Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > History for GCSE/IGCSE > Why Did Stalin Introduce Collectivisation?
Why Did Stalin Introduce Collectivisation? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
How Significant was Collectivisation for the USSR? - Summary
- Collectivization, a key policy initiated by Stalin in 1928, aimed to merge individual farms into collective entities, some of which were owned and managed by the state. This policy had profound ramifications for the USSR.
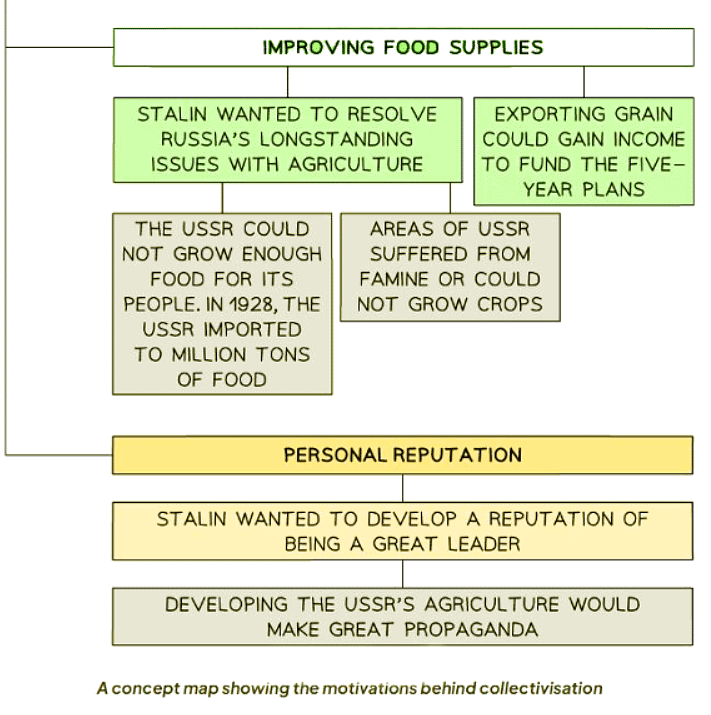
- From an economic standpoint, collectivization sought to bolster agricultural productivity by consolidating farms, allowing peasants access to modern resources and farming techniques. However, the coerced implementation of collectivization sparked widespread resistance among peasants, resulting in the destruction of crops, livestock, and infrastructure. Collective farms often operated inefficiently, exacerbating food shortages and triggering widespread famine, notably in Ukraine, known as the Holodomor.
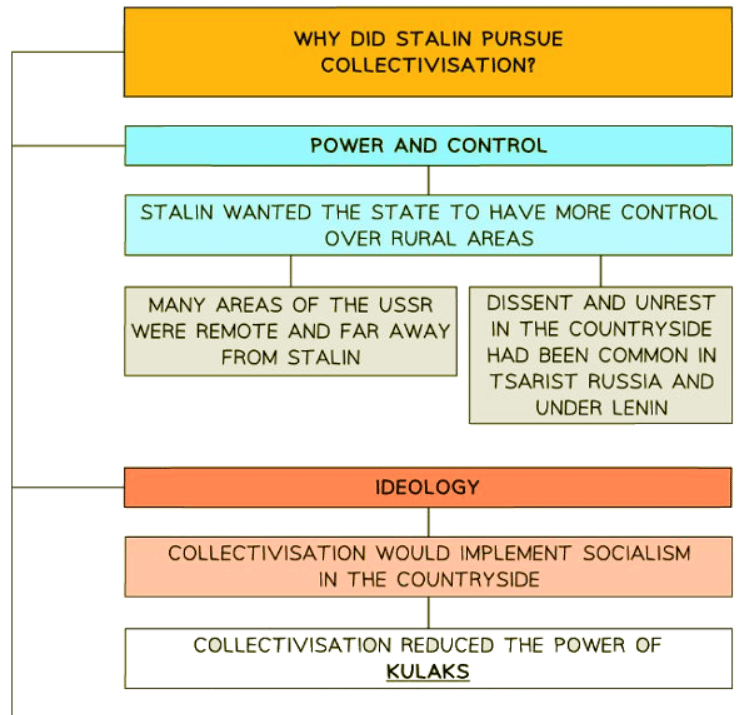
- Moreover, collectivization served to solidify Stalin's control over agricultural communities, initiating the process of dekulakization, which aimed to eradicate the influence of affluent kulaks perceived as a threat to the socialist regime. Consequently, collectivization bolstered the state's authority over the rural populace.
- On a social level, collectivization inflicted immense suffering upon millions of peasants. State-enforced relocations led to the loss of land, while dissenters faced severe repercussions. Traditional rural communities were disrupted, sparking social turmoil and unrest.
Reasons for Collectivisation
- While the Five-Year Plans prioritized rapid industrialization, collectivization aimed at enhancing agricultural productivity.
- Stalin introduced the concept of collectivization in 1928.
- There were numerous motivations driving the implementation of collectivization.
How did Collectivisation Work?
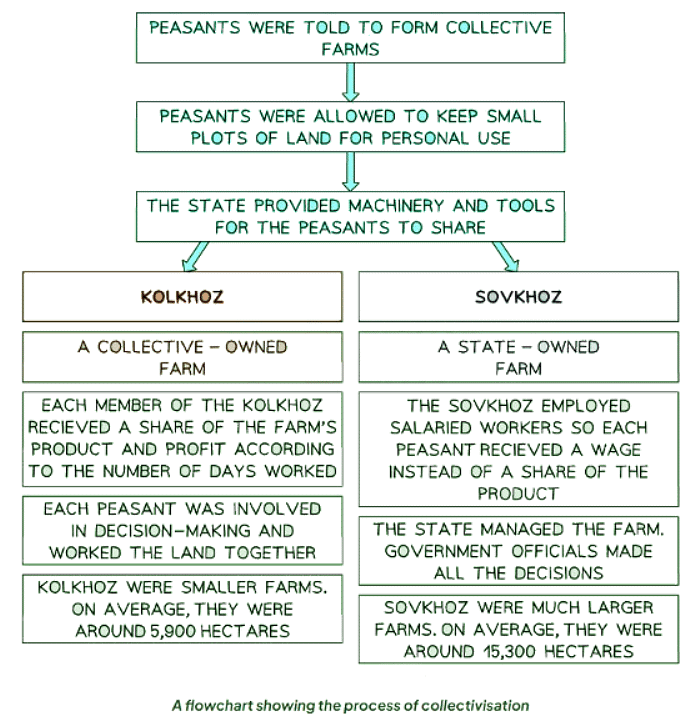
- Stalin was forced to introduced collectivisation in two stages:

The Process of Collectivisation
What Issues did Collectivisation Cause?
- Peasants were coerced by the state to join collective farms, leading to dissatisfaction among both affluent and impoverished farmers who resented leaving their homes.
- Rebellions ensued as peasants protested against the government's actions, resulting in the destruction of crops and livestock rather than surrendering them to authorities.
- Ukraine, a vital agricultural region within the USSR, suffered significantly from collectivisation, facing economic turmoil and cultural suppression.
- The Ukrainian peasantry faced severe repercussions for resisting collectivisation, with the government implementing harsh measures to enforce compliance, even amidst poor harvests.
- The forced seizure of food from peasants who couldn't meet government quotas led to widespread famine, known as the 'Holodomor' or 'death by hunger.'
Question for Why Did Stalin Introduce Collectivisation?Try yourself: What was the main goal of collectivization in the USSR?View Solution
The document Why Did Stalin Introduce Collectivisation? | History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course History for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
79 videos|87 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Why Did Stalin Introduce Collectivisation? - History for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. How did collectivisation impact the agricultural sector in the Soviet Union? |  |
Ans. Collectivisation in the Soviet Union resulted in the consolidation of individual farms into collective farms, leading to significant changes in agricultural production and distribution.
| 2. What were the main reasons for Stalin to introduce collectivisation in the USSR? |  |
Ans. Stalin introduced collectivisation in the USSR to increase agricultural productivity, modernise farming practices, and eliminate the influence of wealthy landowners.
| 3. What were the social consequences of collectivisation on the Soviet population? |  |
Ans. Collectivisation led to widespread resistance and opposition among peasants, causing social unrest, forced relocation, and famine in some regions.
| 4. How did collectivisation impact industrialisation efforts in the Soviet Union? |  |
Ans. The increased agricultural output from collectivisation provided food for the growing urban population and supported the industrialisation efforts of the Soviet government.
| 5. What long-term effects did collectivisation have on the Soviet economy and society? |  |
Ans. Collectivisation had lasting effects on the Soviet economy, leading to inefficiencies, food shortages, and a shift towards a more centrally planned economy. It also changed the social structure of rural communities and impacted the relationship between the state and the peasantry.
Related Searches















