Year 7 Exam > Year 7 Notes > Pure Substances
Pure Substances - Year 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Pure substances |

|
| Impure Substances |

|
| Particle diagrams |

|
| Fixed boiling points |

|
Introduction
- Most materials we use are mixtures, where two or more compounds or elements coexist without being chemically bonded together.
- In chemistry, a pure substance is a singular substance composed of only one type of particle.
- An impurity is a substance comprising more than one element or compound, affecting the temperature at which a substance melts and boils.
Pure substances
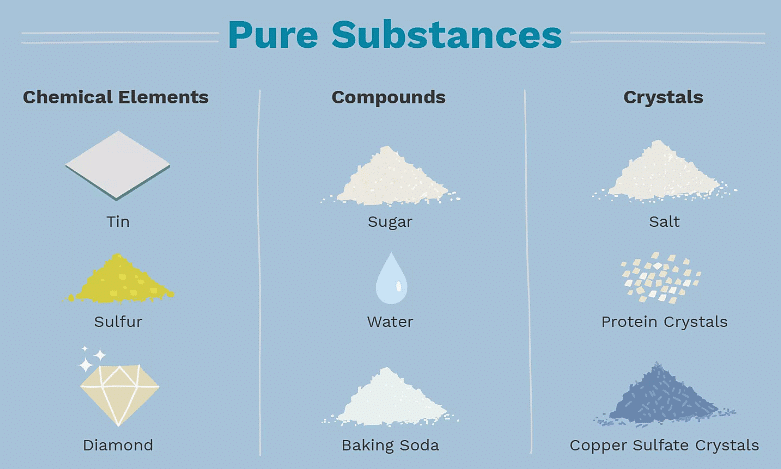
- A pure substance consists of either one element or one compound.
- A pure substance is composed of only one type of atom or one compound.
- Elements are individually listed on the periodic table.
- Compounds are formed by chemically bonding two or more elements in fixed ratios.
- For instance, salt represents a pure substance since it consists solely of sodium chloride.
Question for Pure SubstancesTry yourself: What is a pure substance?View Solution
Impure Substances
Impurities
- An impure substance is a material composed of more than one element or compound, creating a mixture where these components are not chemically bonded.
- Impurities refer to the presence of two or more compounds or elements within a substance without a chemical bond between them.
- For instance, mineral water might contain impurities like sodium and nitrate, making it challenging to achieve purity.
Particle diagrams
Particle diagrams are visual representations that illustrate the arrangement of chemicals.
Elements
An element's particle diagram depicts only one type of atom. For instance, pure oxygen comprises solely oxygen atoms, which are represented by a red circle in the diagram.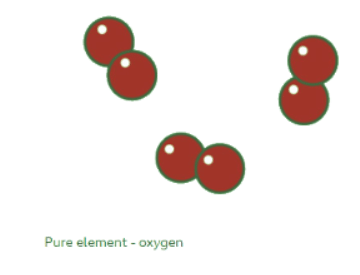
Compounds
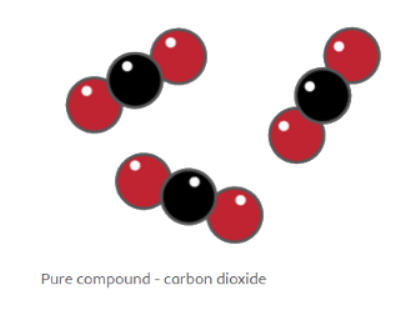
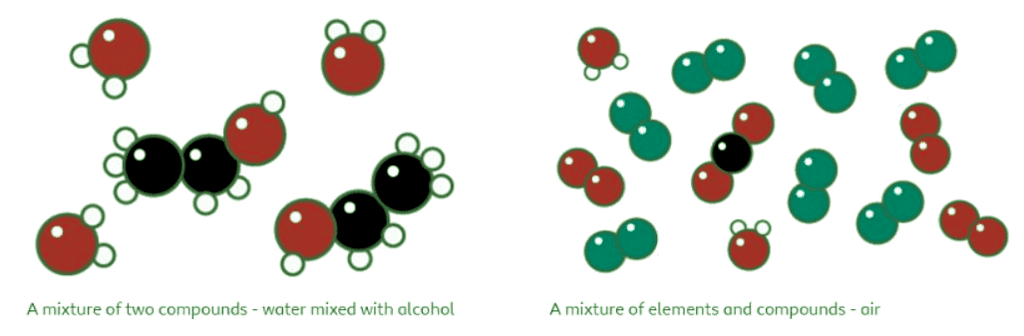
- A compound's particle diagram consists of two or more types of atoms bonded together in a fixed ratio.
- In the case of carbon dioxide, the compound comprises one black (carbon) and two red (oxygen) atoms, represented accordingly in the diagram.
- The diagram visually shows the fixed ratio of one black atom connected to two red atoms.
Mixtures
A mixture comprises more than one type of atom or molecule that is not chemically bonded. It involves a combination of different elements or compounds that are physically intermingled but not bound together.
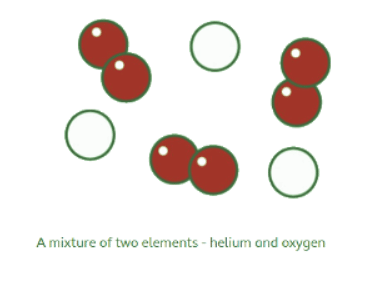
- Particle Diagram: This representation illustrates mixtures containing various atoms or molecules that are not chemically connected. For example, a diagram with white helium atoms and red oxygen atoms signifies a mixture of these two elements.
- Impurities Effect: Impurities within a mixture can alter the melting and boiling points of substances. These foreign particles can shift the temperatures at which substances change states.
Fixed boiling points
Impurities change the melting and boiling point:
- When a substance contains impurities, its melting and boiling points are altered.
- For instance, when salt is introduced to water, the freezing point of the mixture drops below 0°C, while the boiling point rises above 100°C.
- Determining the purity of a substance can be achieved by assessing its melting or boiling point.
Question for Pure SubstancesTry yourself: What is the primary characteristic of impure substances?View Solution
FAQs on Pure Substances - Year 7
| 1. What is a pure substance? |  |
Ans. A pure substance is a type of matter that has a fixed chemical composition and distinct properties. It is made up of only one type of particle, either atoms or molecules.
| 2. How are impure substances different from pure substances? |  |
Ans. Impure substances are composed of more than one type of particle, leading to varying properties and compositions. In contrast, pure substances have a uniform composition and consistent properties.
| 3. What do particle diagrams represent in the context of pure substances? |  |
Ans. Particle diagrams are visual representations that show the arrangement and motion of particles in a substance. They help us understand the behavior of particles in pure substances.
| 4. Do pure substances have fixed boiling points? |  |
Ans. Yes, pure substances have fixed boiling points. This is because the particles in a pure substance are uniform, leading to consistent boiling points under specific conditions.
| 5. Can impurities affect the properties of pure substances? |  |
Ans. Yes, impurities can alter the properties of pure substances. They can change the chemical composition, melting and boiling points, and other characteristics of the substance.
Related Searches













