Types of microorganisms | Year 7 Biology (Cambridge) - Class 7 PDF Download
Introduction to Microorganisms
Microorganisms are tiny living beings that consist of one single cell, also known as unicellular organisms. These organisms are so small that they are invisible to the naked eye, which is why we call them microorganisms. Other common names for microorganisms include germs and microbes.

Observing Microorganisms
- To see microorganisms, we need specific instruments like microscopes.
- In ancient times, scientists began to suspect that diseases in humans might be caused by these tiny, invisible organisms.
- This led to the study of microorganisms.
Historical Background
- Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first scientist to observe microorganisms in the 17th century.
- His work with microscopes paved the way for future scientists to explore how diseases are caused and how they can be cured.
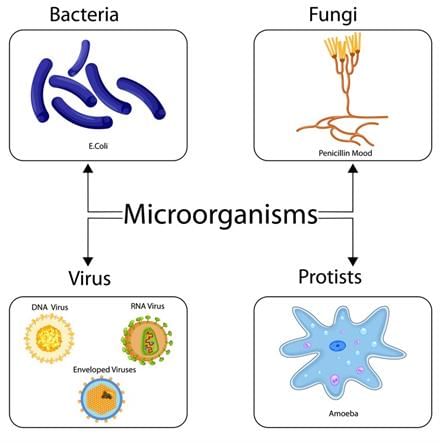
Types of Microorganisms
There are three main types of microorganisms:
Bacteria
- Bacteria are prokaryotic cells, which means they do not have a nucleus. They are found everywhere and can be both beneficial and harmful.
- Examples:
- Beneficial Bacteria: Some bacteria are useful in food fermentation processes, such as making yogurt and cheese.
- Harmful Bacteria: Other bacteria can cause infections. These harmful bacteria can be treated with antibiotics.
Viruses
- Viruses are not considered living beings because they cannot carry out life functions on their own. They need a host, which is a living organism, to survive and reproduce. Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and can even infect bacteria.
- Examples:
- Diseases Caused by Viruses: Some viruses cause diseases like the flu or chickenpox.
- Prevention: Vaccination is important to prevent diseases caused by viruses, although not all viruses have vaccines.
Fungi
- Fungi are generally larger than bacteria and viruses. They can be found in various places such as air, plants, and water.
- Examples:
- Beneficial Fungi: Some fungi, like yeasts, are used to make foods.
- Harmful Fungi: Molds that grow on fruit or bread are also a type of fungi.
Importance of Hygiene
Since microorganisms are present everywhere and are not visible to the naked eye, maintaining good hygiene habits is essential to prevent diseases and infections.
Key Points to Remember
- Microorganisms: Tiny, single-celled organisms invisible to the naked eye.
- Microscopes: Essential tools for observing microorganisms.
- Bacteria: Prokaryotic, can be beneficial or harmful, treated with antibiotics.
- Viruses: Not living, need a host to survive, cause diseases like flu and chickenpox, preventable by vaccines.
- Fungi: Larger than bacteria and viruses, found in air, plants, and water, includes beneficial yeasts and harmful molds.
Examples
- Yogurt and Cheese Production: Beneficial bacteria are used in the fermentation process.
- Flu and Chickenpox: Common diseases caused by viruses.
- Yeasts in Baking: Beneficial fungi used to make bread rise.
- Mold on Bread: A common example of harmful fungi.
Conclusion
Now you know the basics about microorganisms, including how to differentiate between bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Remember to practice good hygiene to stay healthy.
|
7 videos|17 docs|4 tests
|
FAQs on Types of microorganisms - Year 7 Biology (Cambridge) - Class 7
| 1. What are the different types of microorganisms? |  |
| 2. How do microorganisms impact human health? |  |
| 3. What are some common examples of pathogenic microorganisms? |  |
| 4. How do microorganisms play a role in food production? |  |
| 5. Can microorganisms be beneficial for the environment? |  |





















