Notes: Multiplication | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
Multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation essential for building advanced mathematical skills. It is a critical topic in the Central Teacher Eligibility Test (CTET) and state-level Teacher Eligibility Tests (TETs). Understanding multiplication enables students to perform calculations efficiently and lays the groundwork for more complex mathematical concepts.
Multiplication is the process of adding a number to itself a specified number of times. For example, 3 multiplied by 4 (3 × 4) means adding 3 four times (3 + 3 + 3 + 3).

Multiplication is a basic arithmetic operation that combines two numbers to find their product. It is often denoted by the symbol "×" or "*", and the result is called the product. In multiplication, the numbers being multiplied are called factors.
Multiplication is a way of adding the same number many times. 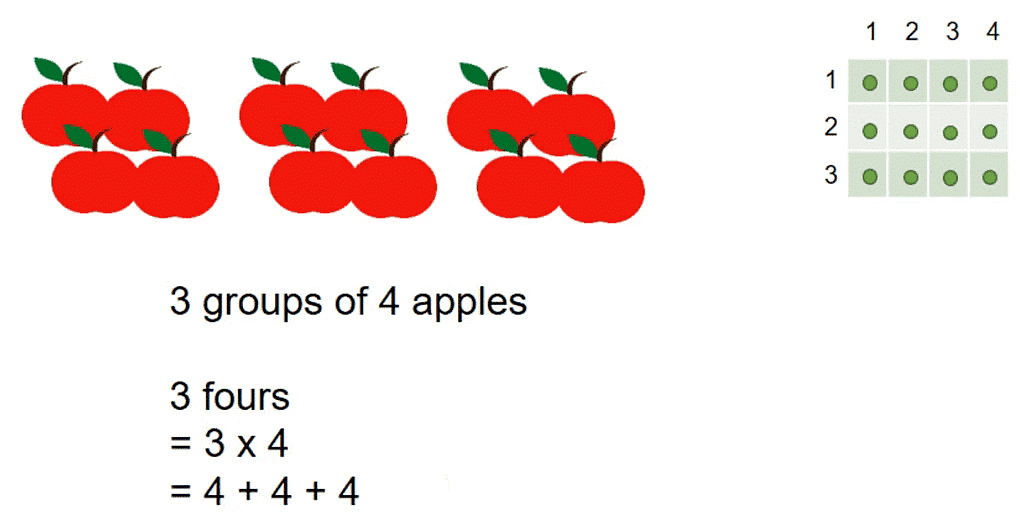
For example, if you have 3 groups of 4 apples, you can add 4 + 4 + 4 to get 12 apples. But there is another way to write this. You can multiply 3 by 4, which means 3 groups of 4. You write it like this: 3 x 4.
Terms Related to Multiplication
We know that multiplication is repeated addition.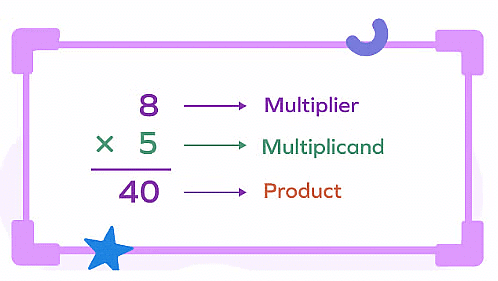
- The number which is to be repeated or multiplied is called the multiplicand.
- The number which expresses how often the multiplicand is repeated is called the multiplier.
Multiplier times multiplicand = Product
Multiplication is also used to find the number of objects in an array.
(An array is a group of objects or symbols arranged in columns and rows.)
Example: Find the number of squares on this chess board.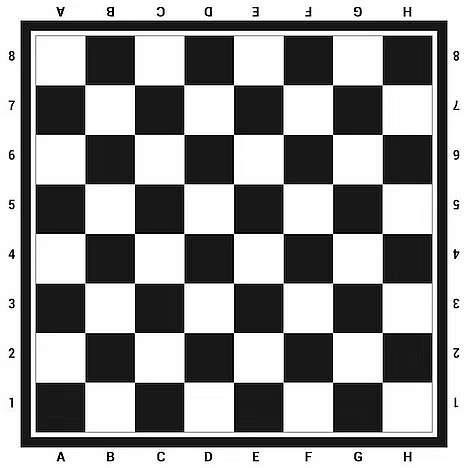 Chess Board
Chess Board
You can Count the squares but that would be a long method. There is an easy way to do this. just count the number of rows and number of columns and multiply them.
Multiplication fact for the given array
8 Rows & 8 Columns in the above chess board:
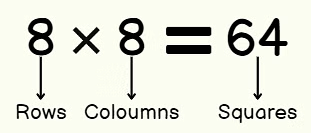
=> Total number of squares in a chessboard = 8 x 8 = 64
Properties of Multiplication
There are five main properties of multiplication which are as follows:
1. Order Property(Commutative Property)
Two numbers can be multiplied in any order. The product remains the same.
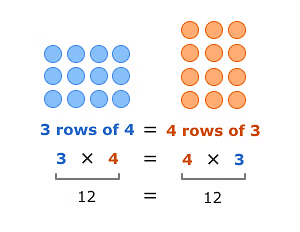 Examples:
Examples:
- 6 × 5 = 5 × 6 = 30;
- 12 × 3 = 3 × 12 = 36.
2. Grouping Property(Associative Property)
The product of three or more numbers remains the same, even if we change the grouping of numbers.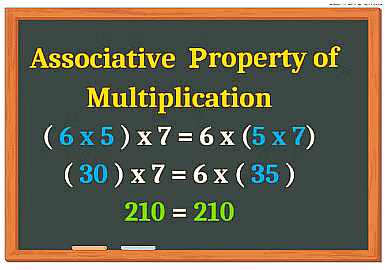 Example:
Example:
- (4 × 6) × 3 = 24 × 3 = 72;
- 4 × (6 × 3) = 4 × 18 = 72;
- (4 × 3) × 6 = 4 × (6 × 3) = 72.
3. Multiplication by 1(Identity Property)
If we multiply a number by 1, the product is the number itself.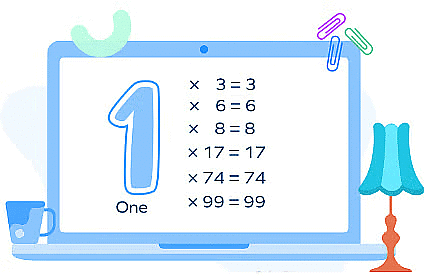 Examples:
Examples:
- 7 × 1 = 7;
- 6 × 1 = 6;
- 9 × 1 = 9;
- 18 × 1 = 1 × 18 = 18.
4. Multiplication by 0(Zero Property)
If we multiply a number by 0, the product is 0.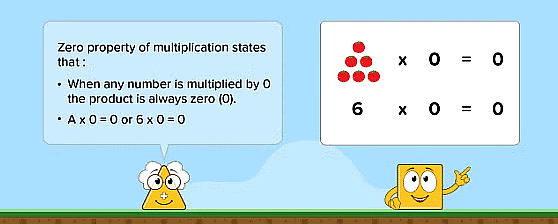 Examples:
Examples:
- 0 × 6 = 0;
- 7 × 0 = 0;
- 0 × 17 = 17 × 0 = 0.
5. Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition
a×(b+c)=(a×b)+(a×c)
When you multiply a number (a) by the sum of two other numbers (b and c), it is equivalent to the sum of the products of a multiplied by each of those two numbers separately.
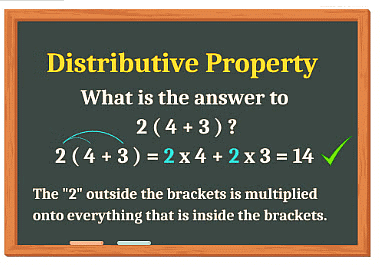
For example, if each of the five children buys a pencil and an eraser. How much money did they spend altogether?
You might also think that each child pays 12 rupees for a pencil, so they spend 5 × 12 rupees for a pencil. Each child pays 5 rupees for an eraser, so they spend 5 × 5 rupees for the erasers. The children spend (5 × 12) + (5 × 5) rupees altogether.
Is the same amount of money spent in each case?
Yes, Since 5 × 17 = 5 × (12 + 5) = (5 × 12) + (5 × 5) = 60 + 25 = 85
Multiplication Table
A multiplication table is a table where you can find the products of multiplying two numbers from 1 to a certain limit.
The multiplication table from 1 to 20 is given below.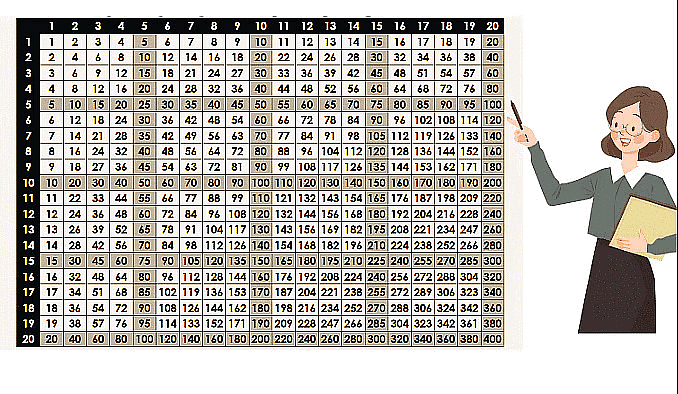
You can read the table as shown by the color lines.
Thus, 4 × 5 = 20, 7 × 5 = 35, 7 × 7 = 49, 18 × 9 = 162.
Multiplying by 10, 100, 1000
Study the following multiplication facts.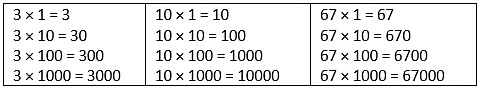 What do you observe?We observe that
What do you observe?We observe that
- To multiply a number by 10, put 1 zero on the right of the given number.
- To multiply a number by 100, put 2 zeros on the right of the given number.
- To multiply a number by 1000, put 3 zeros on the right of the given number.
- To multiply a number by 10000, put 4 zeros on the right of the given number.
- To multiply by 10,0000, put 5 zeros on the right of the given number, and so on.
Multiplying by a Multiple of 10, 100, 1000
Observe the following:
- 387 × 30 = 387 × 3 × 10 = (387 × 3) × 10 = 1161 × 10 = 11610
- 609 × 50 = 609 × 5 × 10 = (609 × 5) × 10 = 3045 × 10 = 30450
- 1821 × 800 = 1821 × 8 × 100 = (1821 × 8) × 100 = 14568 × 100 = 1456800
- 120 × 900 = 12 × 10 × 9 × 100 = (12 × 9) × (10 × 100) = 108 × 1000 = 108000
What do you observe?
Multiply the non-zero factors. Put as many zeros at the end of the product as the number of zeros at the end of the factors.
Multiplication by a 1-Digit Multiplier
Example 1: Multiply 4872 by 4.
Sol: We proceed as per these steps:
Step 1: Arrange the multiplicand and multiplier, as shown.
Step 2: Multiply the ones.
Step 3: Multiply tens, regroup and carry.
Step 4: Multiply hundreds, regroup and carry.
Step 5: Multiply thousands.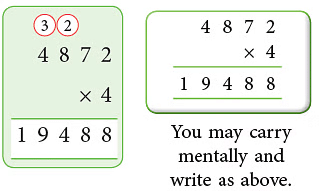
Multiplication by a 2-Digit Multiplier
Example: Multiply 137 by 23.
Sol: We have,
137 × 23 = 137 × (20 + 3)
= 137 × 20 + 137 × 3
= 2740 + 411 = 3151.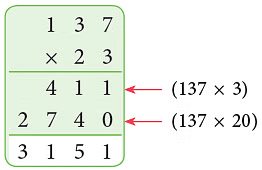
Example: Multiply 3598 by 67.
Sol: 3598 × 67 = 3598 × (60 + 7) = 3598 × 60 + 3598 × 7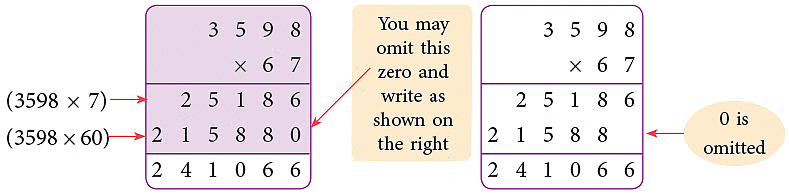
Problems Based on Real-Life Situations
Example: Ashok ordered 32 gross pencils for the school. How many pencils were ordered?
Sol: 1 Gross = 144
So, 32 gross pencils = 144 × 32 = 4608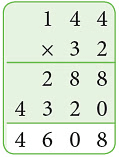 So, Ashok ordered 4608 pencils.
So, Ashok ordered 4608 pencils.
Example: A cricket stadium has 456 rows with 20 seats in each row. How many seats are there in the stadium?
Sol: Number of seats in each row = 20
Number of rows = 456
Total number of seats = 456 × 20 = 9120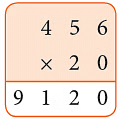 Then, there are 9120 seats in the stadium.
Then, there are 9120 seats in the stadium.
Multiplication by a 3-Digit Multiplier
Example: Multiply 256 by 248.
Sol: 256 × 248 = 256 × (200 + 40 + 8)
Step 1: Multiply 256 by 8. Step 2: Multiply 256 by 40.
Step 2: Multiply 256 by 40.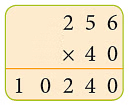 Step 3: Multiply 256 by 200.
Step 3: Multiply 256 by 200. Step 4: Add the above three products.
Step 4: Add the above three products.
2048 + 10240 + 51200 = 63488.
Short Method: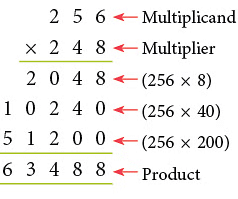
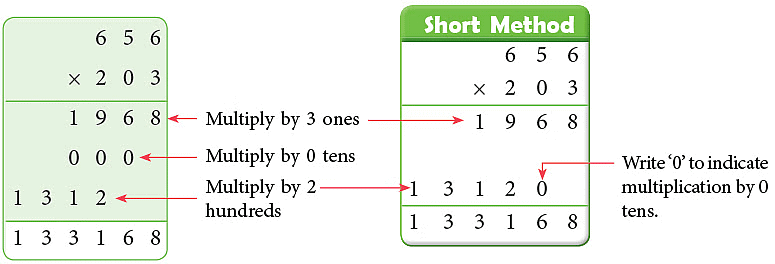
Example: Multiply 656 by 203.
Sol:
Example: Multiply 432 by 350.
Sol:
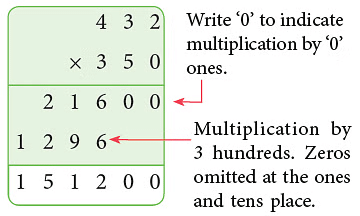 ∴ 432 × 350 = 151200.
∴ 432 × 350 = 151200.
Example: Multiply 1038 × 809.
Sol:
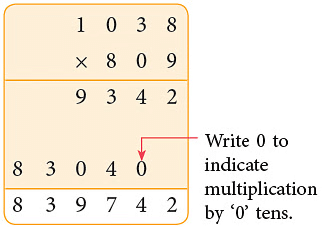 ∴ 1038 × 809 = 839742.
∴ 1038 × 809 = 839742.
Problems Based on Real-Life Situations
Example: A baker bakes 765 cakes in a day. How many cakes does he bake in a normal year?
Sol:
Number of cakes baked in a day = 765
Number of cakes baked in a year = (765 × 365)
1 year = 365 days = 279225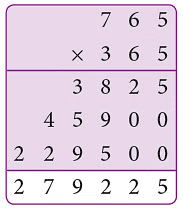 ∴ Thus, the baker bakes 2,79,225 cakes in a year.
∴ Thus, the baker bakes 2,79,225 cakes in a year.
Estimating Products
When we give an approximate answer close to the exact answer, we are estimating.

Let us understand this with an example. Mr Das wants to buy the toys shown below for his daughter Kiran. He would like to know approximately how much the toys will cost him. Here, he wants to know the approximate cost.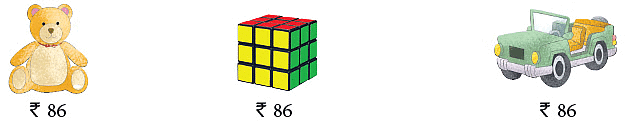
We round off the numbers and then estimate the product. Here, the cost of the three toys is 3 × ₹ 86.
Rounding up 86 to 90, the estimated cost = 3 × ₹ 90 = ₹ 270.
Example: Estimate the product 38 × 44.
Sol:
 Actual product = 38 × 44 = 1672
Actual product = 38 × 44 = 1672
By approximation, the product obtained is 1600.
Example: Estimate the product 516 × 393 to the nearest
(a) tens
(b) hundreds
Sol:

 Actual product = 516 × 393 = 202788
Actual product = 516 × 393 = 202788
However, 520 × 390 involves more calculations than 500 × 400.
From the above results, we see that rounding off to the nearest ten produces a closer approximation of the exact product than rounding off to the nearest hundred.
Edurev Tips: To estimate a product, we round off the multiplier and the multiplicand to the nearest ten, hundred or thousand, whichever is more convenient. Then, multiply the rounded numbers to get the estimated product.
|
30 videos|210 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Multiplication - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the properties of multiplication? |  |
| 2. How do you multiply by 10, 100, or 1000? |  |
| 3. How can you estimate products in multiplication? |  |
| 4. What is the process of multiplication by a 2-digit multiplier? |  |
| 5. How do you multiply by a 3-digit multiplier? |  |
















