Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Angles in Polygons
Angles in Polygons | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
What is a polygon?
- A polygon is a flat shape with n straight sides.
- For example, a triangle has 3 sides, a quadrilateral has 4 sides, and a pentagon has 5 sides.
- In a regular polygon, all sides are of equal length and all angles are equal.
- For example, an equilateral triangle is a regular polygon with 3 sides, and a square is a regular polygon with 4 sides.
Question for Angles in PolygonsTry yourself: How many sides does a regular hexagon have?View Solution
What are the sums of angles in polygons?
- To work with angles in polygons, you need to calculate the sums of their angles.
- Use the formula to find the sum of the interior angles in a polygon with n sides:
- SUM OF INTERIOR ANGLES = 180° × (n – 2)
- This is because the polygon can be divided into (n – 2) triangles.
- For regular polygons, divide this sum by n to find each individual interior angle.
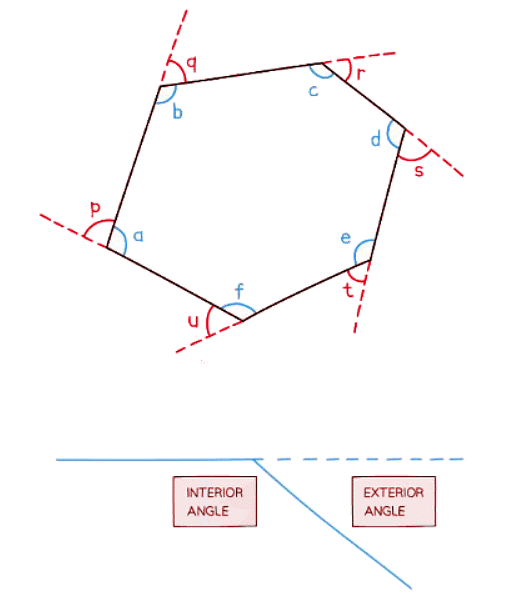
- The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon always equals 360°.
- TOTAL OF EXTERIOR ANGLES = 360°
- Exterior angles are the angles formed by extending each side of the polygon along a straight line.
- Note that the interior and exterior angles at each vertex lie on a straight line, summing to 180°.
The document Angles in Polygons | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
38 videos|395 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Angles in Polygons - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is a polygon? |  |
Ans. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional shape with straight sides. It is formed by connecting line segments called edges, which meet at points called vertices.
| 2. What are the sums of angles in polygons? |  |
Ans. The sum of interior angles in a polygon can be calculated using the formula (n-2) * 180 degrees, where n represents the number of sides of the polygon.
| 3. How can I calculate the measure of each interior angle in a regular polygon? |  |
Ans. To find the measure of each interior angle in a regular polygon, divide the sum of interior angles by the number of sides in the polygon. This will give you the measure of each interior angle.
| 4. Are there any special properties of angles in certain types of polygons? |  |
Ans. Yes, regular polygons have all angles and sides congruent, while in irregular polygons, angles and sides can vary in size and length.
| 5. How can I determine the type of polygon based on its interior angles? |  |
Ans. By calculating the sum of interior angles in a polygon and comparing it to the known formulas for different types of polygons, you can determine the type of polygon based on its angles.
Related Searches















