Worksheet: Structure and Properties of Material | IGCSE Cambridge Science for Year 7 - Class 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| MCQ |

|
| True or False Questions |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Match the Column |

|
MCQ
Q1. What is the significance of a material's melting point?
A) It indicates how malleable a material is.
B) It is the temperature at which a material changes from solid to liquid.
C) It determines the electrical conductivity of the material.
D) It shows how soluble the material is in water.
Answer: B) It is the temperature at which a material changes from solid to liquid.
Explanation: The melting point is the temperature at which a material transitions from a solid to a liquid state. Knowing a material's melting point is crucial for selecting appropriate materials for applications that involve high temperatures.
Q2. Which of the following is not a physical property of materials?
A) Reactivity
B) Density
C) Boiling Point
D) Electrical Conductivity
Answer: A) Reactivity
Explanation: Reactivity is a chemical property that refers to the likelihood of a substance undergoing a chemical reaction, not a physical property.
Q3. Which property would be most important when choosing a material that needs to withstand high temperatures without melting?
A) Solubility
B) Hardness
C) Melting Point
D) Density
Answer: C) Melting Point
Explanation: A high melting point would be the most important property when selecting a material that needs to withstand high temperatures without melting.
Q4. What does the pH scale measure?
A) The boiling point of substances
B) The acidity or alkalinity of substances
C) The thermal conductivity of substances
D) The hardness of substances
Answer: B) The acidity or alkalinity of substances
Explanation: The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of substances, ranging from 0 (highly acidic) to 14 (highly alkaline), with 7 being neutral.
Q5. Which of the following is a chemical property?
A) Melting Point
B) Density
C) Flammability
D) Mass
Answer: C) Flammability
Explanation:
Flammability is a chemical property that indicates how easily a material will catch fire.
True or False Questions
Q1. The boiling point is the temperature at which a material changes from liquid to solid.
Answer: False
Explanation: The boiling point is the temperature at which a material transitions from a liquid to a gaseous state.
Q2. Density can be measured by dividing mass by volume.
Answer: True
Explanation: Density is calculated by dividing the mass of a substance by its volume.
Q3. Chemical properties can be observed without changing the identity of the substance.
Answer: False
Explanation: Chemical properties involve changes in the identity or composition of the substance.
Q4. Hardness is a measure of a material’s resistance to deformation or penetration.
Answer: True
Explanation: Hardness refers to a material's ability to resist scratching, indentation, or deformation.
Q5. Solubility refers to the ability of a material to conduct electricity.
Answer: False
Explanation: Solubility is the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent, not its ability to conduct electricity.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1. The ___________ point is the temperature at which a material changes from a liquid to a gas.
Answer: Boiling
Q2. A material’s ability to resist scratching or indentation is referred to as its ___________.
Answer: Hardness
Q3. ___________ is the measure of a material's potential to undergo a specific chemical change.
Answer: Reactivity
Q4. Materials that dissolve in water to form a solution with a pH greater than 7 are called ___________.
Answer: Alkalis
Q5. A pH of 7 is considered to be ___________.
Answer: Neutral
Match the Column
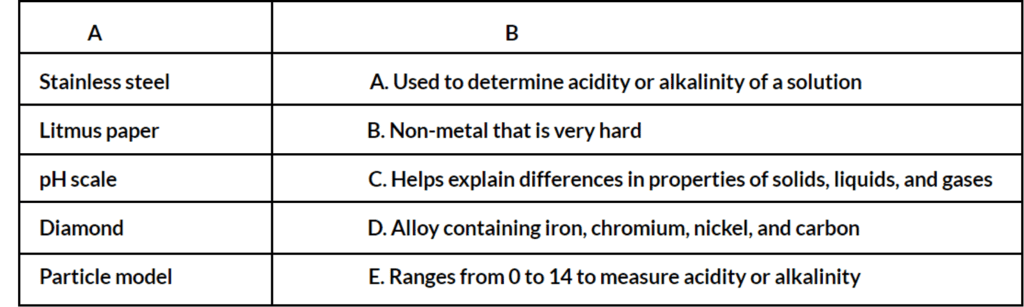
Answers:
- D
- A
- E
- B
- C
Explanations:
- D: Stainless steel is an alloy containing iron mixed with small amounts of chromium, nickel, and carbon.
- A: Litmus paper is soaked in litmus solution and changes color when dipped in a solution, indicating its acidity or alkalinity.
- E: The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Solutions with a pH below 7 are acidic, and those above 7 are alkaline.
- B: Diamond is a non-metal that is very hard, contrary to the general properties of non-metals being dull and having low melting and boiling points.
- C: The particle model is a simplified representation used to understand complex real-world phenomena and helps explain differences in properties among solids, liquids, and gases by showing variations in particle arrangement and movement.
|
32 videos|61 docs|22 tests
|
FAQs on Worksheet: Structure and Properties of Material - IGCSE Cambridge Science for Year 7 - Class 7
| 1. What are the different types of structures found in materials? |  |
| 2. How does the structure of a material affect its properties? |  |
| 3. What are some common properties of materials that are important to consider in engineering applications? |  |
| 4. How can the properties of a material be modified by changing its structure? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand the structure and properties of materials in various industries? |  |















