Notes: Shapes & Spatial Understanding | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Shapes? |

|
| Types of Shapes |

|
| Point |

|
| Straight and Curved Lines |

|
| Circle |

|
Shapes and spatial understanding play a fundamental role in early childhood learning, particularly in the context of the Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET). These concepts not only enhance a child's cognitive development but also help them interpret and navigate their surroundings effectively.
Shapes form the basis of visual recognition and classification, enabling children to identify, name, and describe geometric figures such as circles, squares, triangles, and rectangles. Mastering these shapes strengthens their ability to categorize objects, improving overall perception and analytical skills.
Spatial Understanding involves grasping the position, direction, and movement of objects in space. It includes recognizing patterns, understanding symmetry, and differentiating concepts like near and far or above and below. Strong spatial reasoning is essential for subjects like mathematics and science and fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills from an early age.
By developing both shape recognition and spatial awareness, children build a strong foundation for future learning, enhancing their ability to analyze patterns, solve puzzles, and approach problems logically.
What are Shapes?
In Mathematics, shapes define the outline or the boundary of an object. The shapes can be classified into different types based on their properties. In general, the shapes are closed by an outline or boundary, which is made up of points, lines and curves, and so on.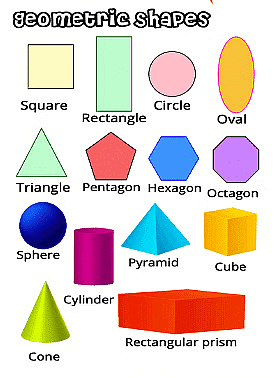
Types of Shapes
- Plane shapes are known as 2D shapes (Two dimensional shapes).
- Solid shapes are called 3D shapes (Three dimensional shapes).
➤ 2D Shapes
Shapes like circle, triangle, square, rectangle and oval are called flat or plane shapes.
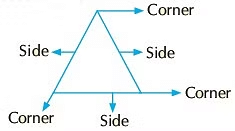
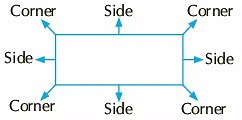
- Triangle: A triangle has 3 corners and 3 sides. The sides may or may not be equal.
- Square: A square has 4 corners and 4 sides. All its sides are equal.
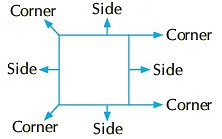
- Rectangle: A rectangle has 4 corners and 4 sides. Its opposite sides are equal.
- Circle: A circle has no corners and no sides.
- Oval: An oval also has no corners and no sides.
➤ 3D Shapes
Shapes like cube, cuboid, cone, sphere and cylinder are called solid shapes.
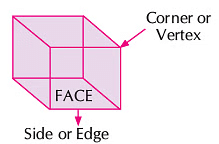
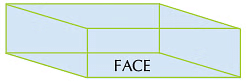
- Cube: A cube has 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 corners. All the faces of a cube are equal.
- Cuboid: A cuboid has 6 faces, 12 edges and 8 corners. Opposite faces of a cuboid are equal.
- Sphere: A sphere has 1 face, 0 edges and 0 corners.

- Cone: A cone has 2 faces, 1 edge and 1 corner.

- Cylinder: A cylinder has 3 faces, 2 edges and 0 corners.

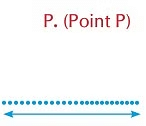
Point
- It is like a dot. A point has no shape, breadth, length or height.
- It is always named by a capital letter.
- For example: Point P.
- A line is formed by placing many points next to each other
Straight and Curved Lines
Hold a thread and stretch it tightly, you get a straight line. Now if you hold it loosely, you get a curved line. Straight line is a line in which both the ends never meet each other. Straight lines may be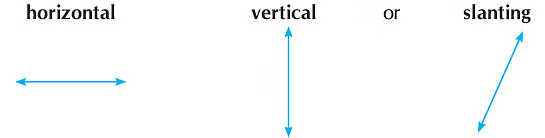
This is a scale. We use it to draw straight lines.
Curved line is a line in which both ends may or may not meet each other.
Circle
A circle can be defined as a simple closed curve all of which points are equidistant (at an equal distance) from the fixed point called its centre.
A bangle, a one rupee coin and a cycle tyre are all examples of circular objects.

Terms Related to Circle
(i) Centre: The fixed point in the centre of a circle is called its centre.
(ii) Diameter: Diameter is a line segment that has its endpoints on the circle and passes through the centre.
Diameter = AB
AB = (OA + OB) = 2 × OA or 2 × OB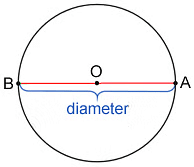
Radius is half of the diameter.
(iii) Radius: Radius is the distance between the centre of a circle and a point on the circumference.
Radius = OA = OB
Diameter = 2 × Radius
Radius = Diameter ÷ 2
(iv) Chord: Chord is a line segment whose endpoints lie on the circle.
LM, PQ, AB are all chords of the circle. The diameter is the longest chord of the circle.
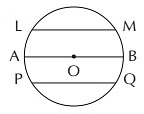
(v) Arc: Arc is any part of a circle. An arc is usually named by three points out of which two are the endpoints and the third point lies between them. ABC is an arc and is denoted by 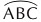 .
.
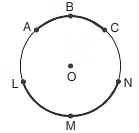
(vi) Minor Arc: Minor arc is shorter and the major arc is longer.
ABC is a minor arc of the circle. LMN is a major arc of the circle.
Half of a circle is called a semicircle. ABC is a semicircle.
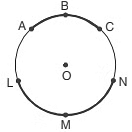
(vii) Circumference: Circumference is the perimeter or boundary of a circle.
Circumference = π × diameter =22/7 × diameter
= 22/7 x 2 x radius
= 2 x 22/7 x radius of the circle
A semicircle is also an arc.
Interior and exterior of a circle
Look at the circle given: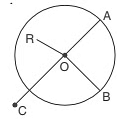
It is clear that
- R lies in the interior of the circle.
Thus, OR < OA. - C lies in the exterior of the circle.
Thus, OC > OA. - B lies on the circle.
Thus, OA = OB.
Concentric circles are circles with the same centre but different radii.
Drawing a Circle with Compass
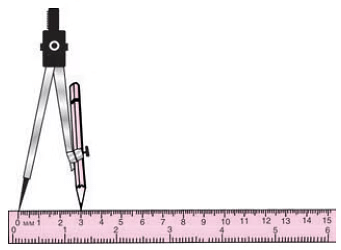
(i) To draw a circle with a compass, fix a pointed pencil in the compass.
(ii) Place a ruler on the table and fix the metal tip of the compass at 0 of the ruler and open the compass to fix the end of the pencil at the given measure (say = 3 cm.)
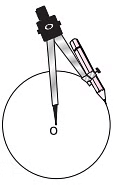
(iii) Next, take a point ‘O’ on a plane paper and rest the metal tip of the compass at point ‘O’.
(iv) Hold the head of the compass firmly and move the pencil around to form a circle of radius 3 cm.
|
30 videos|210 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Shapes & Spatial Understanding - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the characteristics of a circle shape? |  |
| 2. How is the radius of a circle defined? |  |
| 3. Can a circle be classified as a polygon? |  |
| 4. How is the circumference of a circle calculated? |  |
| 5. What real-life objects are examples of circle shapes? |  |




















