Notes: Connotations and Denotations | Logical Reasoning for UGC NET PDF Download
Introduction
Connotations and denotations are essential properties of terms used in propositions, often referred to as the intension and extension of terms, respectively.
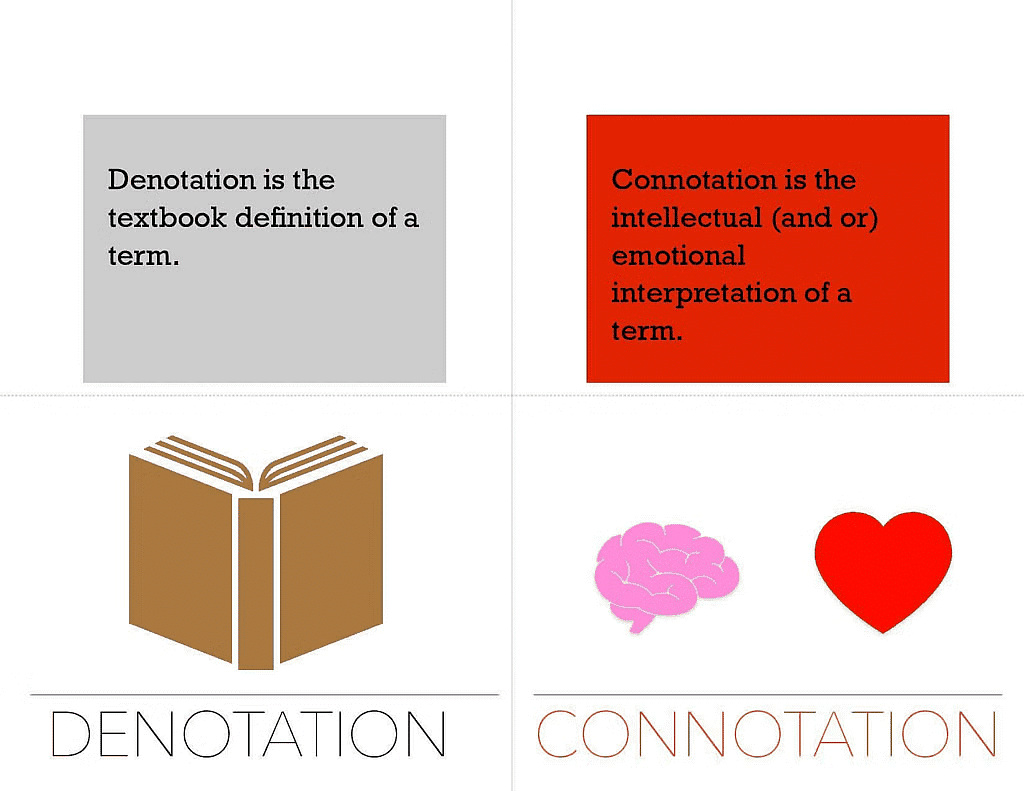
Understanding these concepts is crucial for grasping the full meaning and implications of terms within logical statements.
Connotation
Connotation refers to the attributes and qualities that a term suggests in addition to its explicit meaning. It encompasses the implied or associated characteristics that go beyond the direct definition.
For example, the term "man" not only denotes all human beings but also connotes qualities such as rationality and animality. The connotation of a term involves both the object it refers to and the inherent qualities associated with that object.
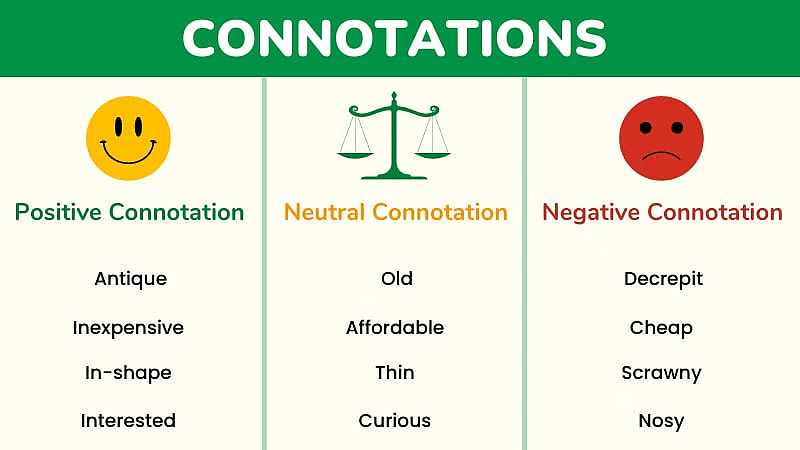
There are three primary views regarding the precise meaning of connotation:
Objective View:
- According to the objective view, connotation includes all the attributes associated with a term, whether known or unknown. This view posits that, in logic, we are only concerned with attributes that are known to human reason. It emphasizes attributes that are relatively agreed upon and commonly accepted as part of the term's meaning.
- Example: The term "triangle" denotes a three-sided polygon. Objectively, it connotes attributes like having three angles, the sum of which equals 180 degrees, and three sides.
Subjective View:
- The subjective view considers only those attributes known to the individual speaker or subject. This perspective allows for variability in the connotation of a term based on personal knowledge and interpretation. As a result, connotations can differ from person to person.
- However, this view poses challenges in achieving consensus and can undermine the purpose of logic, which relies on shared understanding and agreement on terms.
- Example: The term "home" might connotate safety and warmth for one person, while for another, it might evoke memories of conflict or discomfort.
Logical or Conventional View:
- The logical or conventional view maintains that connotation encompasses only the essential and fixed attributes of an object, which are universally agreed upon and necessary for the term's definition.
- This view aims to provide a stable and consistent understanding of terms, facilitating clear communication and logical reasoning.
- Example: The term "bachelor" conventionally connotes an unmarried man. This connotation is fixed and essential for the term's definition, making it universally recognizable and consistent.
 |
Download the notes
Notes: Connotations and Denotations
|
Download as PDF |
Denotation
While the provided text did not elaborate on denotation, it's important to mention that denotation refers to the literal, explicit meaning of a term—the actual object or set of objects it refers to. It is the direct reference, devoid of any additional implied qualities or associations.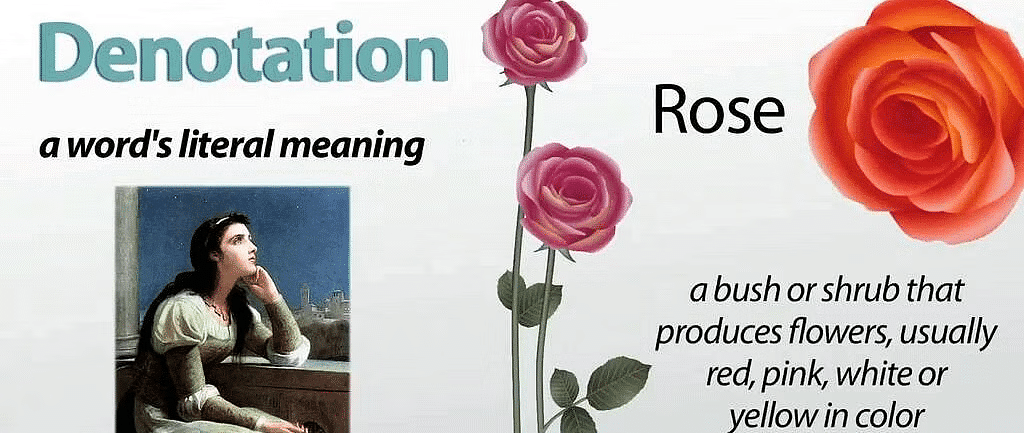
Example: The term "rose" denotes a specific type of flower. Its denotation includes all individual flowers classified as roses. In contrast, its connotation might include associations with romance, beauty, or passion.
Understanding both connotation and denotation is crucial for effective communication and logical analysis. While denotation provides the clear, explicit reference of a term, connotation enriches the term with implied qualities and associations, adding depth to our understanding. The objective, subjective, and logical views of connotation each offer different perspectives on how these implied attributes are determined and understood.
|
31 videos|28 docs|14 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Connotations and Denotations - Logical Reasoning for UGC NET
| 1. What is the difference between connotation and denotation in language? |  |
| 2. How can connotations affect the meaning of a word or phrase? |  |
| 3. Can a word have different connotations in different contexts? |  |
| 4. How can understanding connotations and denotations help improve communication? |  |
| 5. Are connotations and denotations important in literary analysis? |  |




















