Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > Context of the Second World War
Context of the Second World War | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Context of the Second World War - Timeline & Summary
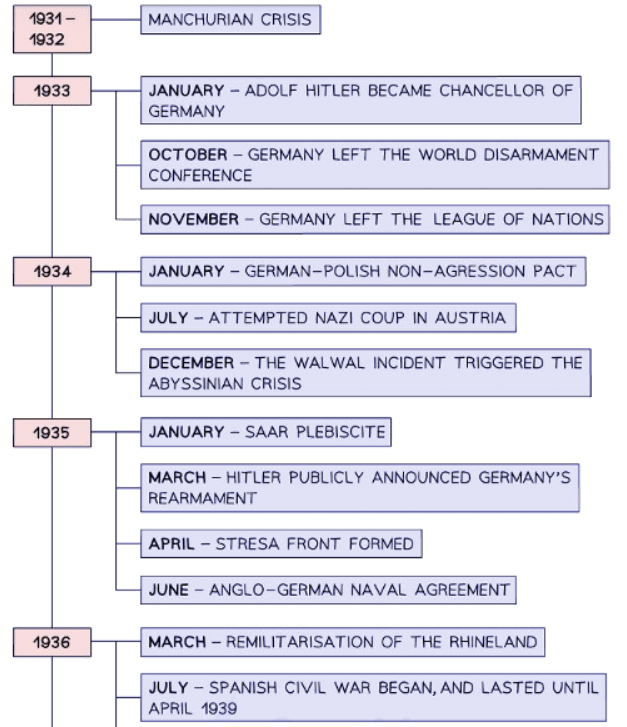
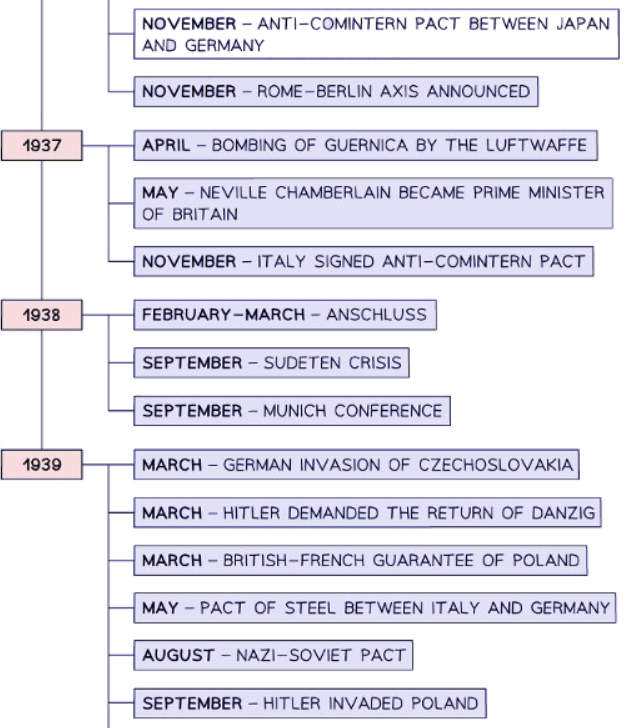
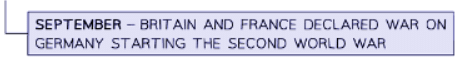
- The Second World War started when Germany invaded Poland on September 3, 1939, just 21 years after the end of the First World War. Germany was allied with Italy and Japan, forming the Axis powers. Britain and France united as the Allies. In August 1939, the USSR signed a non-aggression pact with Germany, known as the Nazi-Soviet Pact. The USSR joined the Allies in 1941 when Germany broke the pact and invaded Russia. The USA entered the war in December 1941 following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, joining the Allied forces.
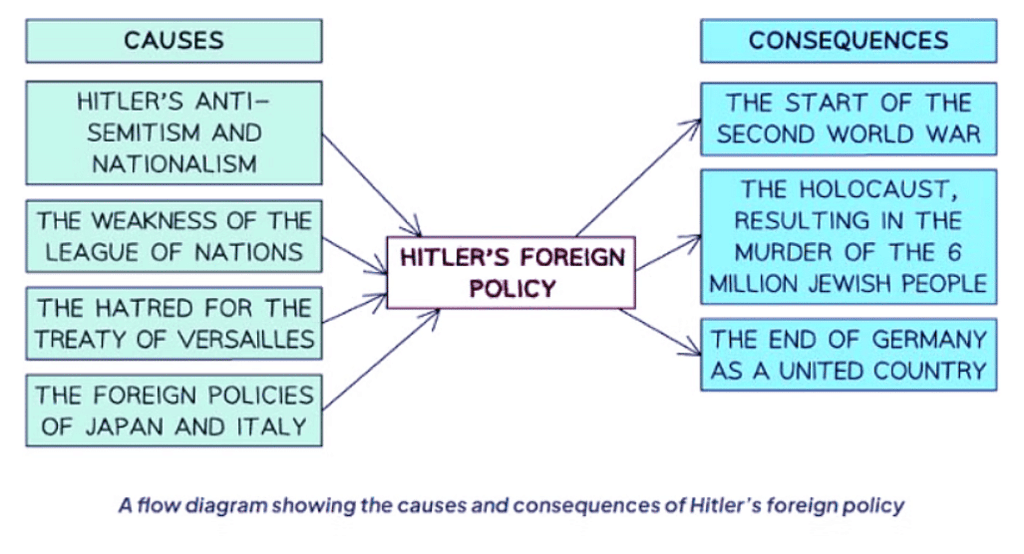
- There are different historical perspectives on why the Second World War began in 1939. The orthodox view is that Hitler caused the war. Many historians argue that Hitler’s foreign policy was deliberately aggressive. They claim he followed a strategic plan for expansion in the 1930s, violating the Treaty of Versailles through the remilitarization of the Rhineland and the Anschluss with Austria. These historians believe Hitler prepared for the possibility of war, as evidenced by Germany’s extensive rearmament program.
- Another perspective on the Second World War criticizes other world leaders. Revisionist historians argue that Hitler did not intend to start a war. They claim he was a typical German leader in his foreign policy aims and was an opportunist. The Great Depression in the 1930s increased support for the Nazi Party. Major League of Nations members, such as Britain and France, lacked the resources or willingness to oppose aggressive nations, rendering the League weak. Many leaders exploited this weakness: Japan invaded Manchuria in 1931, and Italy claimed Abyssinia in 1935. In an environment of militarism and nationalism, Hitler’s actions did not stand out and were similar to those of other extremist or autocratic leaders. Revisionist historians believe the Treaty of Versailles caused the war, being harsh enough to make many Germans resentful yet weakly enforced, allowing Germany to rebuild its power.
- Some historians believe elements of both arguments. They argue that Hitler was a strategist with clear foreign policy aims, but he would not have achieved these aims without the weakness of European leaders and the failure of the League of Nations.
Causes and Consequences of Hitler's Foreign Policy
The document Context of the Second World War | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
81 videos|87 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Context of the Second World War - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What were the main causes of Hitler's aggressive foreign policy leading up to the Second World War? |  |
Ans. Hitler's aggressive foreign policy leading up to the Second World War was primarily driven by his desire to expand German territory, create a greater German empire, and establish Germany as a dominant power in Europe. He also sought to overturn the Treaty of Versailles and unite all German-speaking people under one nation.
| 2. How did Hitler's foreign policy decisions contribute to the outbreak of the Second World War? |  |
Ans. Hitler's foreign policy decisions, such as the invasion of Poland and the signing of the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact with the Soviet Union, directly contributed to the outbreak of the Second World War. These actions violated international agreements and sparked conflict with other European powers.
| 3. What were the consequences of Hitler's aggressive foreign policy during the Second World War? |  |
Ans. The consequences of Hitler's aggressive foreign policy during the Second World War were devastating, leading to widespread destruction, loss of life, and suffering. Germany ultimately faced defeat and was left in ruins, while millions of people across Europe endured the horrors of war.
| 4. How did other countries respond to Hitler's foreign policy in the lead-up to the Second World War? |  |
Ans. Other countries responded to Hitler's foreign policy with a mix of appeasement, diplomatic efforts, and military alliances. Some nations, such as Britain and France, initially sought to avoid conflict through appeasement but eventually realized the need to confront Hitler's aggression.
| 5. What lessons can be learned from Hitler's foreign policy and its impact on the Second World War? |  |
Ans. The lessons learned from Hitler's foreign policy and its impact on the Second World War include the dangers of unchecked aggression, the importance of upholding international agreements, and the need for strong alliances to maintain peace and stability. It serves as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of aggressive and expansionist foreign policies.
Related Searches




















