Energy Chapter Notes | Physics for Grade 11 PDF Download
Introduction
Energy is the ability to do work or cause change and exists in various forms such as kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, and electrical energy.
It is a fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in our daily lives and the natural world. Understanding energy is essential because it helps us comprehend how things move, how machines operate, and how living organisms function.
 Sources of Energy
Sources of Energy
Energy at Work
- Energy is the capacity to do work or cause change.
- It exists in various forms such as chemical, kinetic, potential, thermal, and electrical energy.
- We need energy to perform tasks like moving vehicles, heating homes, and powering electronic devices.
- Energy can be stored in objects like food, batteries, and fuels.
- When energy is transferred, it can do work, such as lighting a lamp, heating a stove, or moving objects.
- However, energy is often wasted as heat due to friction or inefficiencies in energy transfer.
Understanding energy helps us comprehend how things work and how to use energy efficiently.
Energy Sources
- Energy is essential for causing movement and change.
- For humans and animals, food provides the necessary energy.
- Vehicles, such as buses and cars, use fuel as their energy source, which is burned in the engine.
- Both food and fuel store energy and require oxygen to release this energy.
 Type of Energy
Type of Energy
Similarly, batteries store energy due to the chemicals they contain. The chemical reactions within a battery generate an electric current
Motion and Energy Stores
Elastic objects, such as springs or rubber balls, naturally return to their original size and shape. Stretching or squashing them causes them to store energy.
Moving objects store energy known as kinetic energy. Energy due to movement is termed kinetic energy.

Raising an object to a higher position stores energy similarly to how stretching an elastic band requires effort. Lifting heavy objects also stores energy.
A dam holding back water creates a high-level lake that stores energy. This stored energy can be used to generate electricity, known as hydroelectricity.
Energy Stored due to Temperature
- Hot objects store energy due to the motion of tiny particles within them.
- This stored energy is called thermal energy.
- All substances are made of particles that move or vibrate.
- The higher the temperature of an object, the more thermal energy it stores.
Energy Transfers
- Energy transfer involves a decrease in the energy of the source and an increase in the energy of another object or its surroundings.
- When a force moves something, the energy transferred is called work.
Examples of work:
- A bus engine transfers energy from burned fuel to move the vehicle.
- Your legs transfer energy when you walk.
- A snooker ball transfers energy when it strikes another ball.
- Using force to stretch an elastic band.
- Energy transfer causing a temperature rise is called heating.
- Light and sound transfer energy from their sources to other objects.
Examples of energy transfer by light and sound:
- Sound from a vibrating drum transferring energy to your ears.
- Light from the Sun transferring energy to the Earth's surface.
Electricity transfers energy from a battery or power station to electrical devices, enabling them to:
- Do work (motors).
- Emit light (lamps).
- Emit sound (loudspeakers).
- Heat (kettles, ovens).
Energy Dissipation
- Energy can be stored in an object, such as chemical energy in food or potential energy in a spring, and transferred from one object to another.
- When energy is transferred, it changes form but is not lost.
- However, some energy is often transferred into the surroundings as sound, light, or heat due to friction and inefficiencies, which is called energy dissipation.
- For example, when a car moves, some of its fuel's chemical energy is converted to kinetic energy, but some is lost as heat and sound.
- The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed, guiding how we understand energy in different systems and its efficiency.
Wasted and Useful Energy
- When using an electric lamp, energy is transferred from the power supply to the lamp.
- Useful energy: Light emitted from the lamp, which is the intended purpose.
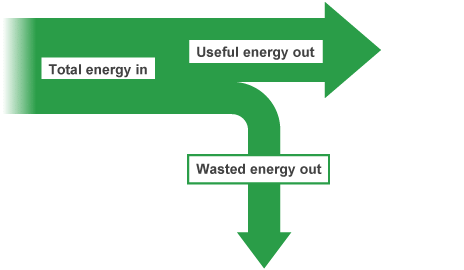
- Wasted energy: Heat produced by the lamp, which is not the intended purpose and is difficult to use for anything else.
- Useful heating: Devices for cooking and heating water transfer energy to increase the temperature of food or water.
- Wasted heating: Energy that heats the air and nearby objects instead of the intended target in a kettle, oven, or stove. The energy that leaves a house through walls, windows, doors, and the roof on a cold day.
Energy Dissipates
- Energy dissipation means that some energy is always wasted during transfers.
- Examples of energy dissipation:
- Electric lamps: Useful light energy and wasted heat energy.
- Electrical devices: Tend to get warmer, wasting energy as heat.
- Moving objects: Slow down due to friction, wasting energy as heat.
- Wasted thermal energy is usually too spread out to be useful.
- Devices can also waste energy by producing unwanted sound, vibrations, or light.
- Once energy spreads out into the environment, it is difficult to use it for anything useful.
|
71 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on Energy Chapter Notes - Physics for Grade 11
| 1. What is energy at work? |  |
| 2. How is energy dissipated in a system? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of energy dissipation in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How can energy dissipation be reduced in a system? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to consider energy dissipation in engineering design? |  |
















