Year 6 Exam > Year 6 Notes > Year 6 Science > Transport of nutrients and water
Transport of nutrients and water | Year 6 Science PDF Download
Circulatory systems in mammals
- The circulatory system is responsible for transporting water and nutrients throughout an organism's body. While the system varies across different animals, mammals like humans have a distinct circulatory setup.
- Components of the Mammalian Circulatory System
- Heart: The heart acts as the central pump that propels blood throughout the body. It ensures a continuous flow of nutrients and oxygen to all cells.
- Blood Vessels: Blood vessels serve as the network of roads through which blood travels. They transport blood to various parts of the body, ensuring delivery of essential nutrients.
- Blood: Blood carries vital substances such as nutrients (like carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids) that are necessary for sustaining life and maintaining health.
- The mammalian circulatory system operates in a double loop, meaning blood passes through the heart twice in each cycle. This double circulatory system is crucial for mammals because they require substantial energy to survive.
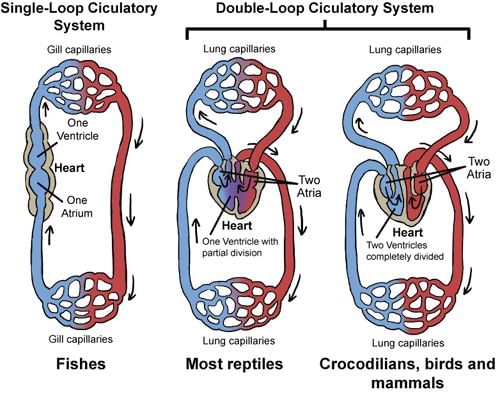
Circulatory System in Fish
- Fish, unlike mammals, have gills as respiratory organs instead of lungs. Oxygen from water diffuses into their blood through these gills.
- Their circulatory system consists of three main parts: heart, gills, and body, although in a different sequence compared to mammals.
- The blood flows through their circulatory system in the following order:
- Heart - Gills - Body
- Within fish, blood follows a single circulatory system, meaning it passes through the heart only once during each circulation loop. This is known as a single circulatory system.
- Similar to mammals, fish have a closed circulatory system where blood remains within blood vessels.
Question for Transport of nutrients and waterTry yourself: Which circulatory system has a double loop where blood passes through the heart twice in each cycle?View Solution
Circulation in Insects
- Insects have a unique circulatory system distinct from mammals and fish.
- They lack lungs or gills for oxygen exchange but instead possess numerous tiny tubes that penetrate their bodies.
- Unlike mammals, they lack a closed network of blood vessels, allowing their blood to flow freely through their organs, known as an open circulatory system.
The document Transport of nutrients and water | Year 6 Science is a part of the Year 6 Course Year 6 Science.
All you need of Year 6 at this link: Year 6
|
11 videos|10 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Transport of nutrients and water - Year 6 Science
| 1. How do nutrients and water get transported in plants? |  |
Ans. Nutrients and water are transported in plants through specialized tissue called xylem and phloem. Xylem carries water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant, while phloem transports nutrients, such as sugars, from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
| 2. What is the role of the roots in nutrient and water transport in plants? |  |
Ans. Roots play a crucial role in absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. They have specialized structures, such as root hairs, that increase the surface area for absorption. Once absorbed, water and nutrients are transported through the xylem tissue to other parts of the plant.
| 3. How does the process of transpiration help in nutrient and water transport in plants? |  |
Ans. Transpiration is the process by which plants lose water through their leaves. This loss of water creates a negative pressure in the xylem, which helps in pulling water and nutrients from the roots to the rest of the plant. Transpiration also helps in cooling the plant and maintaining its shape.
| 4. What factors can affect the transport of nutrients and water in plants? |  |
Ans. Factors such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and soil moisture can affect the rate of nutrient and water transport in plants. For example, high temperatures can increase transpiration rates, leading to faster water uptake by the roots.
| 5. How do plants adapt to different environmental conditions for efficient nutrient and water transport? |  |
Ans. Plants have developed various adaptations to survive in different environmental conditions. For example, desert plants have deep root systems to access water from deep in the soil, while plants in wet environments may have specialized structures to prevent excess water uptake. These adaptations help plants efficiently transport nutrients and water to support their growth and survival.
Related Searches

















