Structure and Function of the Gas Exchange System - Year 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Breathing, Respiration, and Gas Exchange |

|
| Function of the gas exchange system |

|
| Structure of the gas exchange system |

|
| Alveoli |

|
| Ventilation |

|
| Respiration |

|
Introduction
- There are three primary gases present in the air that the body takes in and expels: oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide.
- Gas exchange involves the interchange of gases, where oxygen is absorbed into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is removed from it.
- Diffusion is the overall movement of gas or liquid particles from areas of higher to lower concentration. This process facilitates the transfer of oxygen from the alveoli into the blood.
Breathing, Respiration, and Gas Exchange
- Inhalation and exhalation refer to the act of breathing or ventilation, which is a physical process that involves moving air into and out of your lungs.
- Respiration, on the other hand, is distinct from breathing. It is a chemical process that occurs within all of your cells.
- Gas exchange is a separate process that involves the exchange of gases and takes place at specialized exchange surfaces like the alveoli in your lungs.
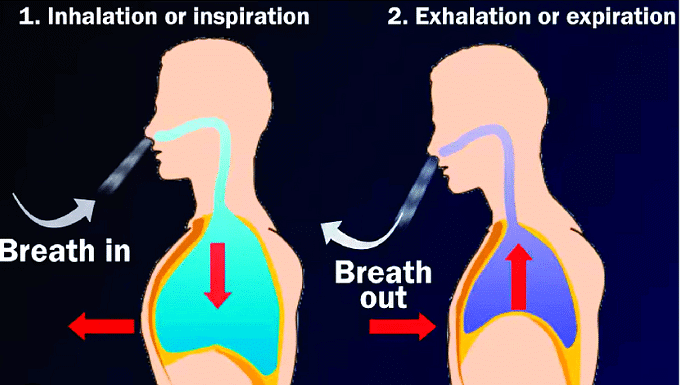
Function of the gas exchange system
- Gas exchange is essential for the transfer of oxygen into cells for respiration and the removal of carbon dioxide, a byproduct of respiration, crucial for energy production from glucose.
Structure of the gas exchange system
- The gas exchange system comprises key components, each serving a distinct purpose.

How does oxygen travel into blood?
- Air enters the lungs via the windpipe known as the trachea.
- The trachea then splits into two tubes referred to as bronchi.
- Further division leads the bronchi to branch into numerous small tubes called bronchioles.
- Bronchioles ultimately terminate in tiny air sacs called alveoli, which are abundant in the lungs.
- These alveoli are encompassed by a network of capillaries, facilitating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood in the capillaries and the air in the lungs. The oxygen is transported within red blood cells.
- The exchange of these gases transpires through a process known as diffusion.
Alveoli
Alveoli are small air sacs found in the lungs where gas exchange occurs during breathing. Within the human lungs, alveoli create an efficient surface for gas exchange by absorbing oxygen, necessary for respiration, into the blood from the air, and transferring carbon dioxide, a byproduct of respiration, from the blood into the lungs and eventually the air.
- Absorbing oxygen: Oxygen required for respiration is taken in by the blood from the air.
- Transferring carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide produced by respiration is moved from the blood to the lungs and then the air.
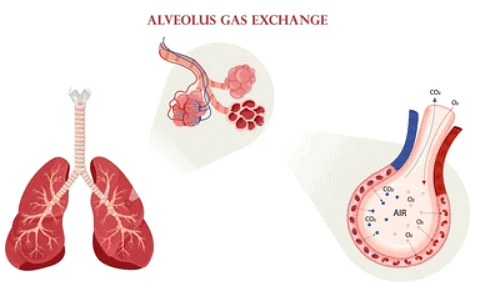
How are the alveoli adapted for gas exchange?
- Alveoli possess a significantly large surface area to enhance the diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream from the alveoli and facilitate the movement of carbon dioxide out of the blood into the alveoli.
- Being only one cell thick, alveoli minimize the diffusion distance, promoting efficient gas exchange.
- They are rich in blood capillaries, tiny vessels that ensure a robust blood supply, thereby maintaining suitable concentration gradients for oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Their moist surfaces facilitate the dissolution of gases, forming a solution that can pass through the cell membrane, which controls the entry and exit of substances in animal cells.
Some water vapor is lost from the alveoli's surface into the lungs, a phenomenon observable as condensation when breathing out on cold days.
 |
Download the notes
Structure and Function of the Gas Exchange System
|
Download as PDF |
Ventilation
Air enters and exits the body through the act of breathing, known as ventilation. This mechanism entails the movement of the ribs, intercostal muscles, and diaphragm to facilitate the flow of air into and out of the lungs.
Changes During Inhalation and Exhalation:

Respiration
Respiration in cells can occur in two ways:
Aerobic Respiration
- Aerobic respiration is the process in which cells convert glucose into energy using oxygen. This type of respiration is highly efficient and occurs in the presence of oxygen.
- Example: Human cells primarily use aerobic respiration to produce energy for various functions.
Anaerobic Respiration
- Anaerobic respiration is the process of producing energy from glucose without the use of oxygen. It is less efficient compared to aerobic respiration.
- Example: Yeast cells undergo anaerobic respiration in the absence of oxygen, producing ethanol as a byproduct.
FAQs on Structure and Function of the Gas Exchange System - Year 7
| 1. What is the function of the gas exchange system? |  |
| 2. What is the structure of the gas exchange system? |  |
| 3. What are alveoli? |  |
| 4. How does ventilation occur in the gas exchange system? |  |
| 5. What is respiration in the context of the gas exchange system? |  |















