Notes: Education | Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Definitions and Meaning of Education |

|
| Major Philosophies and Approaches in Education Sector |

|
| Forms of Education |

|
| Major Aims and Objectives of Education |

|
Definitions and Meaning of Education
- Education, teaching, and learning are interconnected concepts, with education encompassing a broad meaning.
- Education plays a crucial role in individual, social, and economic development. Being educated is a significant achievement, and the opportunity to learn is essential for a person's freedom. Increased literacy and basic education enable better resource utilization.
- The primary goal of education is learning. While teaching is considered a facilitator of learning, it is not the only method. Whenever teaching is mentioned, some form of learning is implied. Universal education includes inclusive education, universal enrollment, universal retention, and improving the quality of schooling.
- The National Policy of Education 1986 emphasizes that teachers should have the freedom to innovate and develop appropriate communication methods and activities. Over the past thirty years, various new teaching and training methods have been developed, tested, and adapted to different learning situations. A range of teaching approaches has emerged to design effective instruction.
- Teaching and learning are distinct processes. A theory of teaching should focus on maximizing learning for children. This unit explores some introductory aspects of education.
Perspectives on Education
- Swami Vivekananda: Education is the process of revealing and nurturing the inherent perfection within individuals.
- Aristotle: Education involves developing a sound mind within a healthy body.
- Heinrich Pestalozzi: Education is the natural, harmonious, and progressive development of a person's innate abilities. Each individual possesses remarkable inborn talents, and education creates an environment conducive to their development.
- John Dewey: Education empowers individuals to control their environment and realize their potential.
- Froebel: Education is the process through which a child develops its inner potential to participate meaningfully in the external world. The purpose of education is to expand an individual's life to engage with the pervasive spirit that manifests throughout the universe.
Major Philosophies and Approaches in Education Sector
Philosophy of Education
- Philosophy is a vast subject and influences all aspects of education, such as aims, objectives, curriculum, teaching methods, teacher, textbooks, and discipline.
- Education is based on philosophical, psychological, and sociological grounds.
- The question of ‘Why’ is answered by philosophy, ‘How’ is decided by psychology, and ‘What’ is decided by social needs.
Different Schools of Philosophy in Education
Idealism:
- Derived from the concept of ‘ideal’, idealism focuses on the mind and self, which are considered spiritual.
- Proponents believe that the universal mind or God is central to understanding the world, and that God is the source of all creation.
- Knowledge, spirit, and mind constitute reality, and values are seen as absolute, eternal, and unchanging.
- Real knowledge is perceived through the mind, which is more important than knowledge gained through the senses.
- Human nature is seen as superior, expressed through intellectual culture, morality, and religion.
- Thinkers associated with idealism include Fröbel, Kant, Plato, Swami Dayanand, Vivekananda, and Sri Aurobindo.
Naturalism:
- In contrast to idealism, naturalism holds that nature alone represents reality. Human life is seen as part of nature, governed by natural matter, force, and laws.
- Naturalism emphasizes the physical world and does not believe in spirituality or supernaturalism.
- Knowledge is gained through the senses, and nature is the source of all knowledge.
- The mind is subordinate to nature, and the educative process should be pleasurable and set in natural surroundings.
- Key figures in naturalism include Tagore, Rousseau, and Herbert Spencer.
Pragmatism:
- Pragmatism, derived from a Greek word meaning practice or action, focuses on utility. what is useful is good, and vice versa.
- Pragmatism emphasizes activity and doing, rejecting absolute values. Truth is seen as something created through experience.
- Humans are active beings capable of solving problems through experimentation and scientific methods.
- Prominent thinkers in pragmatism include John Dewey, Kilpatrick, and Mead.
Constructivism:
- Constructivism posits that learners actively construct knowledge. Jean Piaget and J. S. Bruner argue that learning involves actively processing information, with each individual organizing and constructing knowledge uniquely.
- Educational psychology suggests that there are developmental stages for knowledge organization.
- According to Piaget, ‘accommodation’ and ‘assimilation’ are fundamental to learning. A learner develops a new ‘schema’ through accommodation, while new experiences are either assimilated into existing schemas or accommodated by creating new ones.
Humanism:
- Humanism advocates for a reasonable balance in life, placing humans at the center of all activities. It emphasizes the interests and welfare of all human beings, with the goal of transforming human life for the better.
- Self-actualization is a key aspect of humanistic learning, along with cooperation, mutual tolerance, and social understanding.
- Prominent advocates of humanism include Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow.
Rationalism:
- Rationalists believe that knowledge and concepts can be gained independently of sensory experience.
Empiricism:
- Empiricists argue that sensory experiences are the ultimate source of all concepts and knowledge.
Existentialism:
- Existentialism emphasizes individual existence, freedom, and choice. It highlights the uniqueness and isolation of individual experiences in a universe that may be hostile or indifferent.
- Human existence is viewed as unexplainable, with a focus on the freedom of choice and the responsibility for the consequences of one’s actions.
Behaviorism:
- Behaviorism posits that learners are passive organisms who can be conditioned to learn new behaviors. Learning is understood as a change in observable behavior.
- E. L. Thorndike proposed the law of exercise and the law of effect to explain learning.
- The law of exercise suggests that repeating a conditioned response strengthens the bond between stimulus and response, while the law of effect relates to reinforcement and punishment, determining future behavior based on past experiences.
Gestalt Psychology:
- Gestalt psychology emphasizes that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. For instance, in the human body, the sum of cells, tissues, organs, and systems is greater than the individual parts because they are interrelated.
- Gestalt psychology also highlights the importance of perception and suggests that complex learning can occur through insight rather than prolonged practice.
Eclectic Philosophy:
- Eclecticism involves combining knowledge and ideas from various sources. It is an educational philosophy that integrates the best principles from different philosophies.
There are many philosophies of education, and some of the important philosophies of education have been mentioned below:
Important Concepts in Education and Teaching and their Proponents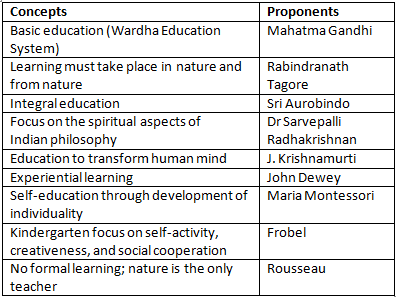
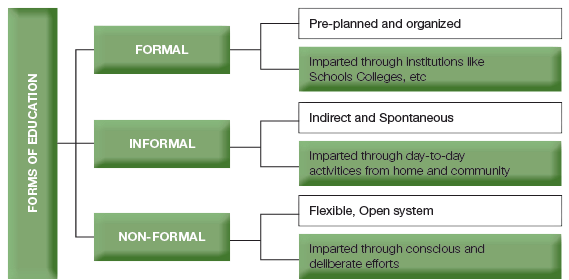
Forms of Education
- Formal Education: This type involves structured learning within schools, colleges, and universities, following a set curriculum and leading to recognized qualifications.
- Informal Education: Informal education occurs outside formal institutions, such as learning through life experiences, family, or community activities. It is unstructured and does not follow a specific curriculum.
- Non-formal Education: Non-formal education includes organized learning activities outside the formal system, such as adult education programs, skill development courses, and workshops. It is planned but more flexible than formal education.
Integration of Education Types
- All three types of education—formal, informal, and non-formal—play a crucial role in the modern education system.
- Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Integrating these three forms of education can create a more holistic and comprehensive learning experience.
Major Aims and Objectives of Education
Functions of Education
Havighurst and Neugarten: Education serves two key functions:
- Reflecting society as it is (stabilizing society)
- Acting as an agent of social change (implementing societal ideas)
George Payne: Identified three main functions of education:
- Assimilation of traditions
- Development of new social patterns
- Creative and constructive role
Emile Durkheim: Emphasized education's role in transmitting society's norms and values.
- Education also trains individuals for specialized roles and occupations.
Education's Functions:
- Cultural transmission and enrichment
- Acceptance and reformulation of culture
- Change and reconstruction of society
Enculturation: The process by which the young generation learns traditional ways of society, formalized through education.
Acculturation: Adopting practices and values of another culture while retaining one's own distinct culture, becoming increasingly relevant in a globalized society.
Factors Determining Educational Aims
- Education is a planned and purposeful activity that requires educational aims to give direction.
- Philosophy is the main factor that determines the aim of education, as education is seen as the best means for propagating philosophy.
- Human nature plays a role in education, with idealists seeing the unfolding of the divine in man as the aim of education.
- Socio-cultural factors require education to preserve and transmit cultural heritage and traditions from one generation to another.
- Religious factors in ancient India emphasized the inculcation of ideals such as ahimsa and truth into the educational system.
- Political ideologies like democracy influence educational aims.
- Exploration of knowledge is essential for good interpersonal relationships, healthy adjustment in life, behavior modification, self-awareness, and social growth, as well as being a source of happiness.
- Vocational education should prepare children to earn a livelihood and be self-sufficient and efficient in economic and social factors.
- Self-actualization and total development involve helping individuals become what they are meant to be according to their potentials.
- Harmonious development, as per Mahatma Gandhi, means drawing out the best in a child and man in body, mind, and spirit through education.
- Moral and character development involves cultivating moral values and virtues such as truthfulness, goodness, purity, courage, reverence, and honesty.
- Citizenship education makes students aware of their duties, functions, and obligations towards society.
- Education for leisure promotes physical and mental balance through the wise use of leisure time, inspiring artistic, moral, and aesthetic developments.
Some Specified Aims of Education in the Indian Context
After gaining independence, India needed to reorient and restructure its social, political, and educational systems to address the socio-economic and political needs of the country. Various committees and commissions were formed to outline the aims and objectives of education in India.
The National Educational Policy of 1986 specified several key aims and objectives for education in India, including:
- All-round development: Fostering both material and spiritual development for all individuals.
- Cultural orientation: Instilling an appreciation for Indian culture and its development.
- Scientific temper: Promoting a scientific attitude and approach among people.
- National cohesion: Encouraging unity and cohesion among diverse groups within the nation.
- Independence of mind: Nurturing independent thinking while upholding the principles of socialism, secularism, and democracy.
- Manpower development: Preparing a workforce suitable for different levels of the economy.
- Research promotion: Encouraging research in various areas crucial for national development.
- Education for equality: Ensuring education promotes equality among all individuals.
|
27 videos|45 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Education - Teaching Aptitude for Teaching Exam - B.Ed Entrance
| 1. What is the definition of education? |  |
| 2. What are the major philosophies of education? |  |
| 3. What are the different forms of education? |  |
| 4. What are the major aims and objectives of education? |  |
| 5. How do different educational approaches impact student learning? |  |
















