Redundant Link Problems | Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Redundant Links in Networks: Issues and Solutions |

|
| Broadcast Storm |

|
| Multiple Copies |

|
| MAC Table Thrashing |

|
| Solution: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) |

|
Redundant Links in Networks: Issues and Solutions
Redundant links are implemented in networks to ensure continuity and reliability by providing backup paths when a primary link fails. However, these redundant links can introduce several problems. Below are the common issues associated with redundant links:
Broadcast Storm
When a broadcast frame (a message sent to all devices) is transmitted, a switch forwards it to all its ports. In the absence of loop prevention mechanisms, switches will perpetually flood broadcasts throughout the network, consuming all available bandwidth.
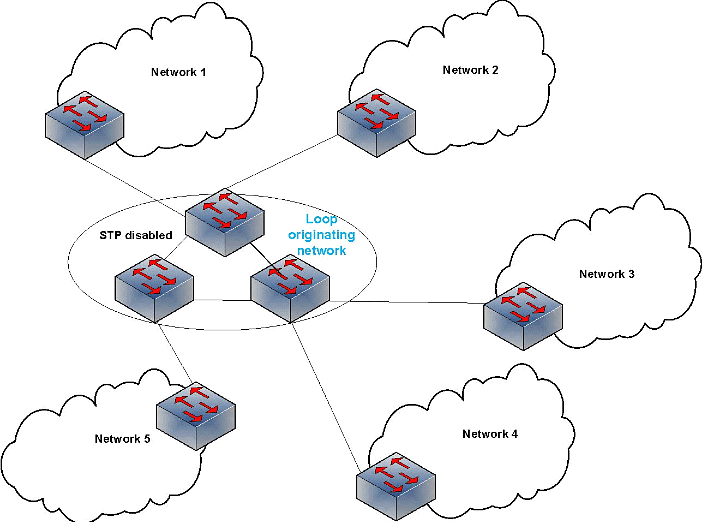
- Impact: A broadcast storm can quickly incapacitate the entire network.
- Example: In a network with three interconnected switches designed for redundancy, if a broadcast is initiated by one device, each switch will forward the broadcast to all its ports. This creates a loop where switches continuously send and receive the broadcast, consuming all bandwidth and potentially shutting down the network.
Multiple Copies
A device can receive multiple copies of the same frame if the frame arrives from different network segments simultaneously.
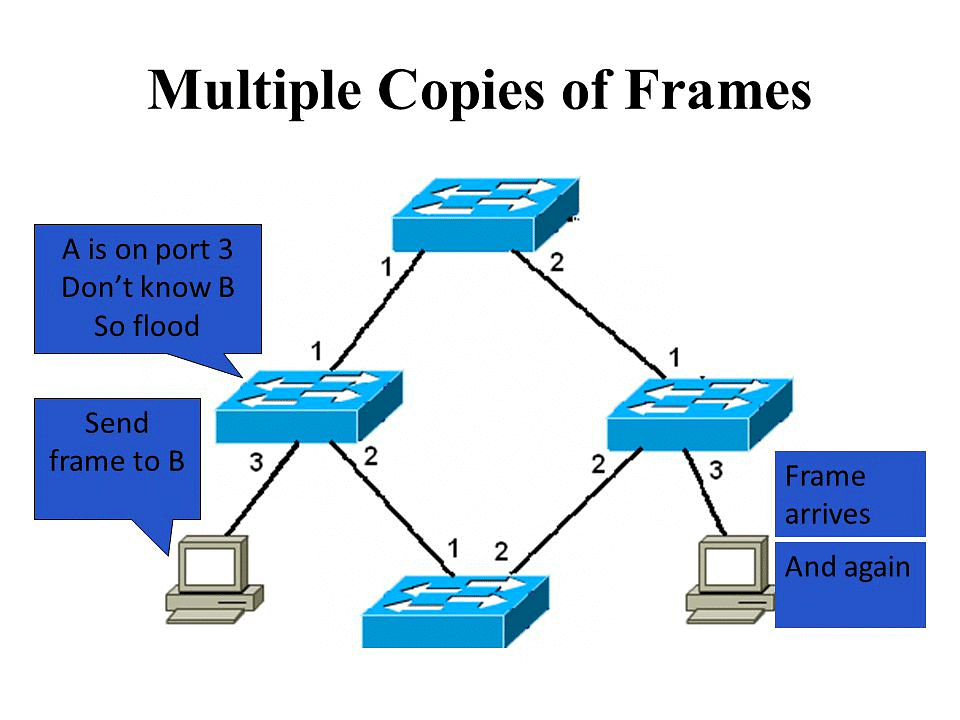
- Impact: Most network protocols are not equipped to handle duplicate transmissions effectively, leading to potential errors.
- Example: In a topology where a router is connected to two switches, if a host sends a unicast frame to the router via one switch, the router may receive the frame directly and through an alternate path involving another switch, resulting in multiple copies of the same frame.
MAC Table Thrashing
Switches maintain MAC address tables to forward frames correctly. When a switch receives frames from the same source through multiple links, it can become confused, leading to instability in the MAC address table.
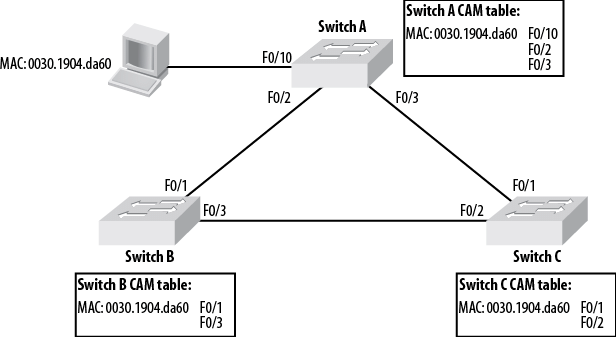
- Impact: Instability in the MAC address table causes unreliable network behavior.
- Example: If a frame from host A is transmitted to host B through multiple switches, each switch may receive the frame on different ports. This confuses the switches and destabilizes their MAC address tables.
Solution: Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
To mitigate these issues, the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is utilized. STP prevents network loops by blocking redundant paths, ensuring only a single active path is used for data transmission at any given time. If the primary path fails, STP dynamically activates a backup path, maintaining network stability and preventing the problems associated with redundant links.
|
21 videos|145 docs|66 tests
|
FAQs on Redundant Link Problems - Computer Networks - Computer Science Engineering (CSE)
| 1. What are redundant links in networks and why are they problematic? |  |
| 2. What is the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and how does it help in resolving redundant link issues? |  |
| 3. How does STP determine which links to block in order to eliminate loops in the network? |  |
| 4. What are the common problems that can arise when redundant links are not properly managed in a network? |  |
| 5. How can network administrators configure and monitor STP to ensure effective management of redundant links in a network? |  |















