Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > The Ideology of the Cold War
The Ideology of the Cold War | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
The Ideology of the Cold War - Timeline & Summary
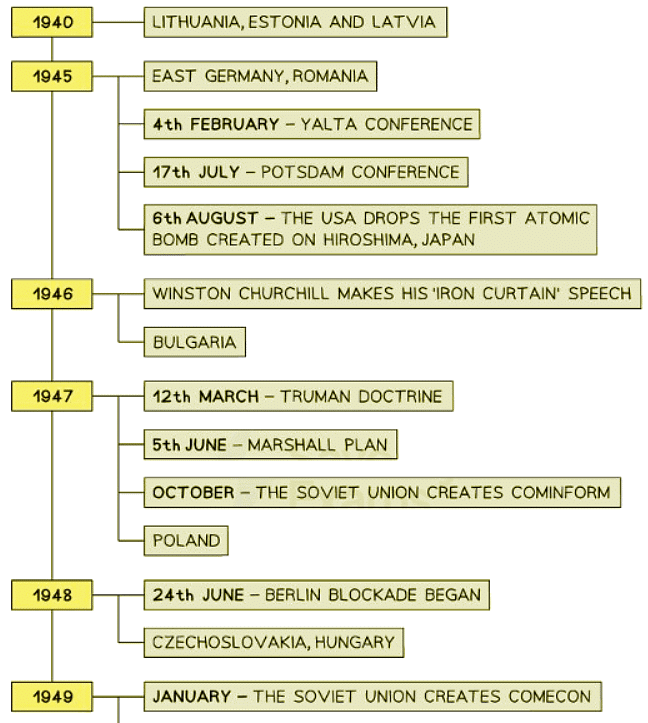
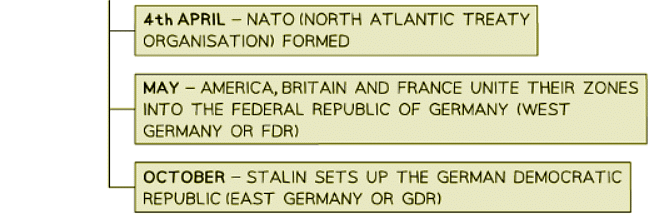
- In 1945, the USA and the USSR had opposing ideologies but fought together during the Second World War to defeat Nazi Germany and Imperial Japan. Despite Germany being a common enemy and general cooperation among the Allies, the USA’s capitalist beliefs were vastly different from the USSR’s Communist beliefs. Both countries set aside their differences during the war, yet remained suspicious of each other.
- Capitalism, an ideology where individuals can own property and businesses to generate profit, was championed by the USA and Britain by 1941. Franklin D. Roosevelt, the President of the USA at the time, led the nation into the Second World War against Germany and Japan following the Pearl Harbor attack in December 1941. Roosevelt was relatively tolerant of Stalin and the USSR.
- Communism, an ideology where the state owns all property to ensure equitable distribution, was led by the USSR by 1941. Joseph Stalin, the leader of the USSR, initially aligned with the Nazis due to the Nazi-Soviet Pact. However, following Hitler's breach of this pact in 1941, the USSR joined the Allies. Stalin's 1930s policies of collectivization and rapid industrialization caused millions of deaths and drew significant criticism from the USA and Britain. Stalin, in turn, was deeply paranoid and distrusted the West.
- After Germany's defeat in May 1945, there was no longer a reason for the USA and the USSR to cooperate. This tension ultimately led to the start of the Cold War, characterized by the lack of direct conflict between the two main countries. Instead, the superpowers engaged in economic and political maneuvers and supported proxy wars worldwide.
- Historians debate the causes of the Cold War. Orthodox historians argue that Stalin’s aggressive expansion of communism into Eastern Europe violated post-war agreements and triggered the conflict. On the other hand, revisionist historians claim the USA was responsible, citing its development of nuclear technology and failure to share this information with the USSR. They argue that the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945 intimidated Stalin, prompting his aggressive actions. Additionally, revisionists assert that the USA's interference in European politics aimed to establish a capitalist Europe for export markets, leading to efforts to contain communism within the USSR.
Question for The Ideology of the Cold WarTry yourself: What were the opposing ideologies of the USA and USSR during the Cold War?View Solution
Causes and Consequences of the Start of the Cold War
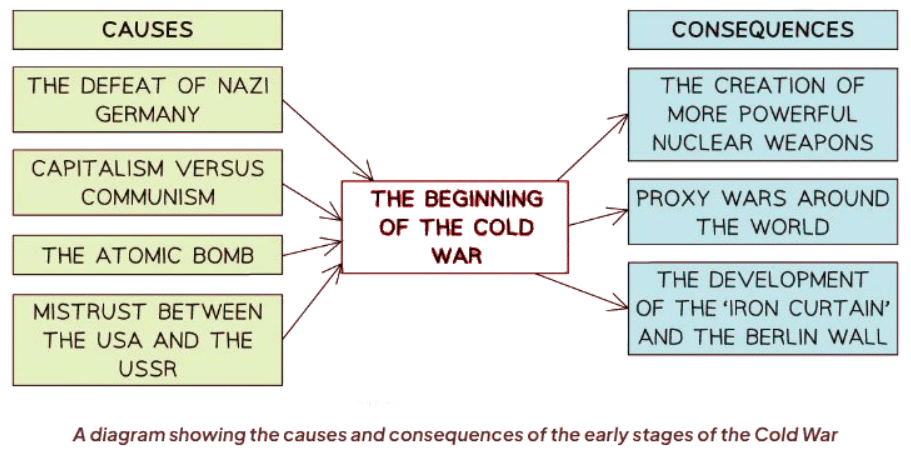
The document The Ideology of the Cold War | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
81 videos|87 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on The Ideology of the Cold War - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What were the main causes of the Cold War? |  |
Ans. The main causes of the Cold War were ideological differences between the United States and the Soviet Union, competition for global influence and power, and the aftermath of World War II.
| 2. How did the ideology of the Cold War impact international relations during that time? |  |
Ans. The ideology of the Cold War led to the division of the world into two opposing camps, the spread of communism and containment by the United States, and the arms race between the superpowers.
| 3. What were some of the key events that marked the escalation of the Cold War? |  |
Ans. Some key events that marked the escalation of the Cold War include the Berlin Airlift, the Korean War, the Cuban Missile Crisis, and the construction of the Berlin Wall.
| 4. How did the ideology of the Cold War influence domestic policies in the United States and the Soviet Union? |  |
Ans. The ideology of the Cold War led to the rise of McCarthyism in the United States, increased government surveillance and control, and the strengthening of the military-industrial complex. In the Soviet Union, it resulted in repression, censorship, and a focus on military buildup.
| 5. What were the long-term consequences of the ideology of the Cold War on global politics and security? |  |
Ans. The long-term consequences of the Cold War include the establishment of a bipolar world order, the proliferation of nuclear weapons, the formation of military alliances such as NATO and the Warsaw Pact, and ongoing regional conflicts influenced by Cold War ideologies.
Related Searches
















