Types of variation - Year 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Variation |

|
| Continuous Variation |

|
| Discontinuous Variation |

|
Introduction
- Variation refers to the differences among individuals of the same species, influenced by genetic and environmental factors.
- Surveys on variation yield data that can be either continuous, appearing in a range, or discontinuous, presenting in distinct groups.
Variation
Variation encompasses all the differences that exist within a population of the same species. These differences are caused by:
- Genetic Variation: These are differences between individuals that are inherited from parents, such as the color of your eyes, hair, and skin.
- Environmental Variation: These are differences between individuals that are not inherited but caused by the environment that the organism lives in, including scars and tattoos.
- Genetic and Environmental Variation: Differences between individuals that are caused by both genetic and environmental factors, such as height and weight.
Data Collection and Analysis
- Data on variation is collected by surveying the population. This data can be described as either continuous variation or discontinuous variation.
- It is important to remember that these are not the causes of variation, which are described above, but how we analyze the results of the surveys.
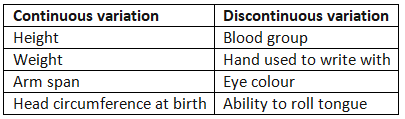
Continuous Variation
Continuous variation refers to a type of variation that demonstrates a broad range of values between two extremes. A classic example of this concept is human height, which spans from the shortest individual to the tallest person. The key characteristic of continuous variation is that any value within this range is possible, illustrating a gradual change over a spectrum of values.
Characteristics of Continuous Variation
- Height
- Arm span
- Weight
When analyzing data related to continuous variation, it is common to represent the results using line graphs or bar charts with a line of best fit. This line provides a visual representation of the trend, even if it does not pass through every individual data point. For instance, when plotting the heights of a group of people, the resulting graph typically includes a line of best fit to showcase the overall pattern.
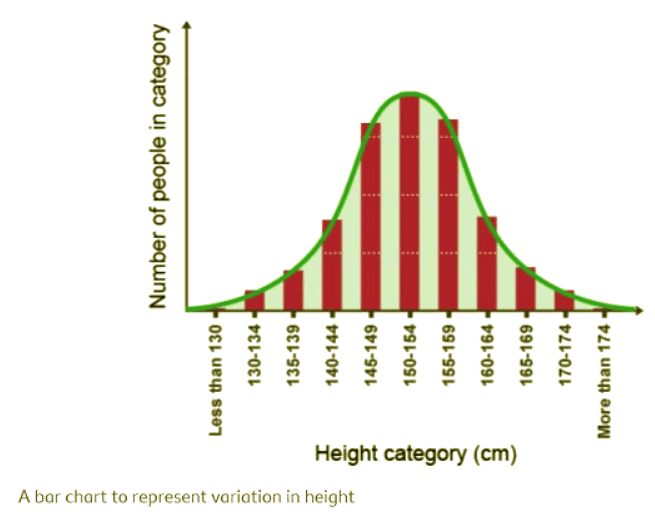
Bell-Shaped Graph
- A bell-shaped graph is a visual representation commonly observed in surveys of continuous variation.
- It exhibits a characteristic shape resembling a bell curve, showcasing a normal distribution pattern.
- This distribution pattern is often seen in various statistical analyses and research studies.
- Values are symmetrically distributed around the mean, with decreasing values as we move away from the center.
- Example: For instance, when measuring the heights of a population, a bell-shaped graph would showcase most individuals clustered around the average height with fewer individuals at the extremes.
Normal Distribution
- Normal distribution represents the spread of values in a dataset that follows a bell-shaped curve.
- It is characterized by a symmetrical, bell-shaped graph with the mean, median, and mode all being equal.
- The distribution is continuous, and its shape is determined by the mean and standard deviation of the data.
- Many natural phenomena and human characteristics tend to follow a normal distribution pattern.
- Example: When plotting exam scores of a large group of students, a normal distribution would show most scores clustered around the average, with fewer students scoring extremely high or low.
Discontinuous Variation
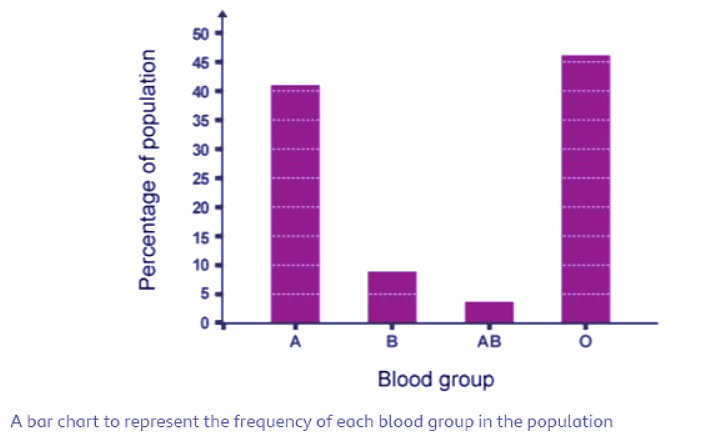
- Surveys of discontinuous variation give us values that come in groups rather than a range. Human blood groups are an example of discontinuous variation. In the ABO blood group system, only four blood groups are possible - A, B, AB, or O. You cannot have a blood group in between these four groups, so this is discontinuous variation.
- Discontinuous variation refers to differences between individuals in a characteristic that can only be put into different groups. It is sometimes called discrete.
Examples of Discontinuous Variation
- Blood group
- Eye color
- Results from surveys of discontinuous variation are presented in charts without a line of best fit drawn because the values on the x-axis (e.g., blood groups) could be placed in any order. If you record the blood groups of a group of people and draw a graph of your results, it usually looks something like this:
More examples
FAQs on Types of variation - Year 7
| 1. What is continuous variation? |  |
| 2. What is discontinuous variation? |  |
| 3. What are the types of variations? |  |
| 4. How does variation occur in living organisms? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding variation important in biology? |  |














