Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE > Bearings
Bearings | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are bearings? |

|
| How are bearings defined? |

|
| What are bearings used for? |

|
| How are bearings used on maps? |

|
What are bearings?
- Bearings describe and use directions in terms of angles.
- They are precisely defined for navigation purposes to provide exact locations and directions.
How are bearings defined?
- There are three rules to follow when defining a bearing:
- Bearings are measured from the North direction, typically shown as straight up on a scale drawing or map.
- Bearings are measured clockwise from North. If confused, refer to a wall clock for guidance.
- Bearings should always be written with three digits, so angles under 100° should have leading zeros (e.g., 059, 008).
- Note that degree symbols are generally not used when referring to bearings.
What are bearings used for?
- Bearings questions typically involve using Pythagoras' theorem or trigonometry to determine missing distances (lengths) and directions (angles) in navigation problems.
- Always draw a diagram for clarity.
- You may be given a scale or need to consider using one.
- Some questions might require using angle facts to find the missing directions.
- To solve a bearings question, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Draw a diagram, including any points and distances provided.
- Step 2: Draw a North line (an arrow pointing straight up) at the point from which you are measuring the bearing. If the bearing from A to B is given, draw the North line at point A.
- Step 3: Measure the given bearing angle clockwise from the North line.
- Step 4: Draw a line and mark point B at the specified distance.
- Use Pythagoras' theorem or trigonometry to calculate any additional distances needed.
How are bearings used on maps?
- If you find yourself needing to determine a direction on a map, here is a step-by-step guide using a protractor:
- Always start by drawing the North line on your map.
- Measure the angle clockwise from the North direction.
- Express the angle using three figures for accuracy.
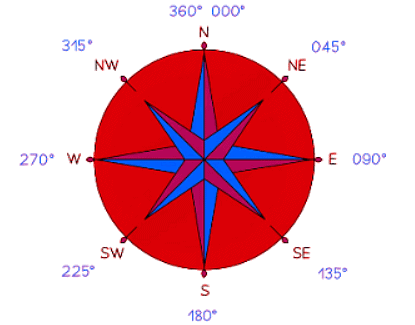
- Understanding the cardinal compass directions can be beneficial. Here are some key bearings and how to represent them:
- Due east corresponds to a bearing of 090°. Draw the line directly to the right.
- Due south corresponds to a bearing of 180°. Draw the line vertically downwards.
- Due west corresponds to a bearing of 270°. Draw the line directly to the left.
- Due north corresponds to a bearing of 360° (or 000°). Draw the line vertically upwards.
- For directions that fall in between these cardinal points, you can use combinations. Here are some examples:
- Due Northeast falls on a bearing of 045°, halfway between North (000°) and East (090°).
- Due Southeast falls on a bearing of 135°.
- Due Southwest falls on a bearing of 225°.
- Due Northwest falls on a bearing of 315°.
- Using the above bearings for compass directions will help you to estimate angles for other bearings on the map
The document Bearings | Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
38 videos|397 docs|19 tests
|
FAQs on Bearings - Mathematics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What are bearings? |  |
Ans. Bearings are a navigation tool used to determine the direction of one point from another point, usually measured in degrees clockwise from the north.
| 2. How are bearings defined? |  |
Ans. Bearings are defined as the angle measured in degrees between the north direction and the direction to the point of interest, usually expressed in three digits (e.g., 045°).
| 3. What are bearings used for? |  |
Ans. Bearings are used for navigation, surveying, and map reading to accurately determine the direction of one point from another point.
| 4. How are bearings used on maps? |  |
Ans. Bearings are used on maps to indicate the direction of one point from another point. They help in determining the relative location and orientation of different features on the map.
| 5. How can bearings help in navigation? |  |
Ans. Bearings help in navigation by providing a clear direction from one point to another, making it easier to plan and follow a specific route or path. They are particularly useful in outdoor activities such as hiking, orienteering, and sailing.
Related Searches




















