. Regulating emotions, responding appropriately and responding to the emotions of others are all important aspects of emotional management.
Example 1: One of your roommates has the habit of speaking loudly on the phone which disturbs you while studying. Despite your repeated requests, his habit seems to be getting worse. You
(a) start speaking loudly when your room-mate is studying to give him a lesson
(b) fight with your room-mate
(c) complain about your room-mate to the hostel warden
(d) Have an open discussion with your room-mate about your problem and try to solve it amicably
Ans: (d) Having an open discussion shows that you have the ability to be calm and exercise control over your emotions while reacting to an adverse situation. Option (c) would mean that you do not have the ability to handle problems effectively to get the desired solution. Fighting with a roommate would also is not an appropriate step as mentioned in option (b). Option (d) is not a peaceful solution to your problem. So, the right answer is (d).
Example 2:You have recently joined a project as a team manager. One of your team members is always criticising you. Once, he severely criticised your working style in front of other team members. What would you do?
(a) Leave the project as you cannot bear your insult
(b) Complete your project and then stop responding to that person
(c) Start criticising that fellow behind his back
(d) Agree to a short break before resuming the discussion
Ans:(d) Option (d) shows your ability to perceive, control and evaluate emotions. It shows that you are able to deal with social or emotional conflicts, expressing feeling and dealing with emotional situations. Option (c) would amount to ridiculous behaviour, option (b) shows your inability to listen to the other person’s perspective and option (a) would be a negative impression among team members as leaving the project in between. Hence, option (d) is correct.
Stress Management
Stress is a state of psychological and/or physiological imbalance resulting from the disparity between situational demands and the individual’s ability and motivation to meet those demands.
Causes for Stress
- Long Hours of Work: Extended work hours can lead to fatigue and burnout, contributing to stress.
- Negative Reactions to Stressors: How individuals respond to stressors can impact their stress levels. Negative reactions can exacerbate stress.
- Problematic Work Relationships: Difficulties in relationships with colleagues or supervisors can create a stressful work environment.
- Insufficient Resources and Communication: Lack of necessary resources and poor communication can hinder job performance, leading to stress.
- Poor Time Management: Inability to manage time effectively can result in missed deadlines and increased pressure.
- Limited Involvement in Decision-Making: Not being involved in decisions that affect one's work can lead to feelings of helplessness and stress.
- Workplace Bullying: Experiencing bullying in the workplace can cause significant emotional distress and stress.
- Unmanageable Workload: Having too much work to handle can lead to overwhelm and stress.
- Inability to Prioritize Tasks: Difficulty in prioritizing tasks can result in confusion and increased pressure.
- Personal Life Interfering with Work: Struggles in personal life can spill over into work, creating additional stress.
- Excessive Commuting Time: Long commutes can add to the overall stress levels by reducing personal time and increasing fatigue.
Types of Stress Management
1. Distress or Negative Stress: It is a difficult situation where one is completely overstraining. Here, one feels like he is at the mercy of a situation beyond his control. It seems like there are no options and no possibilities to change anything.
2. Eustress or Positive Stress: This is often felt when we are confronted with demanding and challenging situation which we are capable of handling. Here, challenges and responsibility give us a sense of thrill and excitement. Types of Stress Management
Types of Stress Management
Techniques to Manage Stress
1. Becoming aware of the signs of stress and avoiding them.
2. Learning the skills of active coping relaxation.
3. Developing lifestyle that creates wall against stress.
4. Maintaining good rapport by using problem-solving techniques.
5. Maximising chances of early success.
6. Getting the work done by cooperation and negotiation.
7. Doing physical activities to release stress causing toxin from body.
8. Making better time management.
Example 3: You are on the doors to enter into security check. It’s already late as you left home early, but got struck at in traffic, your flight is going to take off in 15 min, but the security personnels are doing their duty without any knowledge of your flight timings. You would
(a) shout on security guards to let you inside
(b) inform security people that you are late and about to miss the flight and ask them to let you go as soon as possible
(c) give a call to the police to help you
(d) Both ‘b’ and ‘c’
Ans: (b) Shouting on security check is negative action and giving call to the police would unnecessarily delay the process of security check. So, it is better to request by informing the security persons with whom you are in immediate contact. Thus, it solves the problem. So, the best answer is option (b).
Example 4: You are burdened by the workload given by your boss. This has led to sleepless nights and is also affecting adversely the quality of your work. You would
(a) search for a new job
(b) resign yourself from the job
(c) discuss the problem with the boss
(d) complain to the higher authorities against the boss
Ans:(c) It is natural to anybody, if the workload is very much, it burdens and results on the quality of work.
At this moment, the only best option is to discuss it with the boss, he would lessen the burden. So, the correct answer is option (c).
Leadership Styles
In the past several decades, management experts have gone quite unorthodox to define leadership and what their attitudes are towards it. They have shifted from a very classical autocratic approach to a very creative, participative approach. Somewhere along the line, it was determined that not everything old was bad and not everything new was good. Rather, different styles were needed for different situations and each leader needed to know when to exhibit a particular approach.
Four of the most basic leadership styles are:
1. Autocratic
2. Bureaucratic
3. Democratic
4. Laissez-faire
Although good leaders use all the styles, with one of them normally dominant, bad leaders tend to stick with only one style.
1. Autocratic Leadership Style: The autocratic leadership style is often considered the classical approach. It is one, in which the manager retains as much power and decision-making authority as possible.
The manager does not consult employees, nor are they allowed to give any input. Employees are expected to obey orders without receiving any explanations. The motivation environment is produced by creating a structured set of rewards and punishments.
This leadership style has been greatly criticised during the past 30 years. Some studies say that organisations with many autocratic leaders have higher turnover and absenteeism than other organisations. New-generation employees have proven to be highly resistant to this management style.
2. Bureaucratic Leadership Style: In this type of leadership, the manager manages ‘by the book’. Everything must be done according to procedure or policy.
If it isn’t covered by the book, the manager refers to the next level above him or her. This manager is really more of a police officer than a leader. He or she enforces the rules.
3. Democratic Leadership Style: This leadership style is also called the participative style as it encourages employees to be a part of the decision-making. The democratic manager keeps his or her employees informed about everything that affects their work and shares decision-making and problem-solving responsibilities.
This style requires the leader to be a coach who has the final say but gathers information from staff members before making a decision.
4. Laissez-faire Leadership Style: This leadership style is also known as the hands-off style. It is one in which the manager provides little or no direction and gives employees as much freedom as possible.
All authority or power is given to the employees and they must determine goals, make decisions and resolve problems on their own. It is a new and emerging style usually being practiced in Research and Development (R&D) field.
 Styles of LeadershipExample 5:When it comes to working with others, how does a good leader function?
Styles of LeadershipExample 5:When it comes to working with others, how does a good leader function?
(a) He manages to share the work around equally
(b) He likes to organise all the members of his team
(c) He end up doing most of the work
(d) He prefers to work on his own
Ans: (a) A good leader must have the ability to coordinate any work and distribute work equally among the members of his team. So, the best course of action is as given in option (a).
Example 6: You are the leader of a team. Maximum members of your team are educated and dynamic. Which one of the following leadership styles is best suited to get optimum level of output?
(a) Consultative
(b) Exploitative
(c) Benevolent
(d) Participative
(e) All of these
Ans: (a) In consultative leadership style, the leader, while using the skill, experiences and ideas of others, retains the final decision-making power. In exploitive leadership style, leader uses threats and other fear-bused method to achieve conformance. This type leadership is fatal when team members are educated and dynamic.
The benevolent system also falls under the authoritarian style, but the negative factors are replaced with positive rewards as the primary motivating factor.
A unique managerial style that many educated team members feel comfortable with, is the participative style.
Most of the authority, not all, is given to the team, the manger remains the team leader.
Hence, to get optimum level of output, option (d), i.e. participative leadership style would be appropriate.
Conflict Management
- Conflict may be defined as a struggle or contest between people with opposing needs, ideas, beliefs, values or goals.
- Conflict on teams is inevitable; however, the results of conflict are not predetermined.
- Conflict might escalate and lead to non-productive results, or conflict can be beneficially resolved and lead to quality final products.
- Therefore, learning how to manage conflict is integral to a high-performance team.
- Although, very few people go looking for conflict, more often than not conflict results because of miscommunication between people with regard to their needs, ideas, beliefs, goals or values.
- Conflict management is the principle that believes all conflicts cannot necessarily be resolved, but learned to decrease the odds of non-productive escalation.
- Conflict management involves acquiring skills related to conflict resolution, self-awareness about conflict modes, conflict communication skills and establishing a structure for management of conflict in your environment.
- Listening, oral communication, interpersonal communication and teamwork rank near the top of skills that employers seek in their new hires.
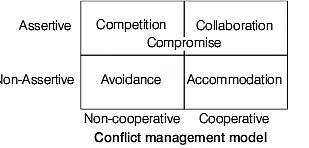
- When you learn to effectively manage and resolve conflicts with others, then more opportunities to get successful team memberships are available to you.
- If, we can learn to manage this highly probable event called conflict (we have average five conflicts per day), then we are less apt to practice destructive behaviours that will negatively impact our team.
- Although, conflict may be misunderstood and unappreciated, research shows that unresolved conflict can lead to aggression.
- Most of us use conflict skills that we observed growing up, unless we have made a conscious effort to change our conflict management style.
- Some of us observed good conflict management, while others observed faulty conflict management.
- Most of us have several reasons to improve our conflict-management skills.
- Most people do not resolve conflicts because they either have a faulty skill set and/or because they do not know the organisation’s policy on conflict management.
- All team members need to know their conflict styles, conflict intervention methods and strategies for conflict skill improvement.
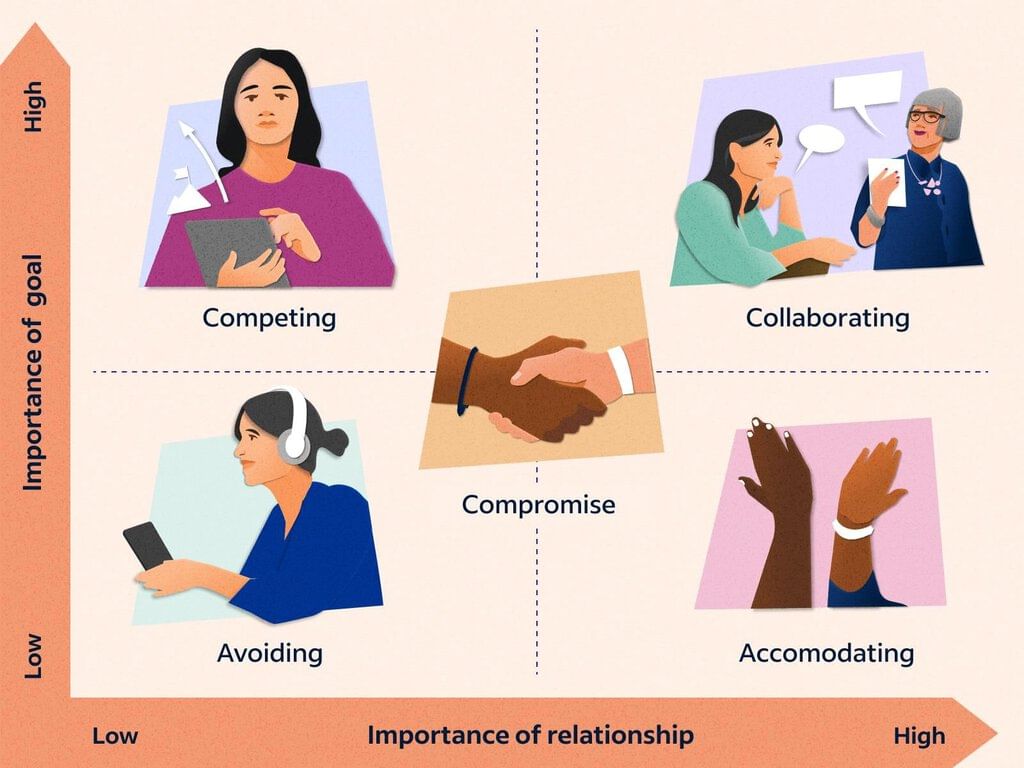 Conflict Management Example 7: The two employees of a company have different ideas and belief which may lead to
Conflict Management Example 7: The two employees of a company have different ideas and belief which may lead to
(a) communication
(b) conflict
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b) Different ideas and beliefs lead to conflict. So, the correct answer is option (b).
Example 8: Conflict can be a constructive force, if it is
(a) resolved through various techniques
(b) presented with many solutions
(c) considered as an essential aspect of an organisation
(d) All of the above
Ans: (c) If the conflict can be managed effectively, then the conflict becomes constructive conflict. Constructive conflicts appropriately balance the interests of both parties to maximise the opportunities for mutual gains.
Options (a) and (b) are the steps in order to manage the conflict effectively. Not all conflicts are essential aspect of an organisation, e.g. destructive conflict. But then also, most of them are considered as an essential aspect. Thus, option (c) is the right answer.
|
208 videos|272 docs|138 tests
|
FAQs on Interpersonal Skills Including Communication Skills-2 - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What is emotional intelligence and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How can emotional intelligence improve stress management? |  |
| 3. What are the different leadership styles influenced by emotional intelligence? |  |
| 4. How does emotional intelligence play a role in conflict management? |  |
| 5. What interpersonal skills are enhanced by emotional intelligence? |  |
















