Year 7 Exam > Year 7 Notes > Pie Charts
Pie Charts - Year 7 PDF Download
Key points
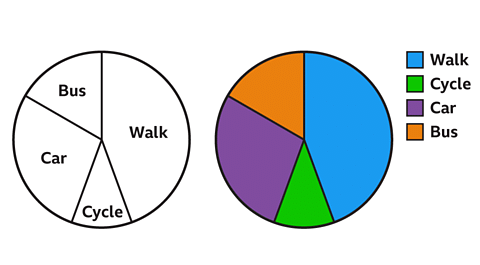 Image caption
Image caption - A pie chart is a graphical representation used to illustrate proportions in a sample of data. It shows a part-to-whole comparison, where each part of a ratio is depicted as a fraction of the entire set. For example, in the ratio 3 : 5, the first part represents 3/8 of the whole dataset. This aids in understanding proportions within a dataset.
- The structure of a pie chart resembles a circle divided into sectors, each sector representing a proportion of the total data sample. The angle of each sector corresponds to the proportion it represents. If colors are used to differentiate sectors, a legend should accompany the chart to explain each color's significance.
- Percentages can be utilized to represent the proportions in a pie chart, making it easier to comprehend the distribution visually. Each percentage reflects a portion out of one hundred, providing a clear indication of the relative sizes of the sections.
- Drawing a pie chart accurately involves using a protractor to measure and draw the angles of each sector. Familiarity with protractor usage is essential for creating precise and informative pie charts.
Proportion
- A proportion is a part-to-whole comparison, where each part of a ratio is seen as a fraction of the whole. For instance, in the ratio 3 : 5, the first part constitutes 3/8 of the whole, showcasing a proportion of the entire entity.
- Understanding proportions is crucial in various scenarios like finance, cooking recipes, and statistical analysis.
Sector
- A sector refers to a portion of a circle demarcated by two radii and an arc.
- In real-life applications, sectors are commonly used in fields such as engineering (for sector gears) and geometry (to calculate areas of shaded regions).
Angle of Sectors
- The angle of each sector symbolizes the proportions within the complete dataset or sample used in a survey.
- For example, in a pie chart representing sales data, each sector's angle denotes the percentage of total sales contributed by a specific category.
Understanding Pie Charts
- If the sectors are colored, a key should be included to explain what each color represents.
- The proportions in a pie chart may be represented as a percentage - a proportion out of one hundred.
- When drawing a pie chart, a protractor will be used to draw the angles accurately. Being familiar with how to use a protractor will be helpful.
Key Points to Remember
- Color Key: In a pie chart, if different sectors are colored, a key is necessary to clarify what each color signifies. For instance, in a sales pie chart, green might represent profits, while red could symbolize losses.
- Percentage Representation: Pie charts often display proportions as percentages. For example, if a sector represents 25% of the chart, it means that this portion constitutes a quarter of the whole.
- Accuracy in Drawing: When creating a pie chart, utilizing a protractor ensures precise angle measurements. Understanding protractor usage is essential for accurately depicting data.
 Image captionBack to top
Image captionBack to topCreating a Pie Chart
- To generate a pie chart, you need data typically organized in a table format.
- Calculating the angle sizes is crucial in pie chart creation.
Examples
- Imagine a scenario where a student surveys their friends about their mode of transportation to school. The resulting data needs to be represented in a pie chart.
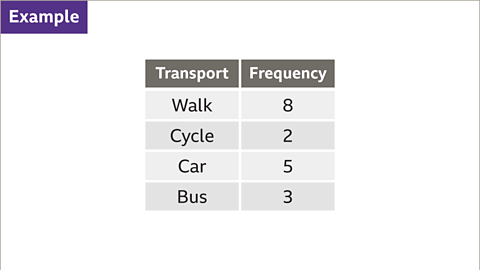
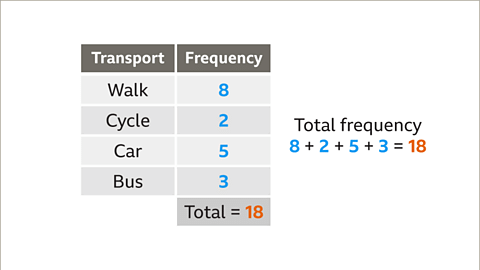
When creating a pie chart, it's essential to calculate the angles. Begin by summing up the frequencies. For instance, in a given table, the total frequency might be 18.
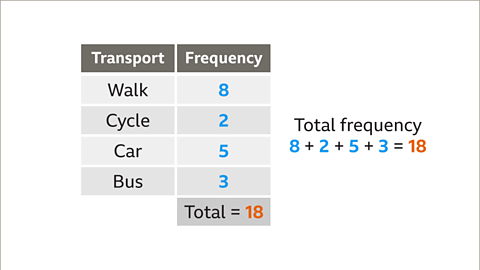
Understanding Pie Charts
Friend Representation in Pie Chart
- Each friend in the pie chart represents an angle of 20°.
- To find the angles for different modes of transport, multiply the frequency by 20.
- If the angles for different modes of transport do not add up to 360°, there might be an error in the calculations.
Constructing the Pie Chart
- Start by drawing a circle and adding a vertical line from the center to the circumference.
- To draw specific sectors like the one for friends who walk to school, use a protractor to mark and draw the angles accurately.
| Mode of Transport | Frequency | Angle (in degrees) |
|---|---|---|
| Walk | 8 | 160 |
| Cycle | 2 | 40 |
| Car | 5 | 100 |
| Bus | 3 | 60 |
| Total | - | 360 |
Steps to Draw Pie Chart Sectors
Friend Transportation Representation
Representing different modes of transportation to school using a pie chart.
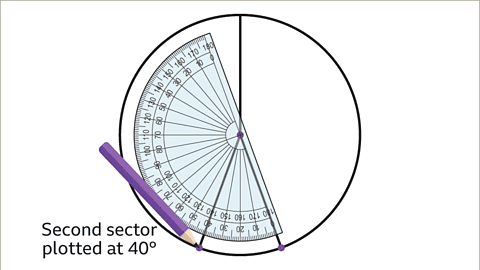
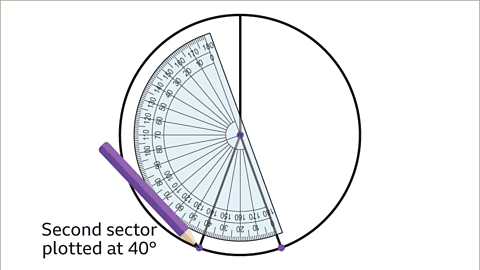
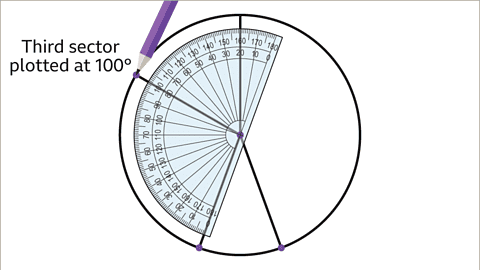
- Draw a sector for friends who cycle to school at 40°:
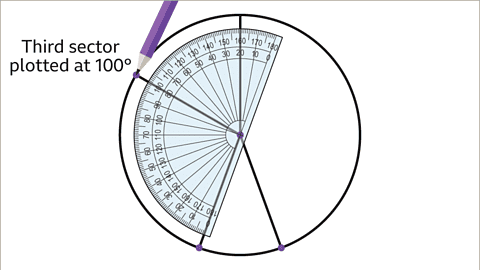
- Draw a sector for friends who use a car at 100°:
- Verify the final sector at 60°:
Rotate the protractor to 40°, aligning with the previous line, and draw.
Rotate the protractor to 100°, aligning with the previous line, and draw.
Ensure the angle is correct by checking with a protractor and marking it.
 |  |
 |  |
Pie Chart Construction Process
- Checking Accuracy of Pie Chart
- Ensure the last sector angle remains at 60°, verified using a protractor.
- Labelling the Pie Chart
- Label each sector or use color codes with a key; suggest a fitting title like 'A pie chart to show mode of transport to school'.
Example: Data Representation
| Transport | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Walk | 8 |
| Cycle | 2 |
| Car | 5 |
| Bus | 3 |
- Students surveyed on their mode of transport to school
- Construct a pie chart based on the provided data
Question
Back to top
 |
Download the notes
Pie Charts
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Interpreting a pie chart
- Understanding a pie chart involves analyzing the proportions of its sectors.
- By examining the angles within a pie chart, we can determine the fraction each sector represents of the whole population, measured in degrees out of 360°.
- A pie chart often displays the percentages corresponding to each sector, aiding in the interpretation of proportions within the entire population.
Examples
Image gallerySkip image gallery- Image caption: The pie chart illustrates the seasonal results of a rugby team, detailing wins, draws, and losses.
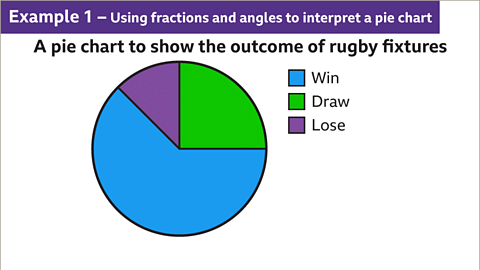 Image caption:
Image caption:The pie chart shows the outcome of results for a rugby team during a season.
Pie Chart Analysis
Finding Draw Results
If a pie chart with 24 fixtures is given, and one quarter represents drawn fixtures, then the number of drawn games can be calculated as follows:- The sector representing draws is 1/4 of the total, hence 1/4 × 24 = 6 games.
- Therefore, there were 6 games that resulted in a draw.
Determining Winning Outcomes
When a sector measuring 225° in a pie chart represents won fixtures, which is 5/8 of the whole chart:- Calculating the number of wins: 5/8 × 24 = 15 games.
- Thus, there were 15 games that resulted in a win.
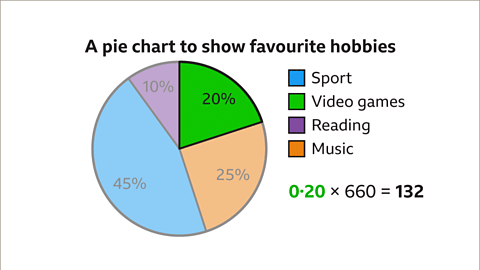
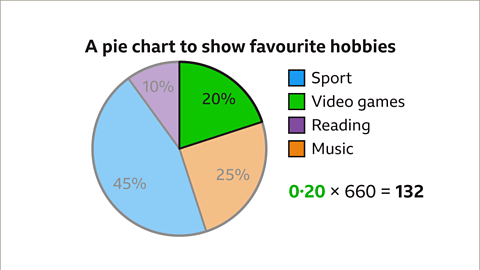
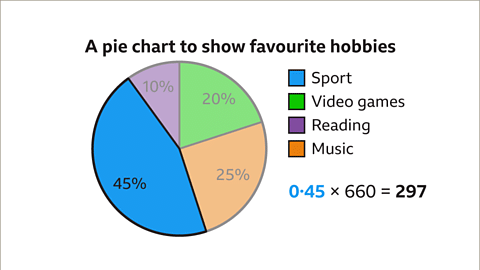
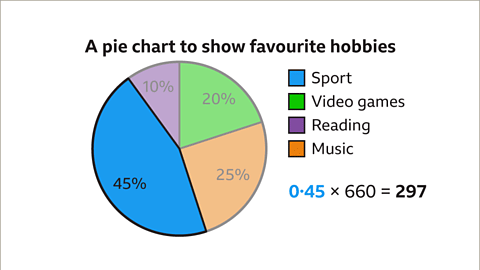
Favorite Hobbies of Pupils
Analyzing a pie chart illustrating the favorite hobbies of 660 students:- Interpreting percentages: green (20%), orange (25%), blue (45%), and purple (10%).
- Correlating colors with hobbies: blue (sport), green (video games), purple (reading), orange (music).
Pupils Enjoying Video Games
If the segment for video game enthusiasts in a pie chart is 20%:- Number of pupils interested in video games: 20% of 660 = 0.20 × 660 = 132.
- Hence, 132 students have playing video games as their favorite hobby.
 |  |
Interpreting Pie Charts
- Key Concept: Understanding Pie Chart Sectors
- Rather than numbers, pie charts represent data in proportions, where each sector corresponds to a portion of the whole.
- Example: In a pie chart showcasing student hobbies, a 45% sector denotes that 45% of 660 pupils enjoy playing sports.
- Visual Representation: Pie Chart Interpretation
- Pie charts visually display data distribution through sectors, each representing a category or value.
- Example: A pie chart depicting rugby match outcomes shows sectors colored green for draws, blue for wins, and purple for losses.
Using Fractions and Angles
- Analysis Approach: Utilizing Angles to Decode Data
- Angles in pie charts help visualize the relative size of each category.
- Example: A sector with a 90-degree angle in a chart could represent a specific data subset.
- Deciphering Results: Linking Colors to Outcomes
- Assigning colors to sectors aids in quickly comprehending chart information.
- Example: In a rugby fixture chart, blue might symbolize wins, green draws, and purple losses.
 |  |
Question
Back to topPractise comparing and interpreting pie charts
Quiz
Practise comparing and interpreting pie charts with this quiz. You may need paper and a pen to help you.
Back to topGame - Divided Islands
Back to topSummary
- Paraphrasing of Information
- Pie Chart Comparison Practice
- Engage in activities to enhance your skills in comparing and interpreting pie charts.
- Quiz Preparation
- Utilize quizzes to test your understanding of pie charts. Have paper and a pen ready for this task.
- Game - Divided Islands
- Explore the game "Divided Islands" to further practice your pie chart interpretation skills.
- Pie Chart Comparison Practice
Download as PDF
Related Searches





















