Year 7 Exam > Year 7 Notes > Density
Density - Year 7 PDF Download
Key points
 Image caption
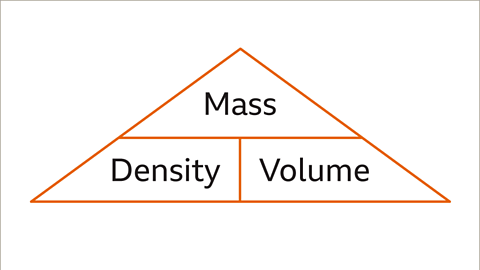
Image caption- The density of an object or substance is determined by its mass divided by its volume:
- Density is a measure of how closely packed particles are within a substance. When particles are tightly packed, the substance has a higher density compared to when they are spread out.
- Mass refers to the amount of matter contained within an object. Unlike weight, which can vary due to gravity, an object's mass remains constant regardless of its location.
- Volume indicates the amount of space occupied by a three-dimensional object, typically measured in cubic units such as cm³, mm³, or m³. It can also be referred to as capacity.
Density = Mass ÷ Volume
Understanding Density
- The density of an object depends on its mass and volume.
- Density is typically measured in g/cm³, where mass is in grams and volume is in cubic centimeters.
- When a substance is denser, it feels heavier because more mass is packed into a given volume.
- You can calculate density using the formula: Density = Mass ÷ Volume.
Density Units
- The units for density are usually g/cm³, based on the mass and volume measurements.
Characteristics of Dense Objects
- Dense objects have a large amount of mass within a specific volume, resulting in closely packed particles.
- These objects feel heavier due to the compact arrangement of particles.
- Comparing the densities of objects with different sizes is possible by using the density formula.
How to compare solids and liquids
- Substances can be compared using density:
- If two liquids that are mixed have different densities, the least dense liquid will float to the top.
- Various types of wood have distinct densities. Hardwood, being denser, feels heavier than softwood.
- Denser objects occupy less space compared to an equivalent mass of a less dense material.
- For instance, a metric tonne of feathers would occupy significantly more volume than a metric tonne of bricks.
If two liquids of different densities are mixed:
- The least dense liquid will float to the top.
Different types of wood and density:
- Hardwood has a greater density than softwood.
Density and space occupation:
- Objects with higher density occupy less space compared to the same mass of a less dense material.
- For instance, a metric tonne of feathers would occupy more space than a metric tonne of bricks.
Metric Units in the Metric System:
- Metric units like metre, centimetre, millimetre, and kilometre are used as measurements.
Examples
Image gallery
Skip image gallery
- Image caption: When different liquids are mixed together in the same container, their densities will affect what then happens. It will depend on the density of each of the liquids. If the liquids are different colors, it is easier to see the physical effect of density.

- Image caption: A small amount of five different liquids are added to one container: vegetable oil, water, washing up liquid, maple syrup, and honey.

- Image caption: The liquid which is the most dense (honey) sinks to the bottom of the container. The liquid which is the least dense (vegetable oil) floats to the top of the container. The different colors of the liquids make it easier to see the effect of density.

Paraphrased Information
- When different liquids are combined in a container, their densities influence their behavior based on their individual densities, especially visible when liquids have distinct colors.
- Example: Mixing vegetable oil, water, washing up liquid, maple syrup, and honey in a container.
- Liquids arrange by density, with honey sinking to the bottom and vegetable oil floating on top, aided by the different colors of the liquids.
Understanding Density in Solids
- When comparing the densities of solids, it's important to note that density is a measure of how much mass is contained in a given volume.
- Density is a physical property unique to each material and can vary significantly between different substances.
Example of Density Variation
- For instance, if we consider two metal bars, one made of aluminum and the other of copper, both having the same volume, the bar made of copper will feel heavier because copper has a greater density compared to aluminum.
- Aluminum has a density of 2.70g/cm³, while copper has a density of 8.95g/cm³, illustrating the difference in density between these two metals.
| Metal | Density (g/cm³) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 2.70 |
| Copper | 8.95 |
Understanding Density Calculation
- Density is calculated as the mass of an object divided by its volume, represented by the formula: Density = Mass / Volume.
- There are various units used to express density, with grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) being a common unit for solids.
- Comparing the densities of different substances is feasible when their densities are provided in the same units, facilitating relative density assessments.
Slide 1 of 6
- An image of three cylindrical measuring beakers. Each beaker is a different size; small, medium, and large. The small beaker contains a blue liquid. The medium beaker contains a red liquid. The large beaker contains a green liquid. When different liquids are mixed together in the same container, their densities will affect what then happens. It will depend on the density of each of the liquids. If the liquids are different colors, it is easier to see the physical effect of density.
Question
- How do the densities of different liquids affect what happens when they are mixed? Explain with examples.
How to work out density
- Density is defined as the mass per unit volume, which represents the amount of space occupied by a 3D shape. This measurement is typically expressed in cubic units like cm³, mm³, and m³ and can also be referred to as capacity.
- Calculating density involves different approaches. For solids, liquids, or gases, a common method is to divide the object's mass by its volume. When dealing with smaller objects, mass is usually measured in grams (g) and volume in cubic centimeters (cm³).
- If the object is larger, density would be determined by dividing the mass in kilograms (kg) by the volume in cubic meters. The formula for density is Density = Mass ÷ Volume. The units for density will depend on the units used for mass and volume.
Volume
The amount of space occupied by a 3D shape, measured in cubic units such as cm³, mm³, and m³. It can also be referred to as capacity.
Calculation of Density
- A common method to determine the density of any solid, liquid, or gas is by dividing its mass by its volume. For instance, for large objects, density is calculated by dividing mass in kilograms by volume in cubic meters. The formula for density is Density = Mass ÷ Volume.
| Mass (kg) | Volume (cm³) | Density (kg/cm³) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5 | 2 |
| 20 | 10 | 2 |
Mass and Density
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object and is typically measured in kilograms (kg).- If an object is large, its density can be calculated by dividing the mass in kilograms by its volume in cubic meters using the formula: Density = Mass ÷ Volume.
- The units for density are determined by the units provided for both mass and volume.
Example
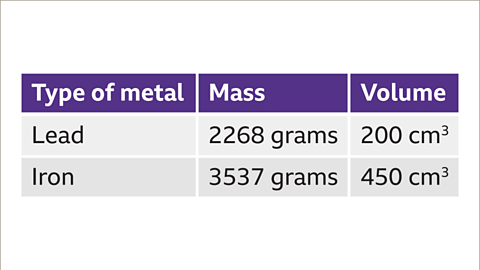
Calculate the density of different types of metals by comparing their mass and volume.- For instance, to compare the density of two different metals like lead and iron, you need to know the mass and volume of each object. For example, a lead pipe with a mass of 2268 grams and a volume of 200 cm³, and an iron bar with a mass of 3537 grams and a volume of 450 cm³.
Calculating Density of Metals
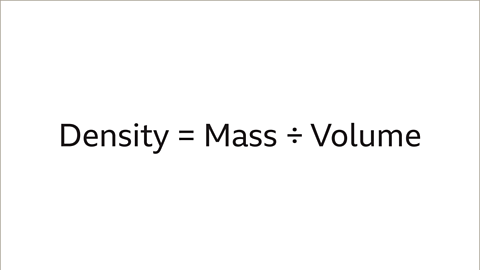
Density Calculations for Various Metals
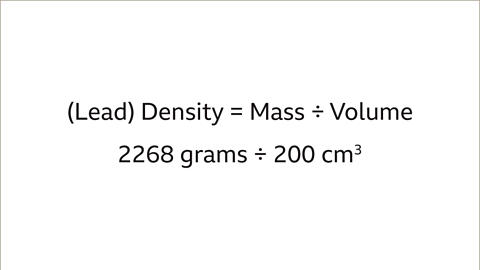
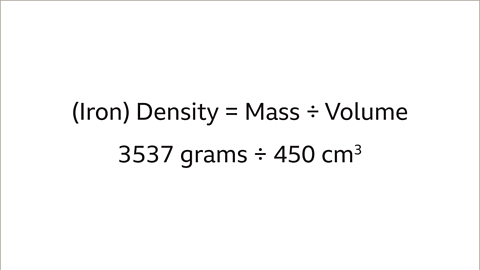
Density Comparison between Lead and Iron

Slide 1 of 7
- An image shows two identical cylinders: one labeled "lead pipe" and the other "iron bar." The lead cylinder appears as a dark metallic grey, while the iron cylinder is a lighter metallic grey.
- We are asked to calculate the density of these different types of metals.
Question
The scenario presents two cylinders, one made of lead and the other of iron, each with specific visual characteristics. We need to determine the density of these materials. Let's delve deeper into this concept.
Practise your understanding of density
Quiz
Practice your comprehension of density in mathematics through this quiz. It's recommended to have a pen and paper handy for your responses.
- Understand the concept of density.
- Calculate the density of various substances.
- Apply the formula for density in problem-solving scenarios.
- Recognize the units of measurement typically used for density.
Game - Divided Islands
- Explore the concept of divided islands.
- Engage in strategic thinking to solve challenges related to divided territories.
- Understand the implications of dividing land masses in a game context.
Related Searches



















