Plants and Animals | GK Olympiad for Class 4 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Animals |

|
| Types of Animals |

|
| Features of Animals |

|
| Habitats of Animals |

|
| Plants |

|
| Types of Plants |

|
| Features of Plants |

|
| Photosynthesis |

|
| Adaptation in Plants |

|
| Adaptation in Animals |

|
| Microbes |

|
Animals
Animals are living organisms that can move, breathe, and need food to survive. They are a major part of our world and come in many different shapes, sizes, and types.
Types of Animals
- Vertebrates: Animals with a backbone.
- Invertebrates: Animals without a backbone.
Vertebrates
Vertebrates are divided into five main groups:
Mammals:
- Features: Warm-blooded, have fur or hair, give birth to live young (most), and produce milk to feed their babies.
- Examples: Humans, lions, dolphins.
Birds:
- Features: Warm-blooded, have feathers, lay eggs, and most can fly.
- Examples: Eagles, parrots, penguins.
Reptiles:
- Features: Cold-blooded, have scales, lay eggs (most), and can live on land or in water.
- Examples: Snakes, lizards, turtles.
Amphibians:
- Features: Cold-blooded, have moist skin, can live both in water and on land, and lay eggs in water.
- Examples: Frogs, salamanders, newts.
Fish:
- Features: Cold-blooded, have scales, live in water, and breathe through gills.
- Examples: Salmon, sharks, goldfish.
Invertebrates
Invertebrates are divided into several groups, including:
Arthropods:
- Features: Exoskeleton, segmented body, jointed limbs.
- Examples: Insects (ants, bees), arachnids (spiders, scorpions), crustaceans (crabs, lobsters).
Mollusks:
- Features: Soft-bodied, most have a hard shell.
- Examples: Snails, clams, octopuses.
Worms:
- Features: Soft, elongated bodies, no limbs.
- Examples: Earthworms, tapeworms, leeches.
Cnidarians:
- Features: Soft-bodied, tentacles with stinging cells.
- Examples: Jellyfish, sea anemones, corals.
Echinoderms:
- Features: Spiny skin, radial symmetry, tube feet.
- Examples: Starfish, sea urchins, sand dollars.
Features of Animals
Body Structure
Body Coverings:
- Mammals: Fur or hair
- Birds: Feathers
- Reptiles: Scales
- Amphibians: Moist skin
- Fish: Scales
Limbs:
- Mammals: Four limbs, some adapted for running, climbing, swimming, or flying.
- Birds: Wings and legs, some adapted for flying, swimming, or walking.
- Reptiles: Legs or no legs (snakes).
- Amphibians: Legs, some adapted for jumping or swimming.
- Fish: Fins for swimming.
Respiratory System
- Mammals: Lungs
- Birds: Lungs with air sacs
- Reptiles: Lungs
- Amphibians: Lungs and skin (for breathing through the skin)
- Fish: Gills
Reproductive System
- Mammals: Most give birth to live young, some lay eggs (e.g., platypus).
- Birds: Lay eggs.
- Reptiles: Most lay eggs, some give birth to live young.
- Amphibians: Lay eggs in water.
- Fish: Most lay eggs, some give birth to live young.
Sensory Organs
- Eyes: Most animals have eyes adapted to their environment (e.g., nocturnal animals have larger eyes).
- Ears: Mammals have external ears, birds have internal ears, and fish have lateral lines for detecting vibrations.
- Nose: Mammals have a keen sense of smell, while fish use their sense of smell underwater.
Habitats of Animals
Animals live in various habitats, each providing the necessary resources for their survival.
- Forest: Home to many mammals, birds, insects, and reptiles.
- Ocean: Home to fish, marine mammals, crustaceans, and mollusks.
- Desert: Home to reptiles, insects, and some mammals adapted to dry conditions.
- Grassland: Home to large herbivores (e.g., elephants, zebras) and predators (e.g., lions, cheetahs).
- Freshwater: Home to fish, amphibians, and some invertebrates.
Importance of Animals
Importance of Animals
Animals play a crucial role in the ecosystem:
- Pollination: Insects like bees help pollinate plants.
- Decomposition: Animals like worms and insects help break down dead organic matter.
- Food Chain: Animals are part of the food chain, maintaining the balance of nature.
Plants
Plants are living organisms that belong to the kingdom Plantae. They are essential for life on Earth as they produce oxygen and provide food, shelter, and other resources. Plants are unique because they can make their own food through a process called photosynthesis.
Types of Plants
Plants can be categorized based on various criteria such as size, lifespan, habitat, and more. Here are some common types of plants:
1. Trees
- Features:
- Large, woody plants with a single main stem called a trunk.
- Can live for many years (some for centuries).
- Examples: Oak, Pine, Mango.
2. Shrubs
- Features:
- Smaller than trees with multiple stems.
- Woody and perennial (live for more than two years).
- Examples: Rose, Hibiscus, Bougainvillea.
3. Herbs
- Features:
- Small, non-woody plants with soft stems.
- Usually complete their life cycle in one growing season (annuals) or two (biennials).
- Examples: Basil, Mint, Spinach.
4. Climbers
- Features:
- Plants that need support to grow upwards.
- Have special structures like tendrils to cling onto supports.
- Examples: Grapevine, Ivy, Pea plant.
5. Creepers
- Features:
- Spread across the ground instead of growing upright.
- Have long stems that trail along the ground.
- Examples: Pumpkin, Watermelon, Strawberry.
Features of Plants
1. Roots
- Function:
- Anchor the plant in the soil.
- Absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
- Types:
- Taproot: A single, thick main root (e.g., Carrot).
- Fibrous root: Many small roots spread out from the base of the plant (e.g., Grass).
2. Stems
- Function:
- Support the plant.
- Transport water, nutrients, and food between roots and leaves.
- Types:
- Herbaceous stems: Soft and green (e.g., Tomato).
- Woody stems: Hard and brown (e.g., Oak tree).
3. Leaves
- Function:
- Main site of photosynthesis (making food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water).
- Exchange gases with the environment.
- Parts:
- Blade: The flat part of the leaf.
- Petiole: The stalk that attaches the leaf to the stem.
- Types:
- Simple leaves: Single, undivided blade (e.g., Maple).
- Compound leaves: Blade divided into leaflets (e.g., Rose).
4. Flowers
- Function:
- Reproductive part of the plant.
- Attract pollinators like bees, butterflies, and birds.
- Parts:
- Petals: Often colorful, attract pollinators.
- Sepals: Protect the flower bud before it opens.
- Stamens: Male reproductive parts (produce pollen).
- Pistil: Female reproductive part (contains ovary).
5. Fruits and Seeds
- Function:
- Fruits protect the seeds and aid in their dispersal.
- Seeds contain the embryo of a new plant.
- Types:
- Fleshy fruits: Juicy and edible (e.g., Apple, Banana).
- Dry fruits: Hard and non-juicy (e.g., Nuts, Peas).
Photosynthesis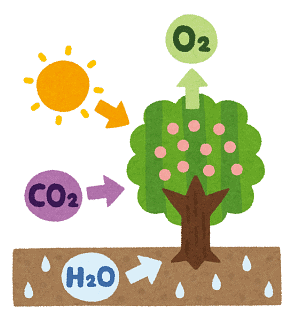
Process
- Light Absorption: Leaves contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that captures sunlight.
- Water Uptake: Roots absorb water from the soil and transport it to the leaves.
- Carbon Dioxide Intake: Leaves take in carbon dioxide from the air through small openings called stomata.
- Food Production: Using sunlight, chlorophyll converts water and carbon dioxide into glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen. The formula is:

Importance
- Provides food for the plant.
- Produces oxygen, which is essential for most living organisms.
Adaptation in Plants
Types of Adaptations:
- Structural Adaptations: Physical features that help plants survive, like thorns on cacti.
- Behavioral Adaptations: Actions plants take, such as curling leaves to conserve water.
- Physiological Adaptations: Internal processes that help plants, like storing water in succulent stems.
Examples of Adaptations:
- Desert Plants: Have thick stems to store water and small leaves to reduce water loss.
- Aquatic Plants: Have air sacs to float and thin leaves for easy nutrient absorption.
Why Adaptation Matters:
- Helps plants survive in different environments.
- Ensures they get what they need to grow and reproduce.
Adaptation in Animals
Types of Adaptations:
- Physical Adaptations: Features like fur for warmth or camouflage for protection.
- Behavioral Adaptations: Actions animals take for survival, like hibernation or migration.
- Physiological Adaptations: Internal changes, such as adjusting body temperature or producing venom.
Examples of Adaptations:
- Arctic Animals: Thick fur and fat layers for warmth in cold climates.
- Camouflaged Animals: Blend into surroundings for protection from predators.
- Nocturnal Animals: Active at night to avoid heat and predators.
Importance of Adaptation:
- Ensures animals can find food, shelter, and mates.
- Helps them avoid dangers and survive in their habitats.
Microbes
Microbes, short for microorganisms, are tiny living beings that are too small to see with the naked eye. They include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. Despite their small size, microbes play crucial roles in nature and human life.
Types of Microbes
Bacteria: These are single-celled organisms that can be found almost everywhere, from soil to water to inside our bodies. Some bacteria are helpful, like those that help us digest food, while others can cause diseases like colds and infections.
Viruses: Unlike bacteria, viruses are not considered living organisms because they cannot survive or reproduce without a host cell. They cause illnesses such as the flu, COVID-19, and the common cold.
Fungi: Fungi are diverse organisms that include molds, yeasts, and mushrooms. While some fungi are beneficial, like those used in making bread or antibiotics, others can cause infections like athlete's foot or thrush.
Protozoa: These are single-celled organisms that can move and feed on other microbes. Some protozoa are harmless, but others can cause diseases like malaria or amoebic dysentery.
Roles of Microbes
Decomposition: Microbes play a vital role in breaking down organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into nutrients that enrich the soil. This process is essential for recycling nutrients in ecosystems.
Food Production: Certain microbes are used in food production processes like fermentation, where they convert sugars into alcohol or acids. Examples include yeast in bread-making and bacteria in yogurt production.
Medicine: Microbes have contributed to the development of antibiotics to fight bacterial infections and vaccines to prevent viral diseases. They are also used in biotechnology for producing insulin and other medicines.
Environmental Balance: Some microbes help maintain environmental balance by participating in nitrogen fixation (converting nitrogen gas into a usable form for plants) and oxygen production through photosynthesis in marine microbes.
Impact on Human Health:
While many microbes are beneficial, some can cause diseases. It's important to practice good hygiene, like washing hands regularly, to prevent the spread of harmful microbes. Vaccinations also help protect against certain microbial infections.
|
20 videos|17 docs|55 tests
|
FAQs on Plants and Animals - GK Olympiad for Class 4
| 1. What are some common adaptations seen in animals to help them survive in their habitats? |  |
| 2. How do plants obtain energy through photosynthesis? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of different types of plants based on their structure and lifespan? |  |
| 4. How do animals adapt to their environments to ensure their survival? |  |
| 5. What are some common features of animals that help them thrive in their habitats? |  |




















