CTET & State TET Exam > CTET & State TET Notes > Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams > Important Formulae: Numbers
Important Formulae: Numbers | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Number System? |

|
| Important Formulas in Number System |

|
| Important Formulas in Algebra |

|
| Divisibility Rules |

|
What is Number System?
A number system, or system of numeration, is a method of representing numbers or symbols in a consistent way. In simple terms, it refers to the way numbers are written.
Here is a list of Important formulas that candidates need to master to crack the exam successfully.
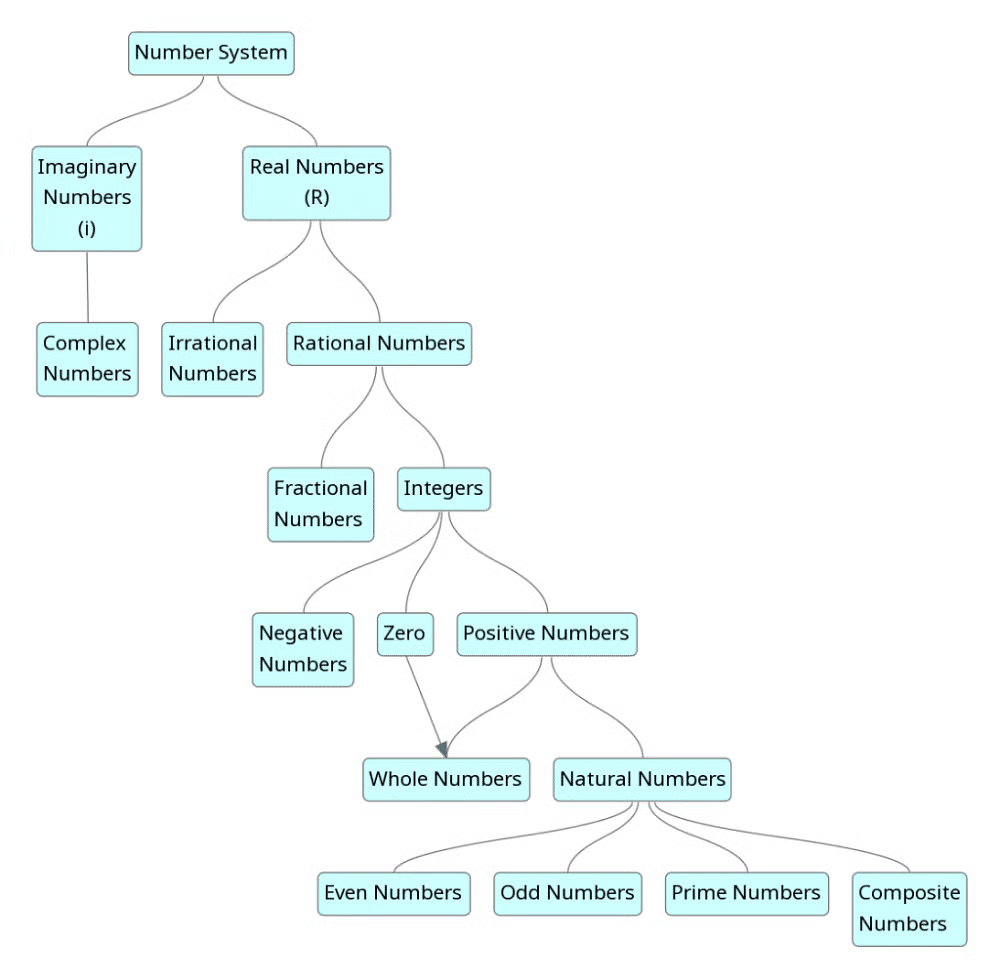
Important Formulas in Number System
- Sum of the first n natural numbers
Formula: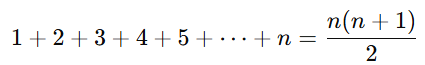 Example: Find the sum of the first 5 natural numbers.
Example: Find the sum of the first 5 natural numbers.
Solution: Using the formula, n = 5,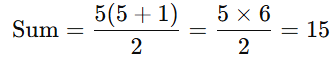
- Sum of the squares of the first n natural numbers
Formula: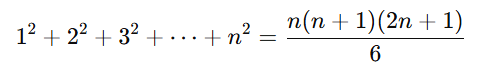 Example: Find the sum of the squares of the first 4 natural numbers.
Example: Find the sum of the squares of the first 4 natural numbers.
Solution: Using the formula, n = 4,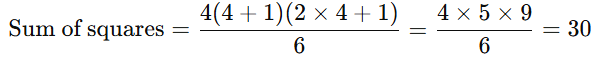
- Sum of the cubes of the first n natural numbers
Formula: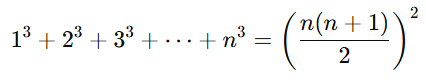 Example: Find the sum of the cubes of the first 3 natural numbers.
Example: Find the sum of the cubes of the first 3 natural numbers.
Solution: Using the formula, n = 3,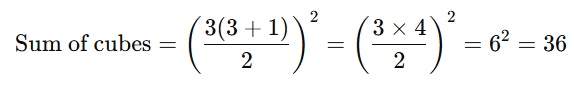
- Sum of the first n odd numbers
Formula: Sum of first n odd numbers = n2
Example: Find the sum of the first 5 odd numbers.
Solution: Using the formula, n = 5,
Sum of first 5 odd numbers = 52 = 25 - Sum of the first n even numbers
Formula: Sum of first n even numbers = n × (n + 1)
Example: Find the sum of the first 4 even numbers.
Solution: Using the formula, n = 4,
Sum of first 4 even numbers = 4 × (4 + 1) = 4 × 5 = 20
Important Formulas in Algebra
- (a + b)(a - b) = (a2 - b2)
- (a + b)2 = (a2 + b2 + 2ab)
- (a - b)2 = (a2 + b2 - 2ab)
- (a + b + c)2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2(ab + bc + ca)
- (a3 + b3) = (a + b)(a2 - ab + b2)
- (a3 - b3) = (a - b)(a2 + ab + b2)
- (a3 + b3 + c3 - 3abc) = (a + b + c)(a2 + b2 + c2 - ab - bc - ac)
- When a + b + c = 0, then a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc
- (a + b)n = an + (nC1)an-1b + (nC2)an-2b² + … + (nCn-1)abn-1 + bn
Divisibility Rules
- Divisibility by 2 → A number that is even or a number whose last digit is an even number i.e. 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8.
- Divisibility by 3 → The sum of all the digits of the number should be divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 4 → Number formed by the last two digits of the number should be divisible by 4 or should be 00.
- Divisibility by 5 → Numbers having 0 or 5 as their ones place digit.
- Divisibility by 6 → A number that is divisible by both 2 and 3.
- Divisibility by 7 → Subtracting twice the last digit of the number from the remaining digits gives a multiple of 7.
- Divisibility by 8 → Number formed by the last three digits of the number should be divisible by 8 or should be 000.
- Divisibility by 9 → The sum of all the digits of the number should be divisible by 9.
- Divisibility by 10 → Divisibility rule for 10 states that any number whose last digit is 0, is divisible by 10.
- Divisibility by 11 → The difference of the sums of the alternative digits of a number is divisible by 11.
- Divisibility by 12 → A number that is divisible by both 3 and 4.
- Divisibility by 13 → For any given number, to check if it is divisible by 13, we have to add four times of the last digit of the number to the remaining number and repeat the process until you get a two-digit number. Now check if that two-digit number is divisible by 13 or not. If it is divisible, then the given number is divisible by 13.
- Divisibility by 14→ A number divisible by both 2 and 7.
- Divisibility by 16 → Last four-digit divisible by 16
- Divisibility by 27 → Sum of blocks of 3 (taken a right to left) divisible by 27
The document Important Formulae: Numbers | Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET is a part of the CTET & State TET Course Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams.
All you need of CTET & State TET at this link: CTET & State TET
|
30 videos|210 docs|69 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulae: Numbers - Mathematics & Pedagogy Paper 1 for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are some important formulae related to numbers for CTET and State TET exams? |  |
Ans. Some important formulae related to numbers for CTET and State TET exams include formulas for calculating LCM, HCF, prime numbers, even and odd numbers, and divisibility rules.
| 2. How can I effectively memorize the formulae for numbers for CTET and State TET exams? |  |
Ans. To effectively memorize the formulae for numbers for CTET and State TET exams, create flashcards, practice regularly, and apply the formulas to solve numerical problems.
| 3. Are the formulae for numbers a crucial topic for the CTET and State TET exams? |  |
Ans. Yes, understanding and applying the formulae for numbers is crucial for the CTET and State TET exams as it forms the basis for solving mathematical problems and questions related to numbers.
| 4. Can you provide examples of how the formulae for numbers are used in CTET and State TET exams? |  |
Ans. The formulae for numbers are used in CTET and State TET exams to solve questions on factors, multiples, prime numbers, and arithmetic operations. For example, finding the LCM and HCF of numbers or determining whether a number is prime or composite.
| 5. How can I practice applying the formulae for numbers for the CTET and State TET exams effectively? |  |
Ans. To practice applying the formulae for numbers effectively for the CTET and State TET exams, solve practice questions, work on sample papers, and seek help from teachers or online resources for clarification on any doubts.
Related Searches















