Notes: Elementary Shapes (2-D & 3-D) | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 2 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
Elementary shapes form the basic building blocks of geometry and are fundamental to understanding more complex geometric concepts. They are a crucial topic for the CTET (Central Teacher Eligibility Test) and other educational exams. Here’s a brief overview of elementary shapes:
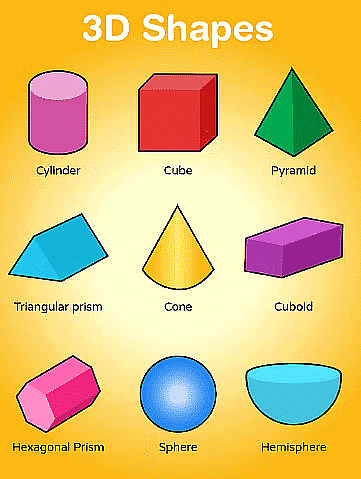
Elementary shapes are the simple geometric figures such as lines, angles, and basic two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) shapes. They are essential for developing spatial awareness and geometric reasoning.
Types of Elementary Shapes:
Lines:
Line Segment: A part of a line with two endpoints. Example: AB
Ray: A part of a line that starts at one point and extends infinitely in one direction. Example: AB
Line: Extends infinitely in both directions with no endpoints. Example: AB
Angles:
Acute Angle: An angle less than 90°. Example:
Right Angle: An angle exactly 90°. Example:
Obtuse Angle: An angle greater than 90° but less than 180°. Example:
Straight Angle: An angle exactly 180°. Example:
Reflex Angle: An angle greater than 180° but less than 360°. Example:
2D Shapes (Plane Figures):
Triangle: A three-sided polygon. Types include equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles.
Quadrilateral: A four-sided polygon. Types include squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and rhombuses.
Circle: A set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point called the center.
Polygon: A closed figure with three or more straight sides. Examples: pentagon (5 sides), hexagon (6 sides), etc.
3D Shapes (Solid Figures):
Cube: A solid with six equal square faces.
Cuboid (Rectangular Prism): A solid with six rectangular faces.
Sphere: A solid where all points on the surface are equidistant from the center.
Cylinder: A solid with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface.
Cone: A solid with a circular base and a single vertex.
Pyramid: A solid with a polygonal base and triangular faces that meet at a single point (vertex).
Properties of Elementary Shapes:
Triangles: Sum of interior angles is always 180°. Types include equilateral, isosceles, and scalene.
Quadrilaterals: Sum of interior angles is always 360°. Types include squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and rhombuses.
Circles: The circumference is 2𝜋𝑟
2πr and the area is 𝜋𝑟2
, where r is the radius.
Cubes and Cuboids: Volume and surface area can be calculated using the lengths of their side
Look at the picture of the pencil box given below. You can only see its length and width. This picture would be a 2D image because it has only two dimensions: length and width. It's like looking at a flat drawing of your pencil box on a piece of paper.

Now, if you could see your pencil box from all sides, including the top, bottom, front, back, and sides, you would have a 3D image. A 3D image shows all three dimensions: length, width, and height. It's like holding your pencil box in your hands and being able to see it from every angle.

In simple terms, a 2D image is like a flat drawing, and a 3D image is like seeing the real object in front of you.
Plane Figures and Solid Shapes
Visualizing solid shapes is an essential concept in mathematics, particularly in geometry. Solid shapes, also known as three-dimensional (3D) shapes, exist in physical space and have three dimensions: length, width, and height. Unlike two-dimensional shapes, such as squares and circles, which exist on a flat plane, solid shapes have volume and occupy space.
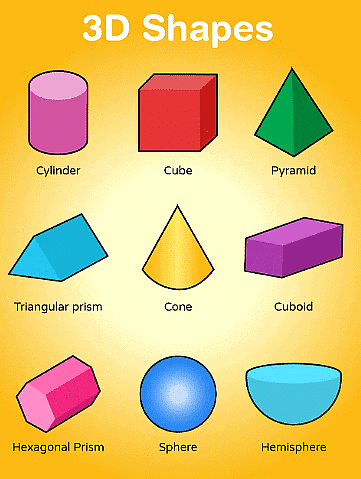
- Plane figures are flat or 2 -Dimension figures, they have no thickness.
For example: Squares, rectangles, circles, triangles etc. - Solid Shapes are 3-Dimensional shapes, and they occupy space and have volume.
For example: Cube, cuboid, sphere, cone, hemisphere etc.
Faces, Edges and Vertices of 3D Shapes
1. Faces
- A 3D shapes is not flat therefore it has 3 dimensions and these are faces, edges, and vertices.
- Faces are simply the face of a 3D shape or the flat surface of the 3D shape.
For example: The number of faces of cube is 6
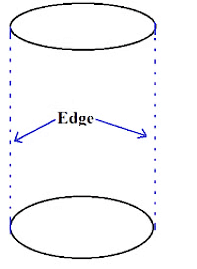
2. Edges
- Edges are the line segments which join one vertex to another vertex.
For example – Edges in a cylinder are 2 and are shown below.
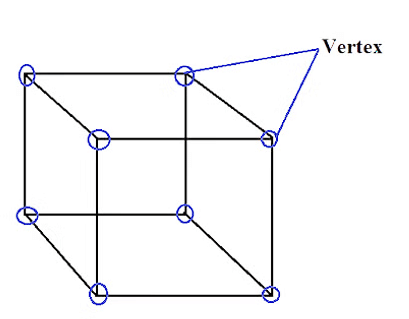
3. Vertices
- Points where two or more edges meet between faces is known vertices of any 3D shape or the corners of 3D shape.
For example: The cube has 8 vertices and is shown below
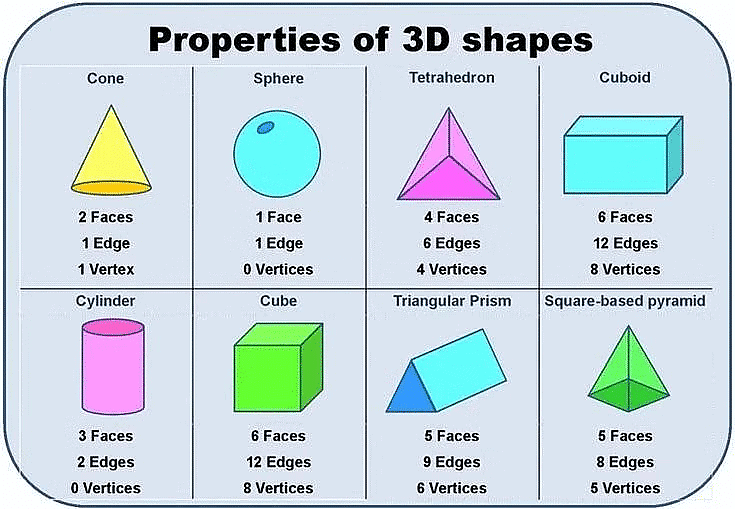
The table shows the number of the faces, edges and vertices of some shapes.
Nets for Building 3D Shapes
The net of a three-dimensional solid is a two-dimensional skeleton outline, which, when folded, results in the three-dimensional shape. Net is used for making 3D shapes.
- It is a basic skeleton outline in 2 -Dimensions i.e., it is flat 3-Dimensional shape which can be folded and joined together with the help of glue.
- Nets for building some shapes are shown below
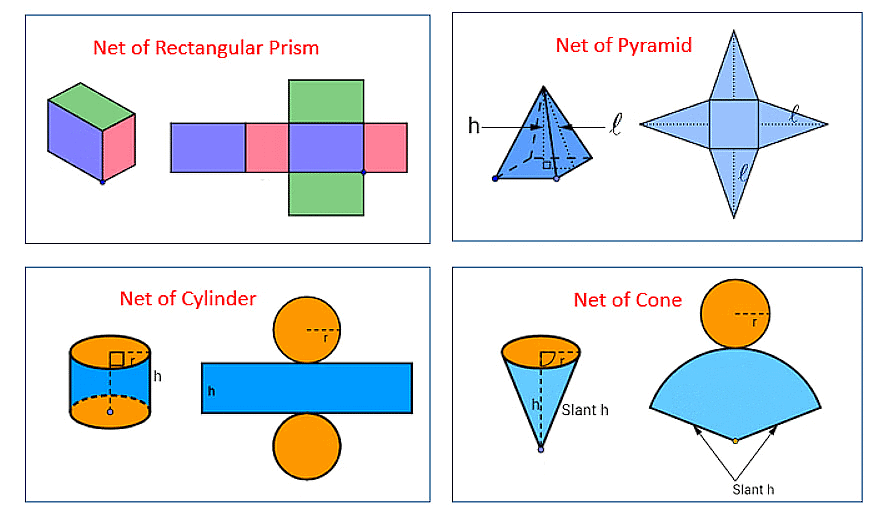 Nets of 3-D Shapes
Nets of 3-D Shapes
Drawing Solids on a Flat Surface
There are two techniques to create the illusion, of three-dimensionality when drawing solid shapes on a flat surface, such as paper.
1. Oblique Sketches
- These drawings show how 3D objects look from different angles.
- They're drawn by hand, without using any tools.
- They don't involve measuring the actual size of the 3D object.
- Below is a sketch of a cube drawn from an angle.
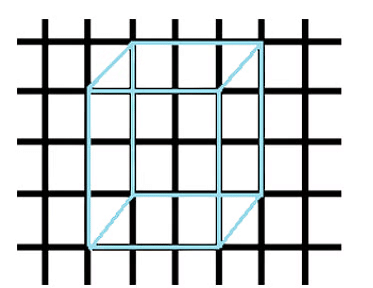
2. Isometric Sketches
- This method involves both drawing the 3D object and taking measurements.
- The drawings are done on special sheets called isometric sheets.
- Below is a sketch of a cube drawn using the isometric method, with the dotted sheet it's drawn on being called an isometric sheet.
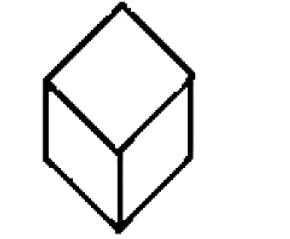
Viewing Different Sections of a Solid
There are many methods to view different sections of a solid:
(a) Slicing and Cutting: This method reveals the inside of a solid by slicing it into cross-sections.
(b) Shadow Casting: This technique creates a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional object by casting its shadow.
(c) Viewing from Different Angles: Observing a solid from various perspectives, such as front, side, and top views, offers valuable insights into its shape and structure.
Example: Different viewpoints of a building are illustrated below.
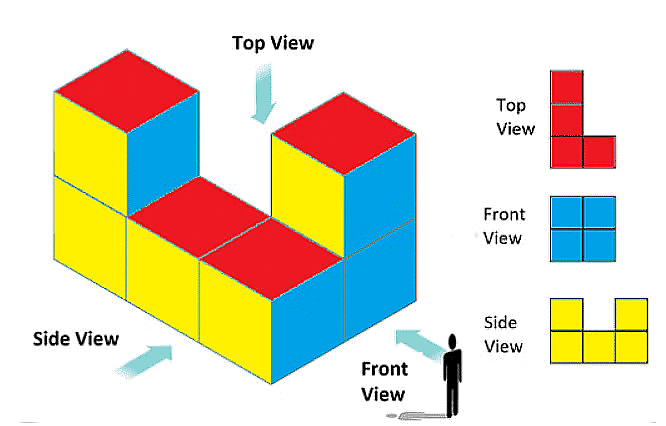
|
75 videos|228 docs|70 tests
|
|
75 videos|228 docs|70 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CTET & State TET exam
|

|

















