Year 7 Exam > Year 7 Notes > Polymers
Polymers - Year 7 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What are polymers? |

|
| Natural polymers |

|
| Synthetic polymers |

|
| Disadvantages of Polymers |

|
Introduction
- Polymers are essentially long chain molecules constructed from small repetitive units known as monomers.
- These materials can be found in nature or be artificially produced.
- In the case of artificially produced polymers, they are commonly referred to as plastics and serve a wide array of purposes.
What are polymers?

- A polymer is a long molecule composed of many repeating units called monomers. These monomers link together to form a chain structure.
- Think of a polymer as a daisy chain - each daisy representing a monomer. When these monomers join together, they create a long chain, just like a polymer.
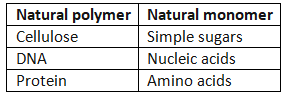
Natural polymers
- Some polymers occur naturally, such as cellulose, DNA, and proteins.
- Cellulose is the primary component of plant cell walls, providing stiffness and structural support.
- The monomer of cellulose is simple sugars. These simple sugars link together in long chain molecules to form the polymer cellulose.

Synthetic polymers
- Synthetic polymers are artificially created through chemical reactions, as opposed to naturally occurring substances. These polymers are produced by combining numerous small molecules to form long chains. For instance, polycarbonate is a synthetic polymer utilized in the production of eyeglass lenses.
- One illustration of this process involves ethene molecules bonding together to form elongated chains of polyethene, a synthetic polymer. This is visually depicted in the accompanying diagram.
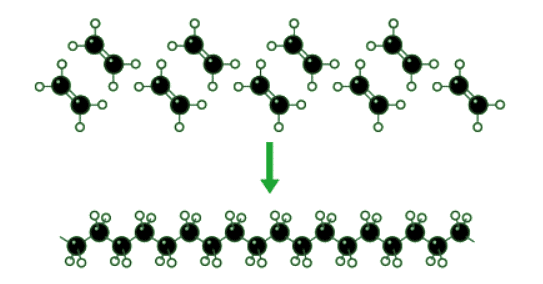
- Commonly known as plastics, synthetic polymers play a pivotal role in our daily lives. They are among the most versatile materials available to us.
- Plastics can be tailored for specific applications by utilizing various monomers, enabling the design of polymers with distinct properties suited for different purposes.
Synthetic Polymers: Key Properties
Synthetic polymers share common properties that make them versatile materials in various applications:
- Chemically Unreactive: Synthetic polymers do not easily react with other chemicals, ensuring stability in various environments.
- Solid at Room Temperature: These polymers maintain a solid state at typical room temperatures, providing structural integrity.
- Malleability: They can be easily molded into different shapes and forms, allowing for diverse manufacturing processes.
- Electrical Insulation: Synthetic polymers are effective insulators against electricity, reducing the risk of electrical hazards.
- Durability: They possess strength and wear resistance, making them suitable for long-lasting applications.
Applications of Synthetic Polymers
Understanding these properties helps us comprehend the widespread use of plastics in our daily lives:
- Packaging: Plastic materials are commonly used for packaging due to their flexibility and protective qualities.
- Medical Devices: Synthetic polymers play a vital role in medical equipment and devices due to their sterilizability and safety.
- Textiles: Many modern fabrics are made from synthetic polymers, offering durability and versatility in clothing.
- Construction: From pipes to insulation, plastics are integral in the construction industry for their lightweight yet robust nature.
Polymer Usage in Everyday Life
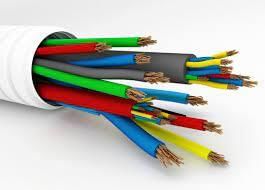
- PVC, polyethylene, or polyester coats electrical wires for insulation purposes.

- Chairs made from poly(propylene) are durable due to the strength of synthetic polymers.

- Synthetic polymers' chemical inertness makes them ideal for chemical containers.

- Synthetic polymers are commonly used in food wrappers for their non-reactive properties.
Additional Details
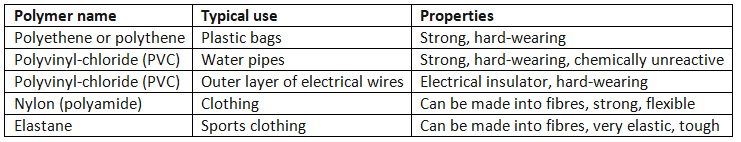
- Synthetic polymers often contain 'poly' in their names, like polyethylene or polystyrene.
- Some synthetic polymers are more commonly known by their commercial names such as nylon or elastane.
Disadvantages of Polymers
- Polymers are typically chemically unreactive, making them useful for applications like plastic bottles, which do not react with their contents.
- For instance, a fruit juice drink contains various acids, and it is crucial that the plastic bottle does not react with them.

- However, this lack of reactivity also makes polymers difficult to dispose of. They do not decompose quickly and thus persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to plastic pollution.
- Plastics decompose even more slowly in water. Due to their strength and durability, plastics are used for fishing ropes. When fishing gear is lost in water, it sinks and is called 'ghost gear' because it no longer belongs to a boat.
- This ghost gear can entangle and harm sea creatures, posing a significant environmental threat.
Question for PolymersTry yourself: Which of the following is an example of a natural polymer?View Solution
FAQs on Polymers - Year 7
| 1. What are polymers? |  |
Ans. Polymers are large molecules made up of repeating units called monomers. They can be found in natural sources like plants and animals, as well as in synthetic materials.
| 2. What are natural polymers? |  |
Ans. Natural polymers are polymers that occur in nature and are derived from sources such as plants and animals. Examples include proteins, starch, cellulose, and DNA.
| 3. What are synthetic polymers? |  |
Ans. Synthetic polymers are man-made polymers that are created through chemical reactions in a laboratory. Examples include plastics like polyethylene, PVC, and nylon.
| 4. What are some disadvantages of polymers? |  |
Ans. Some disadvantages of polymers include their non-biodegradability, which contributes to environmental pollution. They can also release toxic chemicals when burned, and their production process can be energy-intensive.
| 5. How are polymers used in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Polymers are used in a wide range of everyday products, including plastics, textiles, adhesives, coatings, and packaging materials. They are also used in medical devices, electronics, and construction materials.
Related Searches


















