All about Past Tense | Spanish: Elementary A2 Level - Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Pretérito indefinido: The simple past tense |

|
| Pretérito indefinido conjugations: Irregular verbs |

|
| Pretérito indefinido vs. pretérito perfecto |

|
| Wrapping up |

|
Pretérito indefinido: The simple past tense
The simple past tense is used in a variety of situations, from reacting to stories to stating historical facts. Here are five common situations where we use this tense:
- Describing specific past actions or events
- Sharing what you did, saw, or experienced in the past
- Stating past events or facts
- Indicating the exact time or duration of past actions
- Listing a series of actions that have happened in the past
This makes it a great tool for narrating and storytelling, or even just chatting about your day.
To use the pretérito indefinido, you need to know how to conjugate verbs and structure the sentences correctly. Luckily, for regular verbs it’s pretty straightforward.
The sentence structure is as follows:
subject + verb (conjugated in pretérito indefinido) + object
For example:
María compró un libro.
María bought a book.
Does this look familiar? That’s because it’s no different from the sentence structure we use for the present tense. Nice, right?
Let’s move on to conjugations.
The conjugation patterns for regular -ar, -er, and -ir verbs in the pretérito indefinido are as follows:
Pretérito indefinido conjugations: Regular verbs
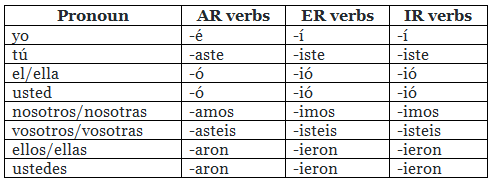
Note: Vosotros / vosotras are mainly used in Spain and not in Latin America, where people tend to use ustedes instead. Check out our article on the difference in Spanish used in Spain and Latin America.
As you can see verb endings are the same for -er and -ir verbs, making things just a bit easier to remember.
Now, let’s take a look at some example sentences using regular verbs in the pretérito indefinido.
- Tú te comiste todas las frutas de la cocina.
You ate all the fruit in the kitchen. - Vosotros hablasteis en voz alta durante la fiesta.
You all spoke loudly during the party. - Nosotras partimos en autobús a las montañas.
We left on the bus to the mountains.
Now that you are feeling confident with regular verbs in the simple past, we’ll move on to some common irregular verbs and their pretérito indefinido conjugations.
Pretérito indefinido conjugations: Irregular verbs
Irregular verbs are… well, irregular. And this means that their conjugations into the simple past tense don’t follow the general rules observed for regular verbs.
Let’s learn four common verbs that are especially useful to know in the pretérito indefinido: venir (to come), tener (to have), poder (to be able to/can), and ser (to be).
Venir (to come): Pretérito indefinido
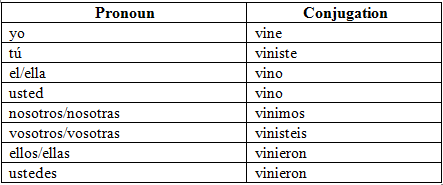
Here are a couple of example sentences for venir in the pretérito indefinido:
- Ayer vine a la fiesta.
Yesterday, I came to the party. - Mis amigos vinieron a visitarme.
My friends came to visit me.
Tener (to have): Pretérito indefinido
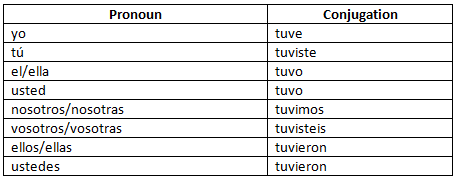
Check out a couple of example sentences for tener in the pretérito indefinido:
- Ayer tuve una reunión importante.
Yesterday, I had an important meeting. - Tuviste mucha suerte en el examen.
You had a lot of luck in the exam.
Poder (to be able to/can): Pretérito indefinido
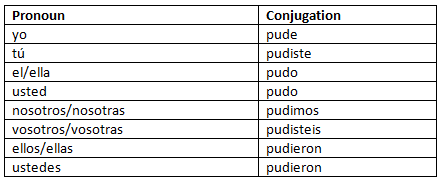
Here are a couple of example sentences for poder in the pretérito indefinido:
- No pude ir al cine ayer.
I couldn't go to the movies yesterday. - Mis padres pudieron ayudarme con el proyecto.
My parents were able to help me with the project.
Pro tip: Did you notice how the endings for venir, tener, and poder were all the same?
Ser (to be): Pretérito indefinido
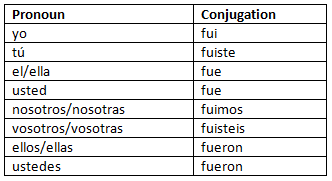
See some example sentences for ser in the pretérito indefinido:
- Yo fui estudiante de medicina.
I was a medical student. - Ustedes fueron los mejores en el equipo.
You were the best on the team.
These four verbs, venir, tener, poder, and ser, are frequently used for telling stories and describing events that occurred in the past.
Because they are irregular, it’s best to memorize them and make sure you practice them as much as possible so that they become natural to you.
Pretérito indefinido vs. pretérito perfecto
While the pretérito indefinido and the pretérito perfecto (simple past) are both used to describe the past, they each have their own specific uses.
We use the pretérito indefinido to describe completed actions in the past and actions that occurred at a specific time and for a specific duration.
In contrast the pretérito perfecto is used for actions that have happened in the recent past, actions that have a connection to the present, and actions where the time in which they occurred is not specified.
Let’s look at some examples of both:
- Juan estudió toda la noche para el examen.
Juan studied all night for the exam.
(pretérito indefinido: past action with a specific duration) - Juan ha estudiado mucho para mejorar su nivel de inglés.
Juan has studied a lot to improve his English.
(pretérito perfecto: happened in the past with results or impact on the present)
On a cultural note, the main past tense used in Spain is the pretérito perfecto, while in Latin America, they tend to use the pretérito indefinido. Of course, this also varies according to region and the speaker’s preference.
If you are unsure about which tense to use, try asking yourself if the event occurred for a specific duration or at a specific time. Also, ask yourself if the action was completed in the past without impact on the present. If so, your best bet is the pretérito indefinido.
Wrapping up
The pretérito indefinido, or simple past, is an incredibly useful tense for storytelling, narrating, or simply conveying actions or events that were completed in the past.
The verbs venir (to come), tener (to have), poder (to be able to/can), and ser (to be) are irregular but commonly used verbs when speaking in the simple past tense. Luckily, venir, tener, and poder share the same verb endings, making them easier to memorize.
|
12 videos|17 docs|11 tests
|
FAQs on All about Past Tense - Spanish: Elementary A2 Level - Class 6
| 1. What is the difference between "pretérito indefinido" and "pretérito perfecto" in Spanish? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of irregular verbs in the "pretérito indefinido" conjugations in Spanish? |  |
| 3. How do you conjugate regular verbs in the "pretérito indefinido" tense in Spanish? |  |
| 4. When should you use the "pretérito indefinido" tense in Spanish? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of using the correct past tense in Spanish when communicating? |  |















