Data Types in C | Programming and Data Structures - Computer Science Engineering (CSE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Primitive Data Types in C |

|
| Integer Data Type |

|
| Character Data Type |

|
| Float Data Type |

|
| Double Data Type |

|
Primitive Data Types in C
In C programming, each variable has a data type that defines the type of data it can hold, such as integer, character, float, or double. Different data types use different amounts of memory and support specific operations. A data type is essentially a set of values with defined properties and behaviors.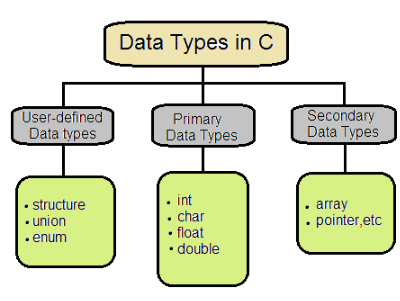
Note: The long, short, signed and unsigned are datatype modifier that can be used with some primitive data types to change the size or length of the datatype.
The following are some main primitive data types in C:
Integer Data Type
The integer datatype in C is used to store the integer numbers(any number including positive, negative and zero without decimal part). Octal values, hexadecimal values, and decimal values can be stored in int data type in C.
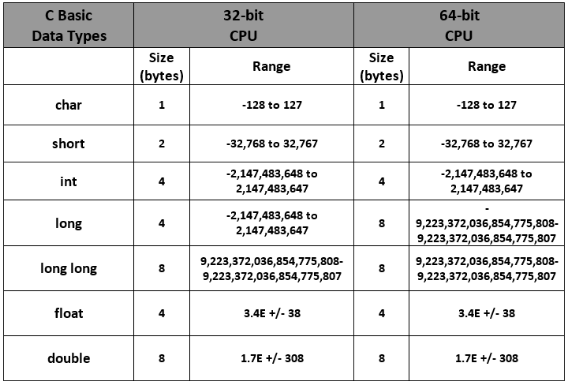
- Range: -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647
- Size: 4 bytes
- Format Specifier: %d
Syntax of Integer
int var_name;
The integer data type can also be used as
- unsigned int: Unsigned int data type in C is used to store the data values from zero to positive numbers but it can’t store negative values like signed int.
- short int: It is lesser in size than the int by 2 bytes so can only store values from -32,768 to 32,767.
- long int: Larger version of the int datatype so can store values greater than int.
- unsigned short int: Similar in relationship with short int as unsigned int with int.
// C program to print Integer data types.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
// Integer value with positive data.
int a = 9;
// Integer value with negative data.
int b = -9;
// Unsigned integer value.
unsigned int c = 89U;
// Long integer value.
long int d = 99998L;
printf("Integer value with positive data: %d\n", a);
printf("Integer value with negative data: %d\n", b);
printf("Integer value with unsigned int data: %u\n", c);
printf("Integer value with long int data: %ld\n", d);
return 0;
}
Output
Integer value with positive data: 9
Integer value with negative data: -9
Integer value with an unsigned int data: 89
Integer value with an long int data: 99998
Character Data Type
Character data type allows its variable to store only a single character. The size of the character is 1 byte. It is the most basic data type in C. It stores a single character and requires a single byte of memory in almost all compilers.
- Range: (-128 to 127) or (0 to 255)
- Size: 1 byte
- Format Specifier: %c
Syntax of char
The char keyword is used to declare the variable of character type:
char var_name;
// C program to print and manipulate character data types.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// Declare a character variable 'a' and assign it the value 'a'.
char a = 'a';
// Declare a character variable 'c' without assigning an initial value.
char c;
// Print the value of 'a'.
printf("Value of a: %c\n", a);
// Increment the value of 'a' by 1. In ASCII, 'a' corresponds to 97, so it becomes 'b' (98).
a++;
printf("Value of a after increment is: %c\n", a);
// Assign the ASCII value 99 to 'c', which corresponds to the character 'c'.
c = 99;
// Print the value of 'c'.
printf("Value of c: %c\n", c);
return 0;
}
Output
Value of a: a
Value of a after increment is: b
Value of c: c
Float Data Type
In C programming float data type is used to store floating-point values. Float in C is used to store decimal and exponential values. It is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point values) with single precision.
- Range: 1.2E-38 to 3.4E+38
- Size: 4 bytes
- Format Specifier: %f
Syntax of float
The float keyword is used to declare the variable as a floating point:
// C Program to demonstrate the use of floating-point types and scientific notation
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
float a = 9.0f; // Declare and initialize 'a' as a float with value 9.0
float b = 2.5f; // Declare and initialize 'b' as a float with value 2.5
// Declare 'c' as a float initialized using scientific notation (2 * 10^-4)
float c = 2E-4f;
// Print the values of 'a', 'b', and 'c'
printf("%f\n", a); // Print 'a' as a floating-point number
printf("%f\n", b); // Print 'b' as a floating-point number
printf("%f", c); // Print 'c' as a floating-point number
return 0;
}
Output
9.000000
2.500000
0.000200
Double Data Type
A double data type in C is used to store decimal numbers (numbers with floating point values) with double precision. It is used to define numeric values which hold numbers with decimal values in C.
The double data type is basically a precision sort of data type that is capable of holding 64 bits of decimal numbers or floating points. Since double has more precision as compared to that float then it is much more obvious that it occupies twice the memory occupied by the floating-point type. It can easily accommodate about 16 to 17 digits after or before a decimal point.
- Range: 1.7E-308 to 1.7E+308
- Size: 8 bytes
- Format Specifier: %lf
Syntax of Double
The variable can be declared as double precision floating point using the double keyword:
double var_name;
// C Program to demonstrate the use of the double data type
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
double a = 123123123.00; // Declare and initialize 'a' as a double with value 123123123.00
double b = 12.293123; // Declare and initialize 'b' as a double with value 12.293123
double c = 2312312312.123123; // Declare and initialize 'c' as a double with value 2312312312.123123
printf("%lf\n", a); // Print the value of 'a' using the %lf format specifier for doubles
printf("%lf\n", b); // Print the value of 'b' using the %lf format specifier
printf("%lf", c); // Print the value of 'c' using the %lf format specifier
return 0;
}
Output
123123123.000000
12.293123
2312312312.123123
|
158 docs|30 tests
|















