Best Study Material for Year 7 Exam
Year 7 Exam > Year 7 Notes > The Role of diffusion
The Role of diffusion - Year 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is diffusion? |

|
| Diffusion of Oxygen in the Body |

|
| Diffusion of glucose in the body |

|
| Diffusion of Water: Osmosis |

|
| Which substances diffuse where? |

|
Introduction
- Diffusion involves the movement of particles from areas of higher concentration to those of lower concentration.
- It occurs naturally and does not require any energy input.
- Essential substances like oxygen, carbon dioxide, and glucose move in and out of cells through diffusion.
What is diffusion?
- Diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, occurring within or between cells. It only takes place in liquids and gases because their particles move randomly. Diffusion is crucial for living organisms as it enables the movement of substances in and out of cells and happens naturally without requiring energy.
- Particles collide with each other or their container, causing them to change direction and eventually spread throughout the entire container. Diffusion occurs independently, without the need for stirring, shaking, or wafting.
- Since diffusion involves particles moving from a higher concentration to a lower concentration, this process is referred to as moving down the concentration gradient.
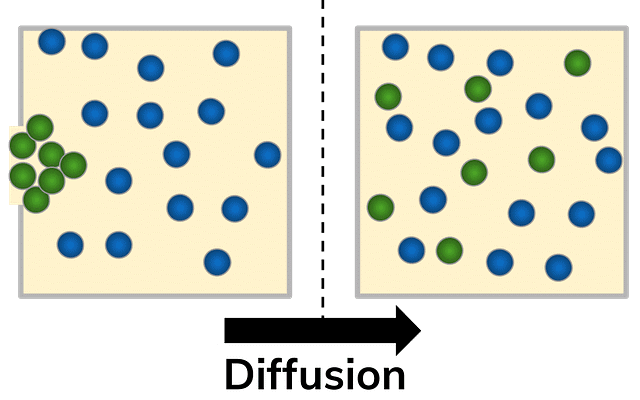
Collide and Gradient
- Collide: This term is synonymous with 'bump into'. It refers to particles coming into contact with each other.
- Gradient: Another word for slope, gradient signifies the gradual change in a physical quantity over a distance.
Understanding Diffusion
- Diffusion involves the movement of particles from regions of higher concentration to regions of lower concentration. This movement along the concentration gradient allows for equalization of particle distribution.
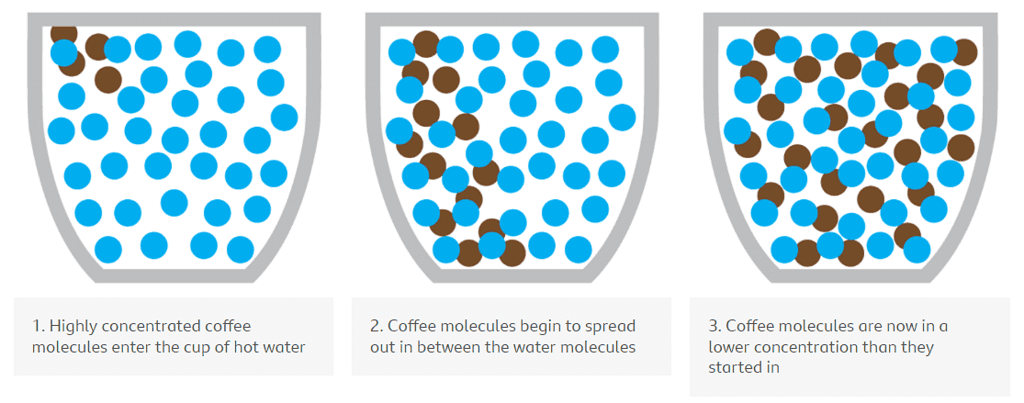
Illustrative Example: Coffee in Water
- Consider the process of diffusion in a cup of hot water with coffee particles. Initially, the coffee molecules are tightly packed. As they enter the hot water, they spread out gradually until they are evenly distributed throughout the water.
Diffusion of Oxygen in the Body
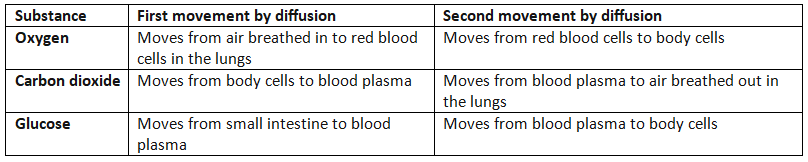
- Oxygen is present in the air we breathe. When we inhale, oxygen moves from the lungs into the bloodstream due to differences in concentration.
- Red blood cells then carry oxygen to all cells in the body, where it is used for various cellular functions.
- The oxygen-rich blood travels through the circulatory system, which includes the heart, blood vessels, veins, arteries, and capillaries, delivering oxygen to tissues and organs.
- Within tissues and organs, oxygen moves from the blood into cells through diffusion, where it is utilized in cellular respiration to produce energy.
- Cells have lower oxygen concentration compared to the blood as they constantly consume oxygen for energy production.
- After oxygen is used by cells, the blood returns to the lungs with a lower oxygen concentration to pick up more oxygen, continuing the cycle.
Carbon Dioxide Movement
- Carbon dioxide, a byproduct of cellular respiration, moves in the opposite direction of oxygen. It diffuses from cells into the bloodstream and then into the lungs to be exhaled.
- Unlike oxygen, carbon dioxide is not carried by red blood cells but is dissolved in the blood plasma.
 |
Download the notes
The Role of diffusion
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Blood Plasma
- Blood plasma is the yellow fluid that transports blood cells, platelets, and dissolved substances throughout the body.
- It serves as the medium for various components of blood to travel and perform essential functions.
- Essentially, blood plasma is a crucial part of the circulatory system.
- For instance, when you get a cut, blood plasma helps in forming a clot to stop bleeding.
Question for The Role of diffusion
Try yourself:
What is the process by which particles move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration?View Solution
Diffusion of glucose in the body
Cells require glucose for respiration, a process vital for their functioning. Glucose, essential for energy production, is obtained from the food we consume.
It is distributed to all cells in the body through the following mechanism:
- During the process of digestion, glucose moves through diffusion from the small intestine, where its concentration is higher, to the bloodstream where it is lower.
- The blood exiting the small intestine carries a concentrated amount of glucose.
- Subsequently, the blood circulates throughout the body, reaching the cells within tissues and organs.
- Within the cells, glucose undergoes diffusion from the blood, which has a higher concentration, to the cells, where it is lower.
- Cells consistently maintain a lower glucose concentration compared to the incoming blood due to their continuous utilization of glucose in respiration.
- As glucose diffuses into the cells, the blood experiences a decrease in glucose concentration. It then returns to the small intestines to replenish its glucose content through diffusion, thus repeating the cycle.
Diffusion of Water: Osmosis
- The movement of water from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a cell membrane is known as osmosis.
- Osmosis typically involves the movement of water across a cell membrane, which acts as a boundary allowing substances to pass in and out of the cell.
- This process is vital for maintaining the balance of water and nutrients inside and outside the cell.
- Osmosis plays a crucial role in various biological processes, such as the uptake of water by plant roots and the regulation of water content in animal cells.
Which substances diffuse where?
FAQs on The Role of diffusion - Year 7
| 1. What is diffusion and how does it work in the body? |  |
| 2. How does oxygen diffuse in the body and why is it important? |  |
Ans. Oxygen diffuses from the lungs into the bloodstream, where it is carried to cells throughout the body. This is important for cellular respiration, where oxygen is used to produce energy for the body's functions.
| 3. Can you explain the process of glucose diffusion in the body? |  |
Ans. Glucose is a type of sugar that is transported through the bloodstream and diffuses into cells where it is used as a source of energy. Insulin helps regulate the diffusion of glucose into cells.
| 4. What is osmosis and how does it relate to the diffusion of water in the body? |  |
Ans. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane, such as cell membranes. In the body, osmosis helps maintain the balance of water inside and outside of cells, ensuring proper cell function.
| 5. Which substances diffuse where in the body and why is diffusion important for overall health? |  |
Ans. Substances like oxygen, glucose, and water diffuse across cell membranes to reach cells where they are needed for various cellular processes. Diffusion is crucial for maintaining the body's internal balance and ensuring that cells receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen for proper function.
Download as PDF
Related Searches