Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > Solidarity in Poland & the Decline of Soviet Influence
Solidarity in Poland & the Decline of Soviet Influence | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
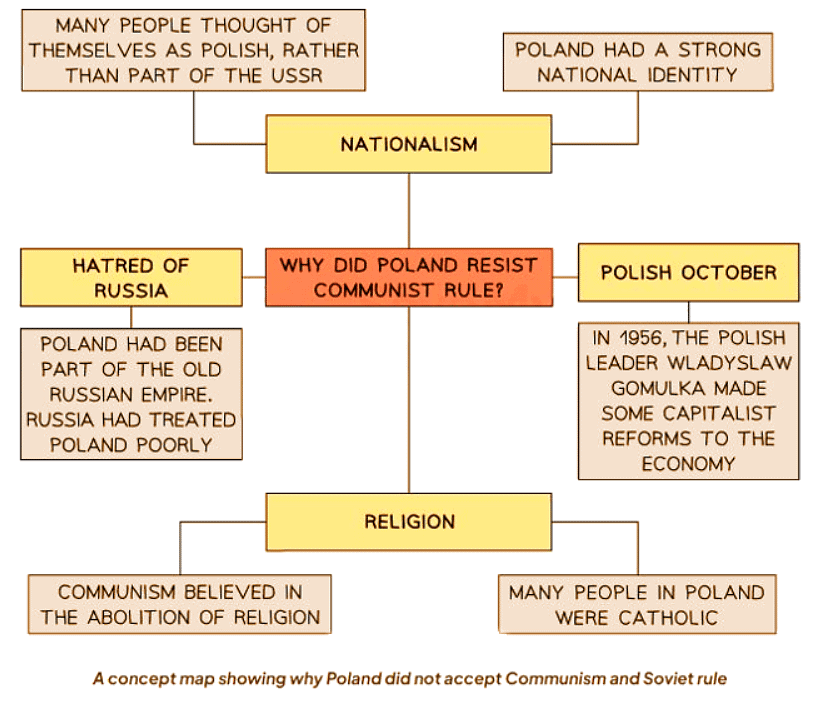
Reasons Why Poland Resisted Communist Rule
Who were Solidarity?
- By the late 1970s, Poland’s economy was struggling.
- Poland's industry was outdated due to insufficient funding.
- The Polish government concealed the severity of the economic decline.
- Workers’ wages were much higher than their productivity.
- In 1980, the government tried to fix the economy by:
- Increasing the prices of consumer goods.
- Decreasing workers’ wages.
- The government's measures led to:
- Popular protests.
- Widespread strikes.
- The strike at Lenin Gdansk Shipyard on August 14, 1980, led to the formation of Solidarity.
- Solidarity began as a trade union and evolved into a protest movement.
 An illustration showing the leadership and some of Solidarity’s demands
An illustration showing the leadership and some of Solidarity’s demands
- On August 30, 1980, the government accepted all 21 demands presented by Solidarity after negotiations.
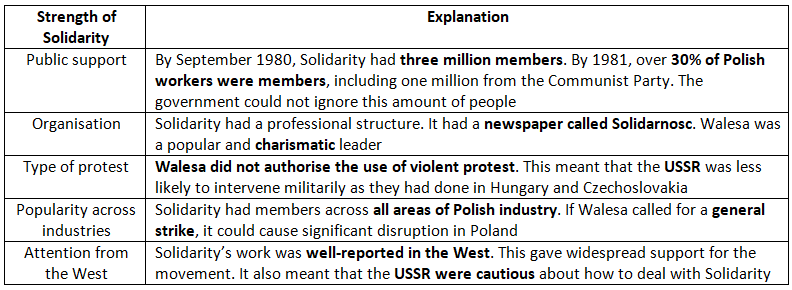
Strengths of Solidarity
Martial Law in Poland
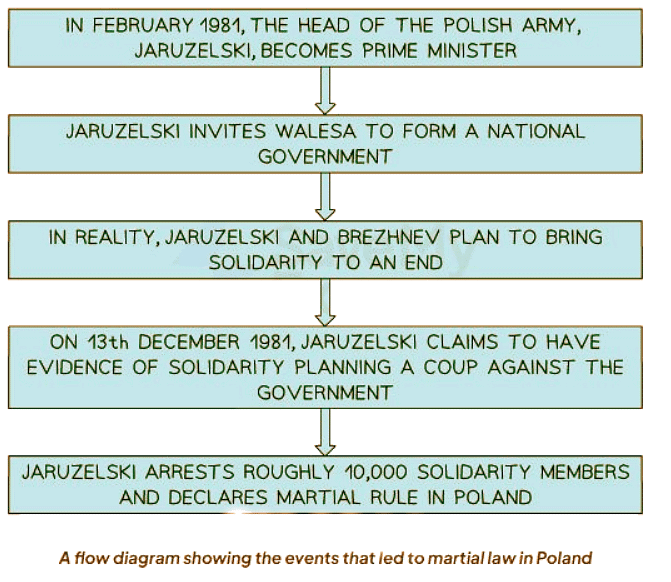
What Led to the Implementation of Martial Law in Poland?
- Solidarity faced internal fragmentation:
- Encouragement of factionalism by the Communist government within Solidarity led to disunity.
- Disputes arose regarding key policies and objectives of the movement, causing discord.
- External Factors Influencing the Government's Decision:
- The government's decision to impose martial law was backed by the USSR.
- Brezhnev, the Soviet leader, couldn't afford Solidarity weakening Poland due to strategic reasons.
- Poland's significance to the USSR's metallurgical needs played a crucial role.
- Reforms in Poland could potentially distance the country from the Soviet sphere of influence.
- Conformity to the Warsaw Pact was essential for Brezhnev's geopolitical goals.
- A Solidarity-led government might have sought more independence, posing a threat to Soviet control.
- Potential withdrawal of Poland from the Warsaw Pact was a concern for Soviet interests.

Question for Solidarity in Poland & the Decline of Soviet InfluenceTry yourself: What were some of the reasons why Poland resisted communist rule?View Solution
How Did Solidarity Show the Decline of Soviet Influence?
The actions of Solidarity demonstrated that by the 1980s:
- Millions of people were willing to stand up against the Communist government.
- The public openly expressed their desire for a better standard of living.
- Communist leaders continued to be:
- Corrupt.
- Resistant to reform.
The document Solidarity in Poland & the Decline of Soviet Influence | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
79 videos|87 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Solidarity in Poland & the Decline of Soviet Influence - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What were the reasons why Poland resisted communist rule? |  |
Ans. Poland resisted communist rule due to a strong sense of national identity, historical experiences of foreign domination, and a desire for political and economic freedom.
| 2. Who were Solidarity and what role did they play in Poland's fight against Soviet influence? |  |
Ans. Solidarity was a trade union movement in Poland that evolved into a major protest movement against Soviet influence, advocating for workers' rights, political freedom, and social change.
| 3. What were the economic measures implemented by the Polish government in 1980, and how did they impact the country? |  |
Ans. The Polish government implemented economic measures in 1980, including price hikes and wage freezes, which led to widespread discontent among the population and fueled support for Solidarity.
| 4. How did Solidarity transform from a trade union into a protest movement, and what were its strengths in challenging the government? |  |
Ans. Solidarity transformed from a trade union into a protest movement by mobilizing a broad spectrum of society and using peaceful resistance tactics. Its strengths included strong leadership, mass support, and the ability to organize strikes and demonstrations.
| 5. What was the impact of martial law in Poland on Solidarity and the fight against Soviet influence? |  |
Ans. Martial law in Poland imposed by the government in 1981 severely restricted Solidarity's activities, leading to arrests, censorship, and repression. However, the movement continued to resist, eventually contributing to the decline of Soviet influence in the country.
Related Searches





















