Understanding Mass Housing | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Rapid urbanization and job opportunities in urban areas attract many people worldwide, leading to unplanned urbanization and low-quality building stock. Mass housing, a response to urban regeneration efforts, aims to address the housing shortage in big cities by providing dense and repetitive housing solutions. The primary focus of mass housing is on rapid construction and cost reduction through grouping similar construction work and utilizing readily available skilled labor. To address these challenges, new approaches involving collaboration among stakeholders, such as Public-Private Partnerships (PPP), are being increasingly adopted.

Mass Housing: Definition & Concept
Mass housing refers to multi-story apartment buildings designed to cater to the housing needs of middle-class families. It is characterized by dense and repetitive housing solutions and has emerged as a response to urban regeneration projects aiming to address housing shortages, particularly in large cities. The primary objective of mass housing is to enable rapid construction to meet the high demand for housing.
While mass housing is often associated with low-cost accommodation, focusing solely on cost reduction cannot fully address the housing needs of everyone due to the sheer scale of demand. A mass housing project involves the construction of standardized residential units within the same project scheme and management structure.
Unique Features of Mass Housing Project
- Every project possesses its own set of characteristics, necessitating specific skills and capabilities from teams, organizations, and companies to effectively manage and execute them. Mass housing projects, in particular, exhibit attributes that distinguish them from unique construction projects. These attributes influence operational, organizational, and managerial actions throughout the construction process.
- Mass housing projects are typically conducted across various geographic locations and involve repetitive and standardized design units compared to traditional construction projects. They often consist of housing units dispersed across different locations, each with its own contextual considerations and specialized subcontracting arrangements. Procurement, labor management, planning, and site management systems in mass housing projects are inherently unique, reflecting the project's scale and complexity.
Moreover, mass housing projects typically entail the simultaneous coordination of multiple engineering elements within smaller unit sizes. This approach facilitates streamlined manufacturing, accelerates construction timelines, and promotes the integration of accompanying engineering components. While mass housing projects share certain commonalities with traditional megaprojects, such as size and institutional complexity, they also possess unique characteristics that necessitate distinct management approaches.

Challenges Faced in Mass Housing
Urban Population Growth and Housing Deficit
- Global population growth is estimated at approximately 83 million annually, representing a growth rate of 1.18% per year.
- The world population has grown significantly from 1 billion in 1800 to 7.3 billion by mid-2015.
- Projections suggest further growth, with an estimated total population of 8.5 billion by 2030, 9.7 billion by 2050, and 11.2 billion by 2100 according to the United Nations (2015).
- Urbanization has intensified, with over half (54%) of the world's population residing in urban areas in 2014, a substantial increase from 34% in 1960.
- Even in underdeveloped countries, the majority of the population is projected to reside in urban areas by 2017.
- This rapid urbanization trend over the past two centuries has had profound effects on living standards, natural resources, and the built environment.
- However, many governments in developing regions have struggled to provide adequate housing, leading to crises in cities characterized by informal settlements, inadequate infrastructure, and overcrowding.
- The shortage of urban housing globally particularly affects economically disadvantaged areas and low- to middle-income groups.
- To address this housing deficit, governments, city planners, and real estate developers have proposed mass or low-cost housing projects, often involving the construction of multi-story residential buildings.
- Challenges in providing mass housing in developing regions include local production capacity to meet the increasing demand of the growing urban population.
- In developed areas, challenges may differ, such as addressing the needs of an aging population or dealing with deteriorating old building stock.
Urban Land Scarcity and Resources Availability
- High population density in established cities has created significant demand for urban land, leading to a surge in urban land prices and restricting housing choices for the general population.
- Countries like Japan, Singapore, and Hong Kong often face challenges due to limited arable land in urban areas, forcing residents to adapt to high-density living environments.
- In such settings where high density is unavoidable, there is growing support for compact urban development as a sustainable approach to urban planning.
Institutional Framework and Major Stakeholders of Housing Delivery
- Apart from population growth and land availability, there are significant challenges within the legal and planning institutional framework governing housing supply.
- Many countries prioritize values of equality and inclusion in their housing visions, aiming for accessible, permanent, and quality housing as outlined in housing objectives and policies.
- Housing processes guide various actors in the sector, including needs assessment, policy formulation, financing mechanisms, and construction capacities.
- The provision of housing is influenced by political will, governance structures, housing finance mechanisms, urban land management, economic factors, and considerations of design, technical, cultural, and social aspects.
- Involvement of diverse actors in collective housing projects often leads to implementation delays.
- Lack of infrastructure and services poses additional challenges for citizens and policymakers, particularly in developing countries.
- Despite global efforts to develop key housing development strategies, realizing national housing visions remains a challenge in many parts of the world.
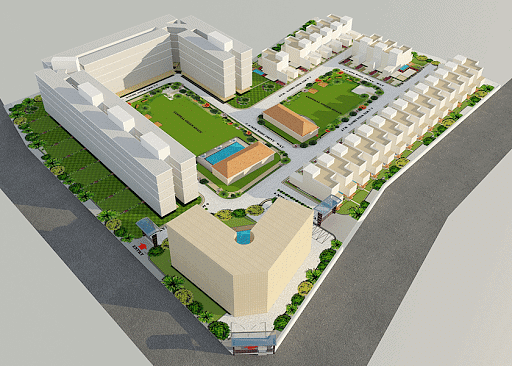
Design Criteria of Mass Housing
The House- Adaptation to different lifestyles is essential, ensuring that the home meets the needs and preferences of its occupants.
- Each home should have a unique identity, reflecting the style and personality of its inhabitants.
- The concept of "architecture" encompasses the design and construction of buildings, considering both aesthetic and functional aspects.
- Homes should meet the expected standard of living, providing comfort and convenience to residents.
- Rooms within the house should be carefully designed to serve their intended purposes efficiently.
- A decent-sized, sunny open space that connects directly from the living area is desirable, along with an outdoor area suitable for young children.
- Apartment extensions, such as gardens or terraces, should be visible from the interior of the home.
- Climate considerations should be integrated into the design, with insulation for colder weather and the ability to open up the house during pleasant weather.
- Provision for cleaning and washing areas within the house helps to maintain cleanliness and organization.
- Sufficient storage space is essential, including built-in storage solutions to accommodate various belongings.
- Easy maintenance is crucial for homeowners to upkeep their property effectively.
- Homes should be constructed in a way that supports each other, fostering a sense of community and cohesion within the neighborhood.
The Immediate Extensions of the Dwelling
- Provision of playing space for children aged three to five years is important, ensuring that they have an area to engage in physical activity and play.
- The design of the apartment should convey a clear external image, reflecting its unique characteristics and identity.
- There should be visible signs of ventilation and access points for residents, ensuring proper airflow and mobility within the apartment complex.
- The development should avoid isolation and the appearance of a warehouse-like structure, instead fostering a sense of community and liveliness.
The Appreciated Unit
- The size of the department (housing unit) should be proportionate to the size of the parent community, ensuring that adding a house does not disrupt the village's pattern. In a large city, an equivalent gesture may require a unit of 5,000 homes to maintain harmony and balance.
- It's essential to understand the community's work pattern and its implications for the housing unit. For example, families who frequently travel to distant places for work, common in both cities and villages, should have their needs accommodated.
- Development should offer protection on the same scale as the parent community, ensuring that residents feel secure and supported within their living environment.
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
FAQs on Understanding Mass Housing - Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the definition of Mass Housing? |  |
| 2. What are the unique features of Mass Housing projects? |  |
| 3. What are some of the challenges faced in Mass Housing projects? |  |
| 4. Who are the major stakeholders involved in the delivery of Mass Housing projects? |  |
| 5. What are the design criteria typically considered in Mass Housing projects? |  |
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















