What is BOOT? | Civil Engineering Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Understanding the BOOT Model in Infrastructure Projects
The Build, Own, Operate, and Transfer (BOOT) model functions as a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) framework for infrastructure projects. Under this model, a private entity, often a consortium or company, is responsible for the entire lifecycle of the project. This begins with designing and constructing the facility using the private entity's funds or through loans and financing. Once the project is completed, the private entity owns and operates the facility for a predetermined period, typically ranging from several years to several decades.- During the operational phase, the private operator handles day-to-day activities, maintenance, and service provision. They may collect user fees or charges, such as tolls or tariffs, to recoup their investment and operational costs, allowing them to earn returns over the agreed-upon duration.
- At the end of the contract period, the ownership and operation of the infrastructure are transferred to the public sector or government, usually at no cost or a nominal fee, depending on the contract terms.
- The BOOT model benefits both parties: the public sector gains access to the private sector's expertise, technology, and efficiency in delivering and managing the project, while also reducing the financial burden on the government as the private entity assumes the risks associated with construction and operation. For the private entity, the BOOT model offers an opportunity for long-term revenue generation through user fees and eventually transferring the infrastructure back to the public sector.
Example #1
Consider a hypothetical example of the Build, Own, Operate, and Transfer (BOOT) model for a toll road project. A private company, Roadway Builders Inc., enters into a BOOT agreement with the local government to construct a much-needed toll road to ease traffic congestion.
Roadway Builders Inc. invests its capital to design and build the road with modern features, including electronic toll collection systems. Once completed, the private entity operates the toll road for a fixed period, maintaining it to high standards and collecting tolls from users for revenue. The contract states that after 25 years, the private entity will transfer the ownership and operations back to the government. During this period, the toll road significantly improves transportation in the region, and Roadway Builders Inc. recovers its investment and earns profits from toll collections.
Example #2
A real-world example of the Build, Own, Operate, and Transfer (BOOT) model is the Hamad International Airport (HIA) in Doha, Qatar. In 2008, the Qatar government awarded a contract to a consortium led by Hamad International Airport Company (HIAH), a joint venture between Qatar Airways and other investors, to design, construct, operate, and maintain the new airport. The project aimed to replace the existing Doha International Airport, which was fast reaching its capacity.
Qatar Civil Aviation Authority (QCAA) and the New Doha International Airport Steering Committee handled the airport development. The Qatar Company for Airports Operation and Management (MATAR) oversees airport operations.
During the “Build” phase, the consortium designed and constructed the state-of-the-art Hamad International Airport, investing significant capital and technical expertise. In the “Own and Operate” phase, the consortium took over the operations and management of the airport, ensuring the smooth and efficient functioning of the facility.
Throughout the operational period, which began with the airport’s opening in 2014, the consortium managed the airport, generating revenue through various sources, including airline fees, retail concessions, and passenger services.
The “Transfer” phase is expected to take place in the future per the terms of the BOOT contract. At the end of the concession period, ownership and operation of the airport will be transferred to the government of Qatar.
The Hamad International Airport project is an exemplary BOOT arrangement that demonstrated successful collaboration between private and public sectors, resulting in the creation of a world-class airport to serve the growing passenger footfall in the region.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of Build, Own, Operate, and Transfer have been discussed in this section.Advantages- Accelerated Infrastructure Development: BOOT projects facilitate the timely development of critical infrastructure by leveraging private sector expertise, funding, and efficiency, leading to faster project completion.
- Private Sector Expertise: Private entities bring specialized knowledge, technology, and innovation, enhancing the quality and performance of the infrastructure.
- Risk Transfer: The private sector agency assumes responsibility for all the construction and operational risks during the concession period, reducing the burden on the public sector.
- User Fees and Cost Concerns: BOOT projects may lead to higher user fees for essential services, raising concerns about affordability and access for some segments of the population.
- Long-Term Commitment: Governments must carefully assess the duration of BOOT contracts to ensure alignment with long-term infrastructure needs and potential changes in technology and demand.
- Regulatory and Contractual Complexity: BOOT agreements require robust contracts and careful regulatory oversight to safeguard public interests, which can be challenging to implement and monitor effectively.
Build, Own, Operate, And Transfer vs Build Lease Transfer
The differences between Build, Own, Operate, and Transfer and Build Lease Transfer are listed in the table below.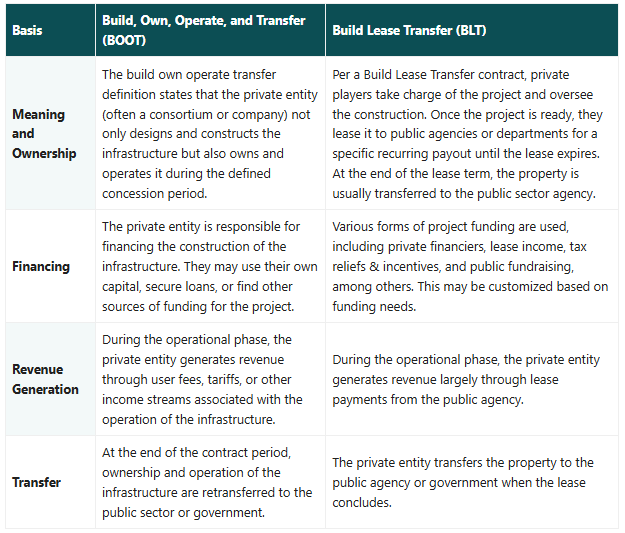
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|
|
350 videos|464 docs|2 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
















