Binary Coded Decimals | Analog and Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
BCD or Binary Coded Decimal
Binary Coded Decimal, or BCD, is another process for converting decimal numbers into their binary equivalents.
- It is a form of binary encoding where each digit in a decimal number is represented in the form of bits.
- This encoding can be done in either 4-bit or 8-bit (usually 4-bit is preferred).
- It is a fast and efficient system that converts the decimal numbers into binary numbers as compared to the existing binary system.
- These are generally used in digital displays where is the manipulation of data is quite a task.
- Thus BCD plays an important role here because the manipulation is done treating each digit as a separate single sub-circuit.
The BCD equivalent of a decimal number is written by replacing each decimal digit in the integer and fractional parts with its four bit binary equivalent.the BCD code is more precisely known as 8421 BCD code , with 8,4,2 and 1 representing the weights of different bits in the four-bit groups, Starting from MSB and proceeding towards LSB. This feature makes it a weighted code , which means that each bit in the four bit group representing a given decimal digit has an assigned weight.
Many decimal values, have an infinite place-value representation in binary but have a finite place-value in binary-coded decimal. For example, 0.2 in binary is .001100… and in BCD is 0.0010. It avoids fractional errors and is also used in huge financial calculations.
Consider the following truth table and focus on how are these represented.
Truth Table for Binary Coded Decimal
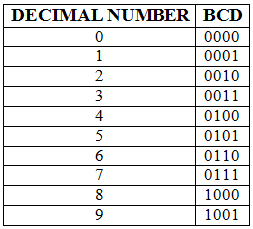
In the BCD numbering system, the given decimal number is segregated into chunks of four bits for each decimal digit within the number. Each decimal digit is converted into its direct binary form (usually represented in 4-bits).
For example:
1. Convert (123)10 in BCD
From the truth table above,
1 -> 0001
2 -> 0010
3 -> 0011
thus, BCD becomes -> 0001 0010 0011
2. Convert (324)10 in BCD
(324)10 -> 0011 0010 0100 (BCD)
Again from the truth table above,
3 -> 0011
2 -> 0010
4 -> 0100
thus, BCD becomes -> 0011 0010 0100
This is how decimal numbers are converted to their equivalent BCDs.
It is noticeable that the BCD is nothing more than a binary representation of each digit of a decimal number.
It cannot be ignored that the BCD representation of the given decimal number uses extra bits, which makes it heavy-weighted.
|
135 videos|181 docs|71 tests
|





















