Animals | GK Olympiad for Class 8 PDF Download
Introduction
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the kingdom Animalia. They are characterized by their ability to move, reproduce sexually, and consume organic material. Animals range from simple invertebrates like sponges to complex vertebrates like humans, playing crucial roles in ecosystems and human societies.
Types of Animals
Animals can be broadly classified into two groups: vertebrates (with a backbone) and invertebrates (without a backbone).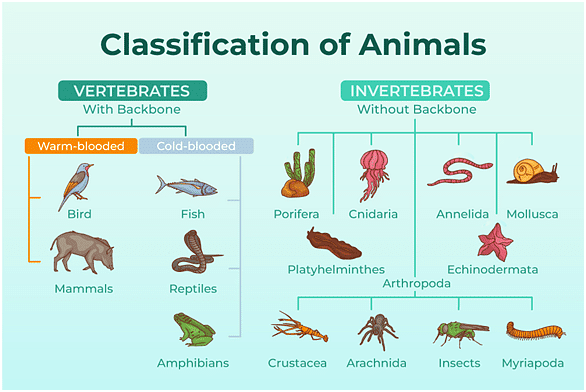
- Invertebrates: Includes insects, mollusks, crustaceans, and arachnids. For example, butterflies (insects), octopuses (mollusks), crabs (crustaceans), and spiders (arachnids).
- Vertebrates: Divided into five classes: Mammals (e.g., humans, lions), Birds (e.g., eagles, penguins), Reptiles (e.g., snakes, lizards), Amphibians (e.g., frogs, salamanders), and Fish (e.g., sharks, salmon).
Habitats and Diets
Animals live in diverse habitats and their diets are closely linked to their environments: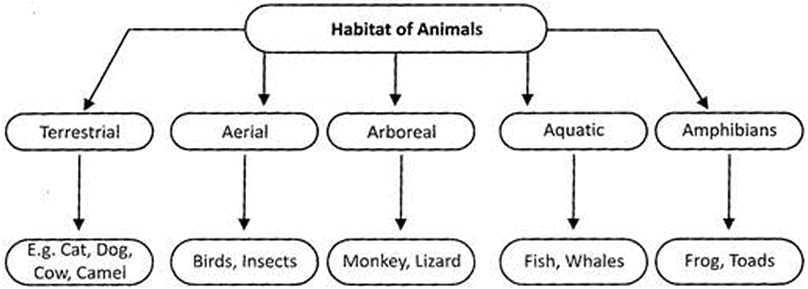
- Aquatic Animals: Live in water; diets include algae, plants, and smaller animals. Example: Fish in oceans eat plankton or other fish.
- Terrestrial Animals: Live on land; diets range from plant-based (herbivores) to meat-based (carnivores) or both (omnivores). Example: Deer (herbivores) eat leaves and grass, while lions (carnivores) hunt other animals.
- Aerial Animals: Birds and some insects; diets often consist of insects, seeds, or small animals. Example: Eagles eat fish or rodents.
Reproduction in Animals
Animals reproduce mostly sexually, though some also reproduce asexually. Reproduction methods vary widely:
- Sexual Reproduction: Involving the combination of genetic material from two parents. Mammals generally give birth to live young, while birds lay eggs.
- Asexual Reproduction: Some species, like certain reptiles and amphibians, can reproduce without a sexual partner, often through processes like budding or fragmentation.
Humans as Animals
Humans are classified as mammals within the animal kingdom. They share many biological characteristics with other animals, such as a vertebral column, warm-blooded nature, and the ability to bear live young. Humans are unique in their advanced cognitive abilities, which allow for complex language, culture, and technology.
Importance of Animals
Animals play essential roles in ecosystems and human life:
- Ecosystem Stability: Many animals are key to their ecosystems, either as predators, prey, or both. Their interactions ensure the stability of food webs.
- Agriculture: Animals such as bees pollinate plants, which is crucial for food crops. Livestock animals like cows and chickens provide meat, milk, and eggs.
- Biological and Medical Research: Many scientific studies rely on animals to understand biological processes and develop medical treatments.
Endangered Animals
Numerous animal species are endangered due to habitat loss, pollution, poaching, and climate change. Examples include the tiger, rhinoceros, and many species of whales and sea turtles.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts to save animals include:
- Protected Areas: Establishing wildlife reserves and national parks.
- Legal Protection: Enforcing laws against poaching and illegal wildlife trade.
- Captive Breeding: Breeding animals in captivity to increase population numbers, followed by reintroduction into the wild.
Zoos and Sanctuaries
Zoos and wildlife sanctuaries play roles in animal conservation and education:
- Conservation: Many zoos participate in breeding programs for endangered species.
- Education: Zoos provide educational resources for the public to learn about animal diversity and conservation issues.
Forest Protection Acts of India
India has implemented several key legislations to protect its forests and promote environmental conservation. Here are some of the primary forest protection acts along with their year of launch:
The Indian Forest Act, 1927
This Act was originally promulgated by the British to consolidate and reserve the areas having forest cover or significant wildlife to regulate movement and transit of forest produce, and duty leviable on timber and other forest produce. It remains one of the key pieces of forest legislation in India.
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972
This Act provides for the protection of India's wildlife, including animal and plant species. It establishes schedules of protected plant and animal species; hunting or harvesting these species is punishable by law. It also helped set up the network of Protected Areas like National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries, Conservation Reserves, and Community Reserves.

The Forest Conservation Act, 1980
This Act was specifically enacted to help conserve the country's forests. It restricts and regulates the de-reservation of forests or use of forest land for non-forest purposes without the prior approval of the central government. This law was crucial in curbing deforestation for industrial and other developmental projects.
The National Forest Policy, 1988
Although not a legislative act, this policy was formulated to ensure environmental stability and maintenance of ecological balance. The policy stresses the preservation of the remaining natural forests with special emphasis on afforestation and reforestation.
The Biological Diversity Act, 2002
This Act was enacted for the conservation of biological diversity, sustainable use of its components, and fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of the use of biological resources. It aims to protect species, their habitats, and also ensures that the local communities benefit from the use of local resources.
The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006
Commonly referred to as the Forest Rights Act, it recognizes the rights of forest-dwelling tribal communities and other traditional inhabitants to forest resources, on which these communities were historically dependent. This Act acknowledges their role in forest conservation and aims to provide a framework for recording the forest rights so vested.

These laws form the backbone of forest conservation efforts in India, aimed at preserving the rich biodiversity while balancing the needs of development and the rights of indigenous communities.
Project Tiger, 1973
Initiated in 1973 to protect tigers in India, this government-led initiative has led to the establishment of numerous tiger reserves throughout the country. The project aims at tiger conservation in specially constituted tiger reserves, which are representative of various bio-geographical regions within the country.
Project Elephant, 1992
Launched in 1992 by the Government of India, this project aims to provide financial and technical support to major elephant bearing states in the country for the protection of elephants, their habitats, and corridors. It also seeks to address issues of human-elephant conflict and welfare of domesticated elephants.
|
16 videos|12 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Animals - GK Olympiad for Class 8
| 1. What are some examples of endangered animals discussed in the article? |  |
| 2. How do forest protection acts in India help in the conservation of animals? |  |
| 3. How do zoos and sanctuaries contribute to the conservation of endangered animals? |  |
| 4. What are some common types of habitats mentioned in the article where animals live? |  |
| 5. How do humans play a role in animal reproduction, as discussed in the article? |  |
















