Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > How Did Appeasement Work in Practice?
How Did Appeasement Work in Practice? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Anglo-German Naval Agreement, 1935 |

|
| Anschluss, 1938 |

|
| The Sudeten Crisis and the Munich Conference, 1938 |

|
| The Munich Conference |

|
| Invasion of Czechoslovakia, 1939 |

|
The Anglo-German Naval Agreement, 1935
- In April 1935, Britain, France, and Italy formed the Stresa Front to oppose Hitler's foreign policy and challenge any attempts to break the Treaty of Versailles.
- However, by June, the Stresa Front agreement had collapsed due to the worsening Abyssinian Crisis, which strained Italy's relations with Britain and France.
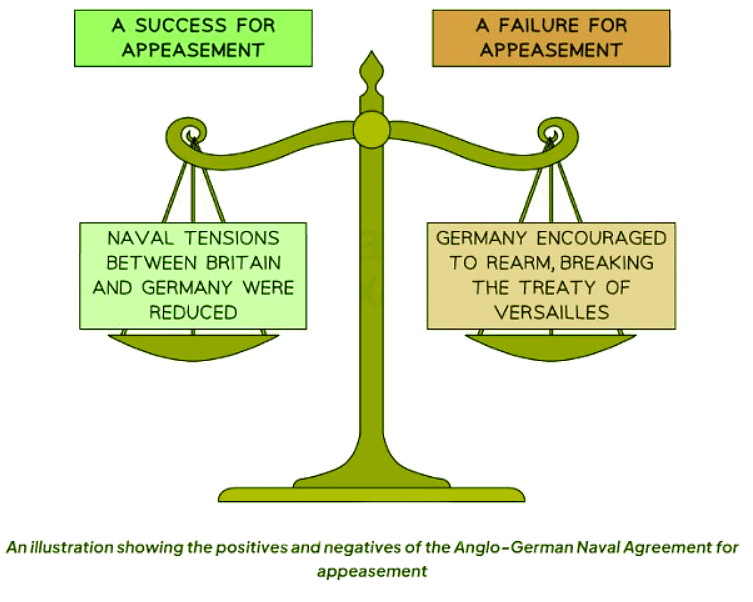
- Subsequently, Britain and Germany signed the Anglo-German Naval Agreement, marking the initial step towards appeasement.
- This agreement granted concessions to Germany's navy with the aim of curbing Hitler's aggressive ambitions.

Was the Anglo-German Naval Agreement a Success for Appeasement?
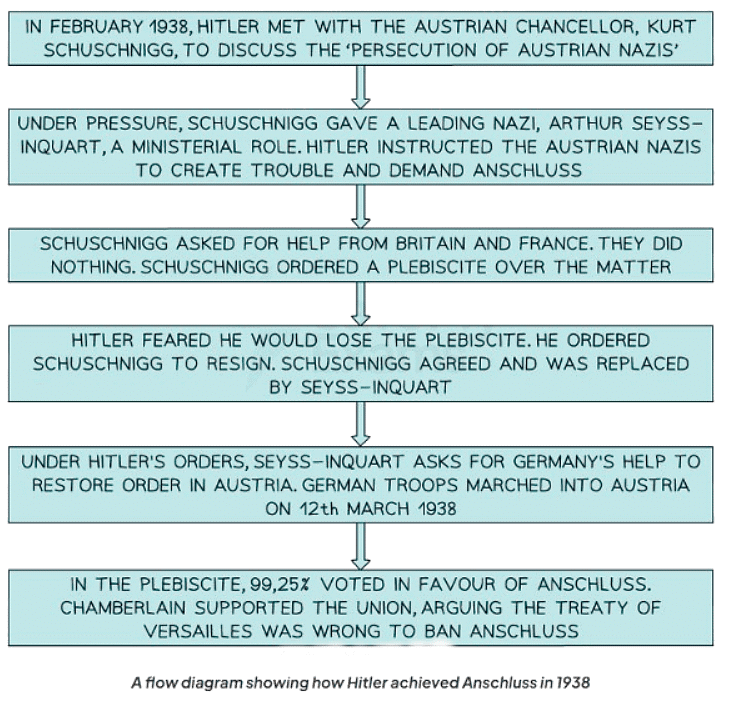
Anschluss, 1938
- Many Austrians supported the idea of Anschluss for various reasons:
- The vast majority, approximately 98%, of Austrians spoke German.
- Austrians perceived their economy as weak without the support of Germany.
- Presence of a strong Nazi Party in Austria influenced support for Anschluss.
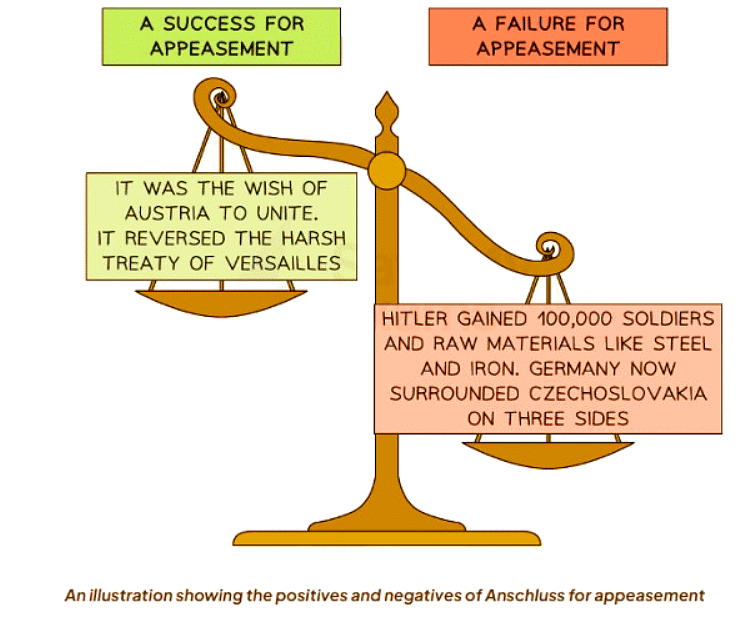
- By March 1938, Hitler was able to annex Austria to Germany without facing significant opposition.


Was Anschluss a Success for Appeasement?
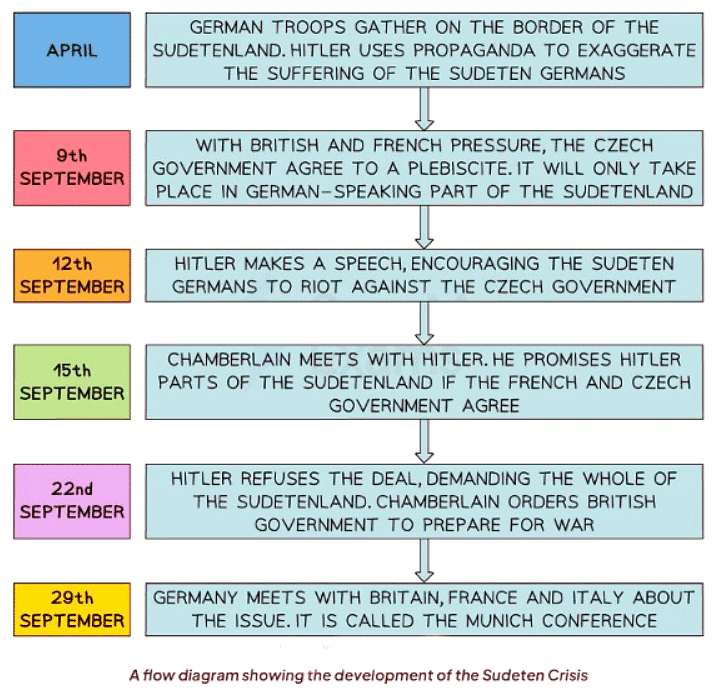
The Sudeten Crisis and the Munich Conference, 1938
- Hitler's Motives for Wanting the Sudetenland, Czechoslovakia:
- Following the Anschluss, Germany shared borders with Czechoslovakia on three sides
- Claiming Czechoslovakia would serve as a protective barrier against potential invasions
- The Sudetenland was rich in mineral resources and housed the Skoda armament factory, aiding Germany's armament industry
- The Sudetenland possessed fortifications, making it strategically valuable for Hitler
- By acquiring this territory, invading the entirety of Czechoslovakia would be facilitated for Hitler
- Over 3.5 million Germans resided in the Sudetenland
- The Sudeten Germans alleged mistreatment by the Czech government
- Hitler aimed to further his foreign policy objectives of Grossdeutchland and Lebensraum
- Following the Anschluss, Germany shared borders with Czechoslovakia on three sides
- In 1938, Hitler initiated his efforts to annex Czechoslovakia
Question for How Did Appeasement Work in Practice?Try yourself: What was the purpose of the Anglo-German Naval Agreement?View Solution
What was the Significance of the Sudeten Crisis?
The Munich Conference
- Delegates from Italy, Britain, France, and Germany were present at the conference.
- Czechoslovakia was excluded from the meeting.
- This exclusion rendered the meeting unfair from the beginning.
- The USSR did not participate in the conference.
- This non-involvement led to distrust between the USSR and the Western powers.
The Munich Agreement
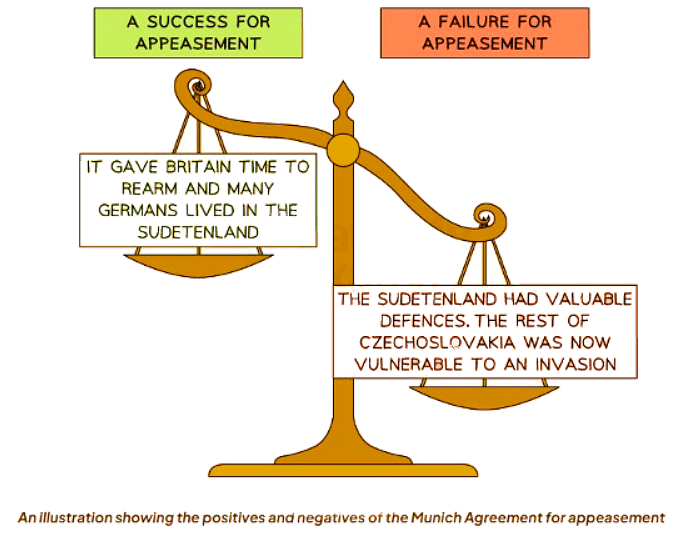
- The Munich Agreement was developed on 30th September 1938 by four nations: Italy, Britain, France, and Germany, in an attempt to prevent war.
- Key Points of the Munich Agreement:
- Hitler was allowed to gain control of the Sudetenland.
- Czechoslovakia retained the remainder of its territory.
- Controversy Surrounding the Munich Agreement:
- Czechoslovakia was compelled to accept the terms imposed.
- Hungary and Poland also made territorial claims on Czechoslovakia.
- Poland successfully annexed Teschen in October 1938.
Was the Munich Agreement a Success for Appeasement?


Invasion of Czechoslovakia, 1939
- Hitler's Acquisition of Czechoslovakia
- By March 1939, Hitler successfully acquired the remainder of Czechoslovakia.
- He demanded that the Czech government surrender control of the country, threatening Prague with Luftwaffe bombings if his demands were not met.
- On the 15th of March, Hitler's forces entered Prague.
- Hitler also managed to prompt Slovakia to declare its independence.
- Hitler's Strategic Intentions
- Hitler's actions were driven by his ambition to enhance Germany's power.
- It's noteworthy that there was no significant German-speaking population in the territories he claimed.
- His ultimate aim was to bolster Germany's influence and control.
- Impact on International Relations
- The invasion of Czechoslovakia marked the end of the policy of appeasement towards Hitler.
- Chamberlain, on the 17th of March, expressed a loss of trust in Hitler's assurances.
- Following this event, Britain and France began to contemplate safeguarding vulnerable European nations from Hitler's aggressive expansion.
 A map showing how far Hitler had extended Germany’s territory by March 1939
A map showing how far Hitler had extended Germany’s territory by March 1939
The document How Did Appeasement Work in Practice? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
81 videos|88 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on How Did Appeasement Work in Practice? - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How did the Anglo-German Naval Agreement of 1935 contribute to the policy of appeasement? |  |
Ans. The Anglo-German Naval Agreement of 1935 allowed Germany to expand its navy to 35% of the size of the British navy, which was seen as a concession to Hitler's demands. This agreement was a key example of appeasement, as it was an attempt to avoid conflict by giving in to Germany's demands.
| 2. What was the significance of the Anschluss in 1938 in relation to the policy of appeasement? |  |
Ans. The Anschluss, the annexation of Austria by Germany in 1938, was another example of appeasement as it showed that Western powers were willing to allow Hitler to violate the Treaty of Versailles without consequence. This event further emboldened Hitler to pursue his aggressive expansionist policies.
| 3. How did the Sudeten Crisis and the Munich Conference of 1938 demonstrate the appeasement policy in action? |  |
Ans. The Sudeten Crisis, where Hitler demanded the Sudetenland region of Czechoslovakia be given to Germany, led to the Munich Conference where Britain and France agreed to Hitler's demands in exchange for a promise of no further territorial expansion. This event showcased how appeasement was used to avoid conflict by giving in to aggressor's demands.
| 4. What were the outcomes of the Munich Conference in 1938 in terms of appeasement? |  |
Ans. The Munich Conference resulted in the ceding of the Sudetenland to Germany, further demonstrating the policy of appeasement. While hailed as a diplomatic success at the time for avoiding immediate conflict, it ultimately failed to prevent further aggression from Hitler, leading to the eventual invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1939.
| 5. How did the policy of appeasement ultimately fail in preventing the outbreak of World War II? |  |
Ans. The policy of appeasement failed to prevent the outbreak of World War II as it emboldened Hitler and allowed him to continue his aggressive expansionist policies unchecked. By giving in to Hitler's demands and avoiding confrontation, Western powers inadvertently allowed Germany to become stronger militarily and politically, leading to the eventual invasion of Poland and the start of the war.
Related Searches














