Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge) > Structure, bonding and the properties of matter
Structure, bonding and the properties of matter | Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge) - Class 9 PDF Download
Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are interactions that hold atoms together in molecules or compounds.
There are three main types of chemical bonds:
- Ionic Bonds: Formed between ions of opposite charges. For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is held together by ionic bonds where sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions attract each other.
- Covalent Bonds: Formed by sharing electrons between atoms. For instance, in water (H2O), each hydrogen atom shares electrons with the oxygen atom to form covalent bonds.
- Metallic Bonds: Found in metals where electrons are shared among a lattice of metal atoms, giving metals their unique properties like conductivity and malleability.
Simple and Giant Structures
Materials can have simple or giant structures depending on their atomic arrangement:
- Simple Molecular Structures: Consist of small molecules held together by weak intermolecular forces. Examples include water (H2O) and oxygen (O2), which have low melting and boiling points due to weak intermolecular forces.
- Giant Covalent Structures: Made of large networks of atoms bonded by strong covalent bonds throughout the structure. Examples include diamond (carbon atoms in a tetrahedral lattice) and graphite (layers of carbon atoms in hexagonal rings), which have high melting points due to strong covalent bonds.
- Metallic Structures: Feature a lattice of metal cations surrounded by a 'sea' of delocalized electrons. This structure accounts for properties such as conductivity and ductility in metals.
Question for Structure, bonding and the properties of matterTry yourself: Which type of chemical bond is formed by sharing electrons between atoms?View Solution
Density
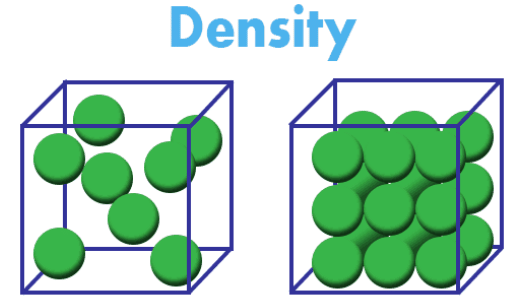
Density is a measure of how tightly packed the particles of a substance are:
- Definition: Density (ρ) is calculated as mass per unit volume
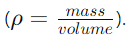
- Effect of Structure: Materials with compact atomic arrangements (e.g., metals) typically have higher densities compared to materials with more open structures (e.g., gases).
- Applications: Density is crucial in various applications such as determining the purity of substances, understanding buoyancy (e.g., why objects float or sink in fluids), and engineering materials with specific properties.
Examples
- Ionic Bond Example: Sodium chloride (NaCl) forms when sodium (Na+) ions and chloride (Cl-) ions attract each other due to their opposite charges.
- Covalent Bond Example: Water (H2O) molecules form when each hydrogen atom shares electrons with the oxygen atom to complete its outer electron shell.
- Giant Covalent Structure Example: Diamond consists of carbon atoms bonded in a tetrahedral lattice structure through strong covalent bonds, resulting in its hardness and high melting point.
- Density Example: Gold has a high density (19.3 g/cm3) due to its tightly packed atomic structure, making it useful in jewelry and electronics.
Question for Structure, bonding and the properties of matterTry yourself: Which type of chemical bond is formed between sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) ions in sodium chloride (NaCl)?View Solution
The document Structure, bonding and the properties of matter | Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge) - Class 9 is a part of the Class 9 Course Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge).
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
9 videos|10 docs|3 tests
|
FAQs on Structure, bonding and the properties of matter - Year 9 Chemistry (Cambridge) - Class 9
| 1. What are the different types of chemical bonds? |  |
Ans. Chemical bonds can be classified into three main types: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers electrons to another atom. Covalent bonds are formed when atoms share electrons. Metallic bonds are formed between metal atoms where electrons are free to move.
| 2. How do simple and giant structures differ in terms of chemical bonds? |  |
Ans. Simple structures have a small number of atoms bonded together, such as in molecules. Giant structures, on the other hand, have a large number of atoms bonded together in a repeating pattern, like in a crystal lattice. The type of bonding present in simple and giant structures can vary, with simple structures typically having covalent or ionic bonds and giant structures often having metallic or covalent bonds.
| 3. How does the structure of a material affect its density? |  |
Ans. The density of a material is influenced by its structure, as the arrangement of atoms or molecules can impact how closely packed they are. Materials with a more compact structure, where atoms are tightly packed together, tend to have higher densities. Conversely, materials with a less dense structure, where atoms are more spread out, have lower densities.
| 4. How do the bonding properties of matter affect its physical and chemical properties? |  |
Ans. The bonding properties of matter play a crucial role in determining its physical and chemical properties. For example, materials with strong covalent bonds tend to have high melting and boiling points, while materials with weak van der Waals forces have lower melting and boiling points. Additionally, the type of bonding can influence a material's conductivity, solubility, and reactivity.
| 5. How can an understanding of chemical bonds help in predicting the properties of different substances? |  |
Ans. By understanding the type of chemical bonds present in a substance, one can predict its properties. For instance, knowing that a substance has ionic bonds can suggest that it will have a high melting point and be soluble in water. Conversely, a substance with metallic bonds may be malleable and conduct electricity well. This knowledge is valuable in fields such as material science and pharmacology.
Related Searches
















