Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st May 2024) Part - 1 | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Criminalisation of Politics
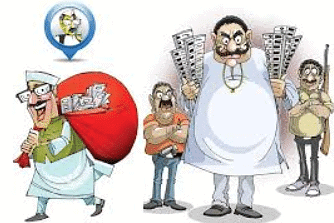
Context: Criminalisation of politics refers to the troubling trend where individuals with criminal backgrounds or charges are elected as politicians, raising concerns about the integrity of the democratic process.
Statistics
- Data from the Association for Democratic Reforms (ADR) highlights a concerning rise in the number of candidates with criminal charges being elected to Parliament in India over the years.
Causes of Increasing Criminalisation
- Nexus between Politicians and Criminals: Many Indian politicians have forged alliances with criminal elements, leveraging their resources to secure electoral victories.
- Weak Law Enforcement and Judicial System: The Indian justice system's inefficiencies and corruption create obstacles to prosecuting and convicting politicians with criminal backgrounds effectively.
- Lack of Internal Party Democracy: Political parties' weak internal structures allow leaders to nominate candidates based on electoral viability rather than ethical integrity.
- Voter Apathy and Lack of Awareness: Some voters prioritize immediate gains offered by criminal-backed candidates over long-term governance considerations.
Ethical Issues
- Absence of Non-partisanship and Accountability: Failure to address misconduct within the political class reflects a lack of ethical standards and accountability.
- Lack of Democratic Accountability: Public outcry may prompt action, but the reactive nature of responses underscores broader accountability deficiencies.
- Culture of Impunity and Individual Accountability: The normalization of impunity in politics places the burden of accountability on individuals rather than systemic reforms.
- Women's Empowerment Challenges: Despite rhetoric, meaningful progress on women's issues remains elusive in political agendas.
Ethical Implications
- Societal Perspective: Criminalization can erode societal ethics, reduce civic engagement, exacerbate inequality, and prioritize short-term gains.
- Democratic Perspective: Politicians with criminal backgrounds undermine democratic principles, distort elections, impede accountability, and hinder national development.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Institutional Mechanisms: Enhancing anti-corruption agencies, judicial oversight, and internal party disciplinary processes.
- Promoting Ethical Conduct: Implementing codes of conduct, ethical training, and stringent penalties for violations.
- Empowering Citizens and Civil Society: Fostering political awareness, citizen participation, and media activism to combat political misconduct.
UN: Trillions Required to Rescue SDGs
Context:
- Recently, a new report from the United Nations highlights the urgent need for increased investment to achieve the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030.
- Developing countries are facing significant challenges due to high debt burdens and soaring borrowing costs, hindering their ability to address the various crises they are confronted with.
Key Highlights of UN Financing for Sustainable Development Report 2024
- Lack of Basic Services: Geopolitical tensions, climate-related disasters, and a global cost-of-living crisis are impeding progress in healthcare, education, and other key development areas.
- Increase in Debt Services: Debt services in the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) are projected to rise significantly, posing challenges to their economic stability.
- Higher Burden of Interest Payment: The poorest nations are allocating a substantial portion of their revenues towards interest payments, affecting their ability to invest in essential sectors like education and health.
- Slowing Development Fundings: Development funding in LDCs is decelerating due to various factors such as tax evasion, falling corporate tax rates, and unmet international aid commitments.
Progress of India in Achieving SDGs
India's Ranking: India has advanced in the global rankings for progress towards the SDGs, reflecting improvements in various key areas.
- Progress in Key Goals:
- No Poverty: India has significantly reduced its poverty rate over the years, lifting millions out of poverty.
- Zero Hunger: Although progress has been made, India still faces challenges in eradicating hunger, given its substantial population of undernourished individuals.
- Good Health and Well-being: India has made notable strides in maternal and child health, reflecting positive trends in healthcare outcomes.
- Quality Education: Efforts are underway to improve literacy rates and educational enrollment, especially in rural areas.
- Gender Equality: India has witnessed an increase in female labor force participation, indicating progress towards gender equality.
Measures to Boost SDG Financing
- Dedicated Investment Funds: Establishing specialized funds can attract investments that align with specific SDGs, fostering public-private partnerships.
- Policy and Institutional Reforms: Implementing policies supportive of SDGs, enhancing resource mobilization through taxation, and combating financial irregularities can enhance funding availability.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts among stakeholders are vital for resource mobilization, debt relief initiatives, and promoting fair tax practices.
- Technology and Innovation: Leveraging data analytics and innovative tools can optimize resource allocation and decision-making processes, enhancing the impact of SDG financing initiatives.
Regulating Misleading Advertisements in India
Context: The Supreme Court of India has issued directives to protect consumers from misleading advertisements. Advertisers are now required to submit self-declarations before promoting products in the media.
Key Directives from the Supreme Court
- Advertisers must submit self-declarations ensuring their advertisements do not deceive consumers.
- They are obligated to declare that their promotions do not contain false information.
- An online portal named 'Broadcast Seva' has been established for TV ads, with a similar portal for print advertisers.
- Endorsers such as social media influencers and celebrities must endorse products responsibly.
- Consumers should have a transparent process to report misleading ads and receive updates on complaints.
Violations of Ethical Principles by Misleading Advertisements
- Misleading ads breach ethical principles like truthfulness and fairness, manipulating consumer perceptions.
- They create unfair advantages for deceptive companies, harming honest competitors and consumer trust.
- These advertisements can lead to financial losses and harm consumers' well-being.
- Repeated exposure erodes trust in products and advertising, impacting market integrity.
Regulation of Misleading Advertisements in India
- The Consumer Protection Act, 2019 defines misleading ads and establishes the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) to regulate violations.
- The CCPA enforces guidelines to prevent misleading ads and ensure consumer rights are protected.
- Penalties for violations can be up to 10 lakh rupees for manufacturers, advertisers, and endorsers.
- FSSAI mandates truthful advertising under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006.
- Legislations like ASCI, Consumer Protection Act, and others govern advertising practices in India.
Employment Trends in India

Context:
- India has experienced a noteworthy increase in employment, with more than 80 million new jobs created between 2017-18 and 2022-23. This growth has sparked debates regarding its sustainability and root causes.
Key Trends in Employment Growth
- Historical Growth: Data analysis from the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) spanning from 1983 to 2023 reveals a consistent rise in principal employment over different periods.
- Consistent Growth: Principal employment, indicating full-time work for most of the year, has steadily increased since 1983.
- Broad-Based Growth: Job opportunities have expanded across rural and urban areas and various sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, construction, and services.
Labour Market Indicators
- Despite long-term challenges, recent years have shown improvements in indicators such as labor force participation rate, workforce participation rate, and unemployment rate, especially during economic distress like the Covid-19 pandemic.
Employment Quality Evolution
- Rise in Informal Employment: Around half of formal sector jobs are informal, with a majority of workers engaged in the informal sector.
- Dominance of Self-Employment: A substantial portion of job growth is in the form of self-employment, influenced by government initiatives like the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana (PMMY).
Wages and Salaries Trend
- Aggregate wages and salaries have shown stagnation in recent years, with minimal real growth after adjusting for inflation. Factors like a large labor supply and stagnant productivity have contributed to this trend.
Youth Employment Dynamics
- Trends: Youth employment and underemployment increased until 2019 but declined during the pandemic. However, unemployment among educated youths has been rising, particularly for those with higher education levels.
- Gender Disparities: Women's participation in the workforce has not met expectations, often leading to informal or low-paying self-employment.
Challenges in Indian Employment Landscape
- Growth of Informal Sector: Many new jobs lack security and benefits, raising concerns about the quality of youth employment.
- Skill Mismatch: The education system may not align adequately with current job market demands, creating challenges for job seekers.
- Job Automation: Automation poses a threat to certain industries, potentially displacing workers and impacting sectors like manufacturing.
Strategies for Improvement
- Promote Formalisation: Encourage informal workers to transition to the formal sector through streamlined registration processes and policy lessons from successful initiatives in other countries like Peru.
- Targeted Programs: Implement specialized skill development programs for marginalized groups to enhance inclusivity and workforce participation.
- Reskilling for Automation: Provide training programs in emerging fields like AI and robotics to prepare the workforce for evolving job market demands.
- Social Security Enhancements: Design flexible social security systems to cater to gig workers and those transitioning between formal and informal sectors.
India's E-commerce Market
Context:
- Recently, Invest India reported that India's E-Commerce Sector is estimated to reach USD 325 billion by 2030, positioning India as the 3rd largest online retail market globally.
Status of the E-Commerce Sector in India
- E-commerce, or Electronic Commerce, involves online buying and selling of goods and services, transcending geographical barriers.
- Encompasses activities from online retailing to digital payments, adapting with technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors.
Key Statistics
- By 2026, the number of online shoppers in India is projected to reach 88 million in Rural India and 263 million in Urban India.
- In 2022-23, Government e-marketplace (GeM) achieved a Gross Merchandise Value of USD 2011 billion.
- As of 2023, the e-commerce sector in India is valued at USD 70 billion, comprising around 7% of the total retail market.
- In 2022, India ranked 7th in the global e-commerce market.
Driving Factors
- The surge in smartphone usage has significantly boosted e-commerce growth in India, providing access to online platforms for over 80% of the population.
- The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) facilitated digital transactions worth USD 1.5 trillion in 2022.
- Cost-effective internet pricing and increased internet penetration are driving forces, with India ranking 7th for cheapest mobile data.
- Efficient logistics, government policies, rising middle-class population, and time-saving convenience are key factors fueling e-commerce demand.
- Wider product choices, competitive pricing, and a focus on rural e-commerce are attracting consumers across demographics.
Challenges
- Issues such as counterfeit products, infrastructural limitations, lack of clear regulations, and cybersecurity threats hinder the e-commerce sector's growth.
Government Initiatives
- Government policies like FDI regulations, National E-Commerce Policy, ONDC, Consumer Protection Rules, Digital India initiative, India Stack, and BharatNet Project aim to foster e-commerce growth and ensure consumer protection.
Measures to Boost E-Commerce Sector
- Enhancing infrastructure, robust payment systems, clear regulatory frameworks, and awareness campaigns are vital for boosting the e-commerce sector.
Amplifying the Global Value of Earth Observation

Context: The World Economic Forum released a report titled "Amplifying the Global Value of Earth Observation," emphasizing the economic and sustainability potential of Earth Observation (EO) data globally.
- Economic Impact: EO data is projected to generate over USD 3 trillion in economic benefits by 2030, with the global value expected to surpass USD 700 billion, contributing USD 3.8 trillion to the global GDP by 2030.
- Environmental Benefits: EO data can aid in reducing 2 gigatonnes of greenhouse gas emissions annually by 2030, offering insights into climate variables, emissions, ecosystems, and biodiversity for climate change mitigation and habitat protection.
- Regional Opportunities: The Asia Pacific region is anticipated to lead in EO value by 2030, with a projected value of USD 315 billion, while Africa and South America are expected to exhibit significant growth.
- Enabling Technologies: Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and digital twins can enhance EO data utilization, with digital twins being virtual replicas of physical objects aiding in decision-making through real-time data and simulations.
Key Areas of Application of Earth Observation Data
- Environmental Monitoring and Management: EO data assists in monitoring activities like deforestation, desertification, coastal changes, and biodiversity, enabling informed actions for environmental conservation.
- Agriculture and Precision Farming: Utilizing EO data for monitoring crop health, estimating yields, practicing precision agriculture, assessing soil moisture levels, and detecting crop pests and diseases.
- Urban Planning and Development: Mapping urban areas, monitoring urban expansion, identifying locations for infrastructure projects, and tracking land use changes in growing cities.
- Natural Resource Management: Monitoring mineral resources, water bodies, and land use patterns to ensure sustainable resource management.
- Climate Change Studies: Tracking changes in glaciers, sea ice, global temperatures, and atmospheric conditions to understand climate change impacts.
- Disaster Management and Emergency Response: Assessing disaster damages, identifying affected areas, and aiding in targeted relief efforts during emergencies.
- Defence and Security: Utilizing EO data for border monitoring, detecting unauthorized activities, and tracking military movements for security purposes.
- Archaeology and Cultural Heritage: Identifying archaeological sites, mapping ancient structures, and preserving cultural heritage utilizing EO data.
India's Management of Earth Observation Data
- Role of EO Data in India: EO data in India is pivotal for applications ranging from disaster management to environmental monitoring, with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) leading satellite deployments for EO purposes.
- Satellites: ISRO operates various EO satellites, including EOS-07 and EOS-06, alongside RESOURCESAT and OCEANSAT series for land and ocean observations.
- EO Platforms: Initiatives like VEDAS, Bhuvan, and MOSDAC provide access to thematic spatial data and meteorological information derived from satellite imagery.
- Future Projects: Collaborative efforts like NISAR between NASA and ISRO aim to launch Earth-observing satellites with advanced radar imaging capabilities for resource management and climate studies.
Facts About the World Economic Forum (WEF)
- About WEF: Founded by Klaus Schwab in 1971, the WEF is an international organization based in Geneva, Switzerland, focusing on economic and social issues, hosting the annual meeting in Davos.
- Historical Evolution: Originally emphasizing management, it expanded to economic and social issues in 1973, aiming to provide a dialogue platform, officially becoming the World Economic Forum in 1987.
- Annual Meeting: The WEF's annual meeting in Davos gathers global stakeholders to discuss diverse issues, predominantly sponsored by partnering corporations with substantial turnovers.
- Major Reports: The WEF publishes reports like the Global Competitiveness Report, Global Gender Gap Report, Energy Transition Index, Global Risk Report, and Global Travel and Tourism Report.
Regional Economic Outlook for Asia And Pacific Report: IMF
Context: Recently, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) released its Regional Economic Outlook for Asia And Pacific Report April 2024. It highlighted India's consistent positive growth surprises, attributed to resilient domestic demand and significant public investment driving the economy.
Key Highlights of the Report
Growth in Asia-Pacific
- Asia-Pacific's growth in late 2023 exceeded expectations at 5.0%. Projections for 2024 anticipate a slight slowdown to 4.5%, with varying inflation rates across economies. Emerging markets saw growth primarily fueled by strong private demand.
India's Growth Forecasts
- The IMF revised India's growth forecast for the fiscal year 2024-25 to 6.8% and maintained it at 6.5% for 2025-26. India and the Philippines have consistently shown positive growth surprises due to resilient domestic demand. Public investment, particularly in countries like China and India, has significantly contributed to growth.
Forecast for China
- China's economy is expected to grow at a rate of 4.6% in 2024, down from 5.2% in 2023, with a further decrease to 4.1% in 2025. The IMF identifies China as a source of both positive and negative risks, emphasizing the importance of policies addressing stresses in the property sector and boosting domestic demand.
Inflation Forecast
- The IMF notes that current inflation levels in emerging markets are stable, but future inflation drivers vary. Core inflation is expected to remain low, while factors like food prices could impact headline inflation in countries like India.
Geoeconomic Fragmentation
- The IMF highlights geoeconomic fragmentation as a major risk, emphasizing escalating economic and trade tensions between countries. This trend could negatively affect global economic growth and stability. Policy makers are advised to handle trade frictions cautiously.
Public Investment's Role in India's Growth
Public investment plays a crucial role in shaping India's economic trajectory by:
Infrastructure Development
- Investing in critical infrastructure like roads, railways, and power plants is essential for economic growth and productivity. The sector requires substantial investments for sustainable development.
Job Creation and Poverty Alleviation
- Public investments in infrastructure and social welfare programs create job opportunities and help alleviate poverty. Initiatives like the MGNREGA have been instrumental in providing employment.
Human Capital Development
- Investing in education and healthcare is crucial for building a skilled workforce, driving economic growth. Public investment ensures balanced regional development and promotes inclusive growth.
Crowding-in Private Investment
- By reducing business costs and enhancing productivity, public investments in infrastructure attract private investments. A conducive environment is created for businesses to thrive.
Sunrise Sectors in India Requiring Public Investments
Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS)
- CCUS technologies are crucial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Public investment in research and deployment of CCUS projects is essential for environmental sustainability.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection
- With increasing cyber threats, investments in cybersecurity infrastructure and data protection frameworks are necessary to secure India's digital economy.
Biotechnology and Precision Medicine
- Investing in biotechnology research can help India lead in healthcare innovation. Areas like genomics and precision medicine hold significant potential.
Circular Economy and Waste Management
- Enhanced public investment is needed for comprehensive waste management strategies, promoting a sustainable circular economy through recycling and resource recovery.
Blue Economy and Marine Research
- India's coastal potential can be tapped through investments in marine research and a blue economy focusing on sectors like offshore wind energy and marine biotechnology.
Sundarbans

- The Sundarbans is home to the world's largest mangrove forests, situated at the confluence of the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers on the Bay of Bengal. This unique mangrove ecosystem serves as an ecotone, bridging the gap between land and sea in tropical and subtropical regions.
- The Sundarbans boasts a diverse range of habitats, from freshwater swamps and intertidal mangroves to saline forests and open water. This variety supports a rich array of species, including endangered wildlife such as the estuarine crocodile, water monitor lizard, Gangetic dolphin, and olive ridley turtle.
Conservation Efforts
- Approximately 40% of the Sundarbans is located in India, with the remainder in Bangladesh. The region has been recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site in both countries, emphasizing its global significance. Initiatives like Project Tiger focus on protecting the Royal Bengal Tigers, ensuring the ecological balance of the ecosystem.
Challenges Faced by the Sundarbans
- Rising Sea Levels: Climate change-induced rising sea levels pose a threat to low-lying mangroves, leading to saltwater intrusion and heightened vulnerability to storm surges.
- Increased Cyclone Intensity: More frequent and intense storms due to climate change can damage mangroves, disrupting vital sediment patterns.
- Agricultural Expansion: The conversion of mangrove areas for agriculture like palm oil or rice paddies destroys habitats and fragments ecosystems, impacting biodiversity.
- Loss of Ecosystem Services: Deforestation diminishes essential services provided by mangroves, affecting coastal communities and fisheries.
- Wildlife Threat: Climate change-induced loss of mangrove habitats endangers species, leading to a decline in populations like molluscs and crustaceans.
- Impact of Pollutants: Pollutants from urban areas and the Indo-Gangetic Plain degrade air quality in the Sundarbans, affecting its ecology significantly.
Proposed Solutions
- Protecting Streambanks: Cultivating native grass species can stabilize streambanks and prevent erosion, promoting ecosystem health.
- Sustainable Agriculture Promotion: Promoting soil-tolerant crops and organic farming practices can enhance agricultural productivity sustainably.
- Wastewater Treatment: Implementing natural wastewater treatment processes can improve water quality and support ecosystem well-being.
- India-Bangladesh Collaboration: Enhancing collaborative efforts between India and Bangladesh can bolster climate resilience for the Sundarbans and its dependent communities.
- Innovative Measures: Introducing sustainable practices like solar energy, electric transportation, and regulated tourism can mitigate environmental impacts.
- Multi-Sectoral Approach: Adopting a comprehensive approach involving various ministries can ensure holistic planning and execution for the Sundarbans' sustainability.
|
164 videos|632 docs|1151 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (15th to 21st May 2024) Part - 1 - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is the concept of criminalisation of politics? |  |
| 2. How does the UN estimate the trillions required to rescue SDGs? |  |
| 3. What measures are being taken to regulate misleading advertisements in India? |  |
| 4. What are the current employment trends in India? |  |
| 5. How is India's e-commerce market evolving? |  |





















