Force and their effects Chapter Notes | IGCSE Cambridge Science for Year 7 - Class 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Gravity |

|
| Air Resistance |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
- Gravity is a force that exists everywhere in the universe. On Earth, gravity pulls objects towards the center of the planet. It is what makes things fall down when we drop them.
- The weight of an object is the measure of the force of gravity pulling on it. Even though we can't see gravity, we can feel its effects every day.
- Gravity keeps us on the ground and governs the motion of planets and stars in space. Understanding gravity helps us explain why objects behave the way they do and how things move in our world and beyond.
Gravity
- Gravity is a fundamental force of nature that affects everything on Earth and in the universe. It is what keeps our feet on the ground and governs the motion of planets, stars, and galaxies.
- Gravity pulls objects towards the center of the Earth, which is why things fall down when we drop them. It is also responsible for the tides and the orbits of planets around the Sun.

- Understanding gravity helps us explain how objects behave in space and on Earth. In this introduction, we will explore the basics of gravity, how it affects us, and its importance in our everyday lives.
Gravity, Mass, and Weight
- All objects on Earth experience a pull force called gravity.
- The weight of an object on Earth is the pull force of Earth's gravity on its mass.
- Objects fall towards Earth due to their weight, a phenomenon known as free fall.

- Gravity always attracts objects towards each other, unlike forces like magnetism which can push objects apart.
- Astronauts in a space station appear weightless because they and the station are falling towards Earth at the same rate, creating the sensation of being in free fall.
- Despite appearing weightless, both astronauts and the space station have weight.
Showing Force of Gravity on Diagrams
You can represent forces as arrows on diagrams. This helps in understanding the forces acting on objects and what these forces will do. The rules for drawing forces are:
- The direction of the arrow shows the direction of the force.
- The length of the arrow is to scale, representing the size of the force.
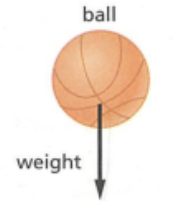
For example, gravity pulls objects towards the Earth's center, so you can draw a downward arrow to represent the force of gravity
Measuring Mass and Weight
Weight is a force, so it is measured using a Newton meter and is given in newtons (N). The weight of an object is proportional to its mass, which can be represented by the equation:
Weight = mass (m) × gravitational field strength (g)

- The symbol m represents mass, and g represents the strength of gravity, also known as gravitational field strength. Near the Earth's surface, g is approximately 10 newtons per kilogram (10 N/kg). The unit for g is N/kg because it indicates how many newtons of force gravity exerts on each kilogram of mass.
Changes in Gravitational Field Strength
- Near the Earth's surface, gravitational field strength (g) is constant, but it decreases slightly further away from the center of the Earth, such as at the top of a high mountain.
- The value of g is different on the Moon and other planets compared to Earth.
- When gravitational field strength changes, the mass of an object remains the same, but its weight changes.
- For example, a person with a mass of 60 kg on Earth would have a weight of about 600 N. On the Moon, where g is about 1/6 of Earth's gravity, their weight would be approximately 100 N, but their mass would still be 60 kg.
Gravitational Forces between Object
- There is a gravitational force between any two masses. The larger the masses and the closer they are together, the greater the attractive force.
- Objects near Earth experience a strong gravitational pull due to its large mass, which we perceive as weight.
- The gravitational force between two objects is proportional to their masses; for example, the Earth pulls on you more strongly than a book because it has a much larger mass.
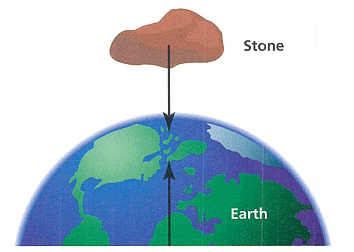
- Gravity is a force that acts at a distance without any physical connection between the masses.
- All objects with mass exert a gravitational force on each other.
- When an object falls towards Earth due to gravity, the Earth also moves slightly towards the object with the same amount of force. However, due to the Earth's much larger mass, this movement is negligible.
- The gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon is strong due to their large masses. Both objects attract each other with equal force but in opposite directions.
Air Resistance
- Friction between solid surfaces acts to slow down and eventually stop movement.
- Gases and liquids also provide resistance to motion; for example, riding a bicycle fast creates air resistance, which feels like a wind pushing you backwards.
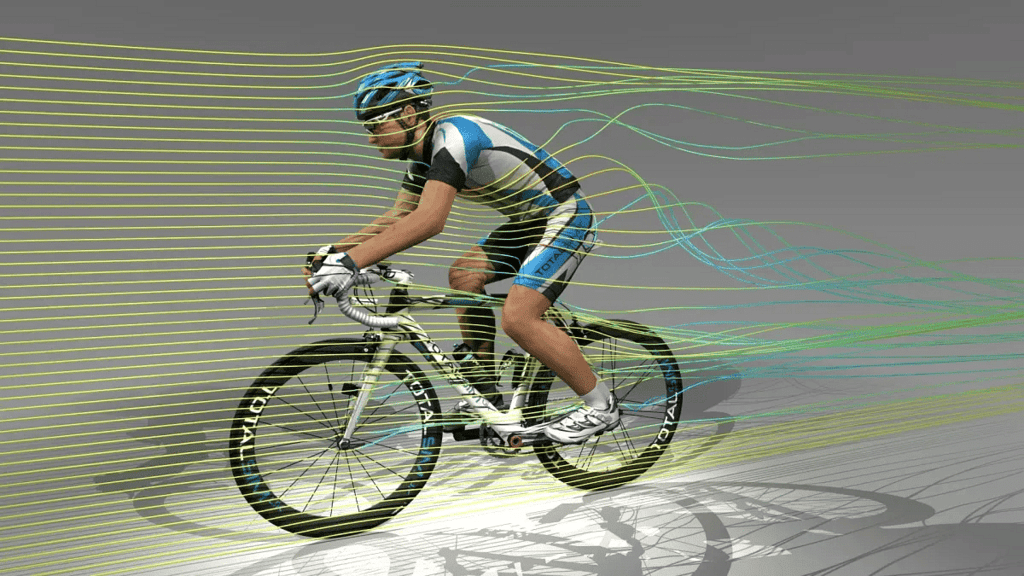
- Air resistance depends on the speed of travel. The faster you move, the greater the air resistance force.
- The magnitude of air resistance also depends on the size and shape of the moving object. Smaller, more smooth, and rounded objects experience less air resistance.
Parachutes
- When skydivers jump out of a plane, they accelerate due to the force of gravity pulling them downward.
- To slow down their descent to a safe speed, skydivers deploy a parachute.
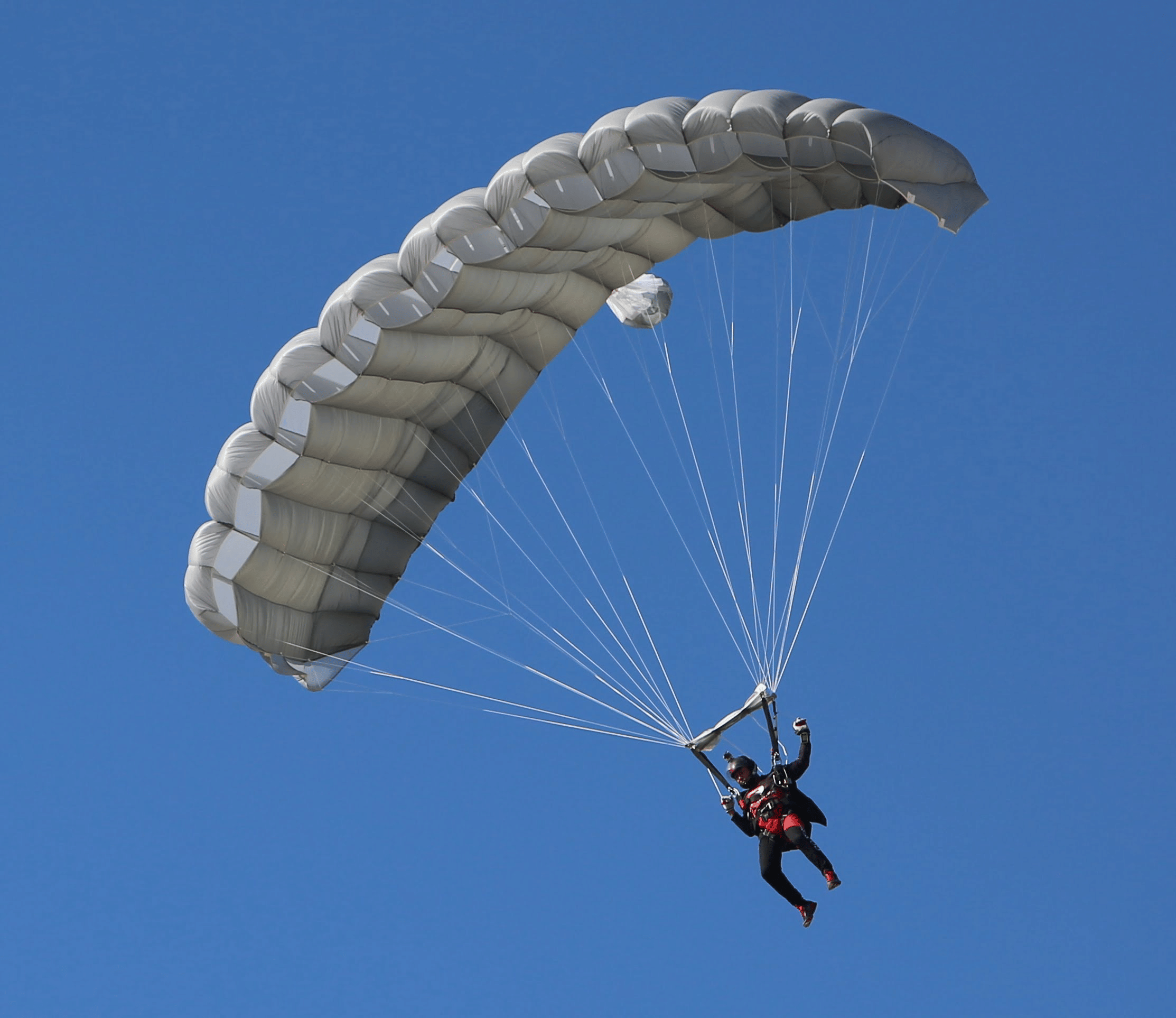

- The parachute increases the air resistance force acting on the skydiver, which opposes the force of gravity (weight).
- This increased air resistance slows down the skydiver's descent, allowing for a safe landing.
Moving Through Particles and Vacuum
- Air particles resist the movement of an object through an area. The larger the surface area of the object, the greater the air resistance because more air particles collide with it and oppose its movement.
- Objects with a larger surface area experience greater air resistance compared to those with a smaller surface area, resulting in more resistance to their movement.
- A vacuum is a completely empty space with no air particles.
- In a vacuum, no air particles are present to collide with moving objects, so there is no air resistance to oppose their movement.
- A vacuum can be created by removing all air particles from an airtight container using an air pump.
- Objects dropped through a vacuum are only affected by the force of gravity pulling them downwards, with no air resistance to oppose their movement.
- The speed at which objects move through a vacuum is determined solely by their weight; lighter objects move more slowly than heavier ones under gravity.
Conclusion
- Definition of Gravity: Gravity is the force that attracts two bodies towards each other.
- Importance: It is crucial for understanding natural phenomena like falling objects, planetary orbits, and ocean tides.
- Newton's Contribution: Sir Isaac Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation explains how mass and distance influence gravitational attraction.
- Daily Life Impact: Gravity affects everyday activities and the motion of celestial bodies.
- Foundation for Advanced Studies: Knowledge of gravity is essential for further exploration in physics and other sciences.
Understanding gravity helps students appreciate the natural laws governing our universe and inspires further scientific curiosity.
|
32 videos|61 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Force and their effects Chapter Notes - IGCSE Cambridge Science for Year 7 - Class 7
| 1. What is the force of gravity? |  |
| 2. How does air resistance affect falling objects? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of forces and their effects in everyday life? |  |
| 4. How does the force of gravity affect the motion of objects on Earth? |  |
| 5. How can you reduce air resistance on an object? |  |















