Parts of Speech | Basic Grammar for IELTS PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Parts of speech? |

|
| Different Parts of Speech |

|
| Other parts of speech |

|
| How to Determine the Part of Speech |

|
What are Parts of speech?
Parts of speech, also known as word classes, categorize words based on their role and function in a sentence. Recognizing these categories can enhance your writing by clarifying how words work together.
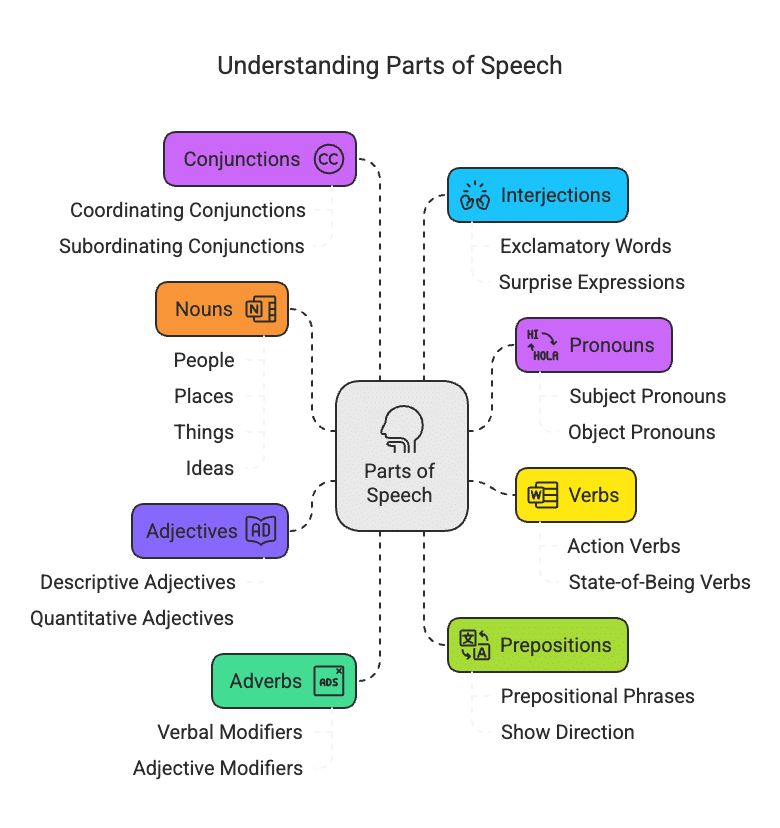
There are eight parts of speech:
- Nouns. Names of people, places, things, or ideas.
- Pronouns. Words that replace nouns to avoid repetition.
- Verbs. Action words or state-of-being words.
- Adjectives. Words that describe or modify nouns.
- Adverbs. Words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
- Prepositions. Words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence.
- Conjunctions. Words that connect clauses, sentences, or words.
- Interjections. Words that express strong emotion or surprise.
Different Parts of Speech
(a) Nouns
A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns can act as the subject (the doer of the action) or the object (the receiver of the action) in a sentence.
Types of Nouns:
- Common Nouns: Refer to general items, such as "city."
- Proper Nouns: Name specific entities, like "London."
- Collective Nouns: Denote groups, such as "team."
Examples of Nouns in Sentences
- "I’ve never read that book."
- "Ella lives in France."
(b) Pronouns
A pronoun is used in place of a noun to avoid repetition. It refers back to a previously mentioned noun and must agree with it. Pronouns, like nouns, can refer to people, places, things, or ideas.
Types of Pronouns:
- Personal Pronouns: Substitute specific names, such as "he" or "she."
- Demonstrative Pronouns: Indicate specific items, like "this" or "that."
- Interrogative Pronouns: Ask questions about items, for instance, "who" or "what."
Examples of Pronouns in Sentences
- "I don’t really know her."
- "That is a horrible painting!"
(c) Verbs
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
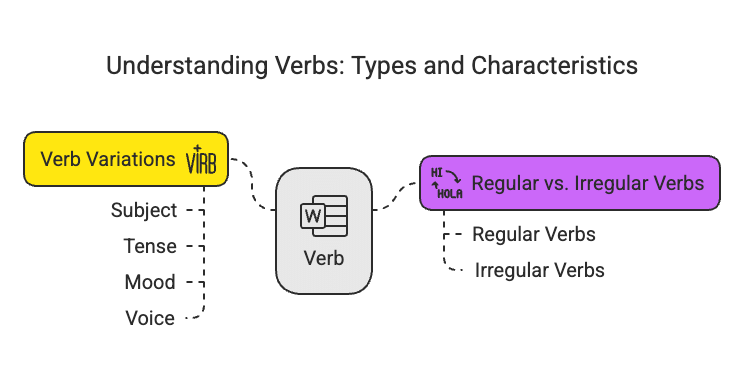
Verb Variations:
- Subject: Changes with the subject (e.g., "I run," "he runs").
- Tense: Indicates the time of action (past, present, future).
- Mood: Conveys the speaker's attitude (e.g., indicative, imperative).
- Voice: Shows whether the subject performs or receives the action (active vs. passive voice).
Regular vs. Irregular Verbs: Regular verbs form their past tense by adding “-ed” (e.g., "play" becomes "played"), while irregular verbs change in unpredictable ways (e.g., "go" becomes "went").
Examples of Verbs in Sentences
- "Will you check if this book is in stock?"
- "I’ve already checked twice."
(d) Adjectives
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive, appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative, appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red”).
Types of Adjectives:
- Comparative Adjectives: Compare two items (e.g., "bigger").
- Superlative Adjectives: Indicate the highest degree (e.g., "biggest").
Examples of Adjectives in Sentences
- "The dog is bigger than the cat."
- "He is the laziest person I know."
(e) Adverbs
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
Types of Adverbs:
- Adverbs of Manner: Describe how an action is performed (e.g., “slowly”).
- Adverbs of Degree: Indicate the intensity of an action or quality (e.g., “very”).
- Adverbs of Place: Specify the location of an action (e.g., “here”).
Examples of Adverbs in Sentences
- "Ray acted rudely."
- "Talia writes quite quickly."
(f) Prepositions
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time, place, and direction.
Examples of Prepositions in Sentences
- "Hasan is coming for dinner at 6 p.m."
- "I left the cup on the kitchen counter."
(g) Conjunctions
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
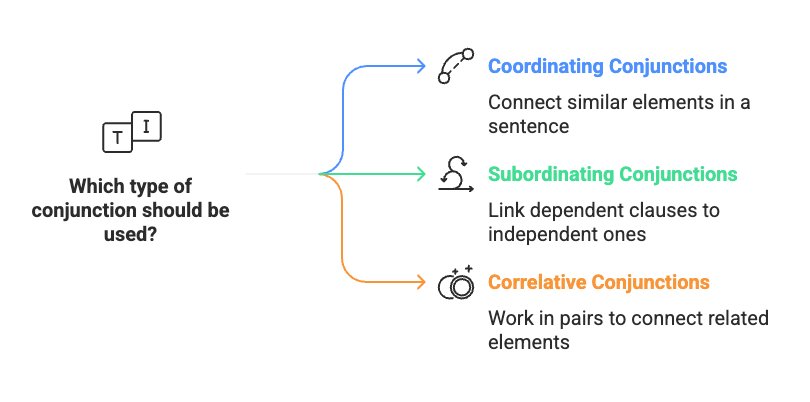
The primary types of conjunctions include:
- Coordinating Conjunctions: Connect similar elements (e.g., "and," "but").
- Subordinating Conjunctions: Link dependent clauses to independent ones (e.g., "because," "although").
- Correlative Conjunctions: Work in pairs to connect related elements (e.g., "either...or," "not only...but also").
Examples of Conjunctions in Sentences
- "Daria likes swimming and hiking."
- "You can choose what movie we watch because I chose last time."
- "We can either go out for dinner or go to the theatre."
(h) Interjections
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of Interjections:
- Volitive Interjections: Used to make requests (e.g., "please").
- Emotive Interjections: Express feelings (e.g., "wow").
- Cognitive Interjections: Indicate thoughts (e.g., "hmm").
- Greetings and Parting Words: Used in conversations (e.g., "hello," "goodbye").
Examples of Interjections in Sentences
- "Ouch! I hurt my arm."
- "I’m, um, not sure."
- "Hey! How are you doing?"
Other parts of speech
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
(a) Determiners
Determiners provide information about a noun, such as its quantity, possession, or location. Common types of determiners include:
- Demonstrative determiners: These indicate the position of a noun, such as "this" and "that."
- Possessive determiners: These show ownership, such as "my" and "his."
- Quantifiers: These indicate the amount of a noun, such as "many" and "few."
Examples of determiners in sentences:
- "This chair is more comfortable than that one."
- "My brother is selling his old car."
- "Many friends of mine have part-time jobs."
Other types of determiners include:
- Distributive determiners
- Determiners of difference
- Numbers
(b) Articles
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general. The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
The indefinite articles "a" and "an" refer to general nouns and can only be used with singular countable nouns, such as "a poster" and "an engine."
Examples of definite and indefinite articles in sentences:
- "I live just outside of the town."
- "There’s a concert this weekend."
- "Karl made an offensive gesture."
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Every word in a sentence plays a role — that role is called its part of speech. Some words change their role depending on how they're used in a sentence.
Key Tip
To figure out the part of speech, ask yourself:
What does the word mean in this sentence?
What is the word doing? (Is it naming something? Describing? Showing action?)
Where is it placed in the sentence?
Interjections
These are the only words that can stand alone and still make sense.
Examples:
Wow!
Oh no!
Hooray!
Words like "work" can be tricky because they can be used in different parts of speech.
Let’s look at some examples:
Noun – Names a thing or idea
Bosco showed up for work two hours late.
→ Here, work is a thing (a place/activity), so it's a noun.Verb – Shows action
He will have to work until midnight.
→ Now, work is what he must do, so it's a verb.Adjective (Attributive noun) – Describes another noun
His work permit expires next month.
→ Here, work is used to describe permit, so it functions like an adjective.
Quick Trick to Practice
Try putting the word in different sentences and see how its role changes. Look at:
Meaning (What does it refer to?)
Function (What is it doing in the sentence?)
Position (What words come before and after it?)
|
18 videos|54 docs
|
FAQs on Parts of Speech - Basic Grammar for IELTS
| 1. What are the eight parts of speech in English? |  |
| 2. How can I identify the part of speech of a word in a sentence? |  |
| 3. Can a word belong to more than one part of speech? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of understanding parts of speech for the IELTS exam? |  |
| 5. How can I practice parts of speech for the IELTS exam? |  |















