Percentage and its applications - Previous Year Questions | Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude for UGC NET PDF Download
Q1: A sum of ₹ 10,000.00 (ten thousand) is invested at rate of interest 8% per annum compounded half yearly. What will be the maturity amount in 1 year? (December 2023)
(a) ₹ 11,248.64
(b) ₹ 10,816.20
(c) ₹ 11,200.00
(d) ₹ 10,108.64
Ans: (a)
Sol: Rate = 8% per annum but compounded half yearly.
1.5 years have 3 parts of half years.
After every 6 months, 4% will be added.
After 6 months = 10,000 + 400 = 10,400
After 1 year = 10,400 + 416 = 10,816
Maturity amount after 1.5 years = 10,816 + 432.64 = 11,248.64
Q2: The population of a village is 11,000. If the number of children increase by 11% and the number of adults increase by 20%, the population becomes 12,660. Find the population of children and adults separately in the village. (June 2023)
(a) 7,000, 4,000
(b) 4,500, 6,500
(c) 6,000, 5,000
(d) 5,500, 5,500
Ans: (c)
Sol: Let the Population of children = X
Then, Population of adult = 11,000 – X
Population of children increasing by 11% and
Population of adults is increasing by 20%
111% of children + 120% of adults = 12,660
(X × 111/100) + (11,000 – X) × 120/100 = 12,660
By solving the above equation X = 6,000
Present Population of children = 6,000
Present Population of adults = 5,000
Rechecking:
6000 + 11% = 6,000 + 660 = 6,660
5000 + 20% = 6,000
Total increased Population = 12,660
Q3: There are fifteen successive percentage discounts given in a series of 2%, 4%, 6%, 8% _____ on an item. After how many such percentage discounts in succession will the effective discount be higher than 50%? (June 2023)
(a) 7th
(b) 10th
(c) 8th
(d) 6th
Ans: (c)
Sol: Let the price be 100
By calculating the successive consecutive discounts -
2% discount
Price = 100 – 2% = 98
4% discount
Price = 98 – 4% = 94.08
6% discount
Price = 94.08 – 6% = 88.44
8% discount
Price = 88.44 – 8% = 81.36
10% discount
Price = 81.36 – 10% = 73.22
12% discount
Price = 73.22 – 12% = 64.43
14% discount
Price = 64.43 – 14% = 55.41
16% discount
Price = 55.41 – 16% = 46.54
Hence, price will become less than 50% after the discount of 16%, and the discount will be more than 50%.
Q4: Salary of a person decreases by 10% every year and his bonus increases by 24% every year. If his salary and bonuses at the end of 2020 were ₹ 8,000 and ₹ 2,500 respectively, find the difference between his total earning in March, 2020 and March 2022. (June 2023)
(a) ₹ 165, increase
(b) ₹ 176, increase
(c) ₹ 180, decrease
(d) ₹ 176, decrease
Ans: (d)
Sol: Salary is decreased by 10%
Bonus is increased by 24%
Salary in 2020 = 8,000
Bonus in 2020 = 2,500
Total monthly income = 10,500
For 2021,
Salary = 8,000 – 10% = 8,000 – 800 = 7,200
Bonus = 2,500 + 24% = 2,500 + 600 = 3,100
For 2022,
Salary = 7,200 – 10% = 7,200 – 720 = 6,480
Bonus = 3,100 + 24% = 3,100 + 744 = 3,844
Total monthly income = 10,324
Difference in total monthly income of March 2020 and March 2022 = 10,500 – 10,324 = 176 (decrease)
Q5: In a competitive examination held in the year 2000, a total of 6,00,000 (6.0 lakh) students appeared and 40% passed the examination. Forty per cent (40%) of the total students were females and the rest were males. The pass percentage among the males was 50%. Find the pass percentage among the females. (March 2023)
(a) 25%
(b) 30%
(c) 35%
(d) 40%
Ans: (a)
Sol: Total students = 6 lakhs
Students passed the examination = (40/100) × 600,000 = 2,40,000
Total female students = (40/100) × 6,00,000 = 2,40,000
Male students = 6,00,000 – 2,40,000 = 3,60,000
Pass percentage among the male students = 50%
Male Students passed = 50% of 3,60,000 = 1,80,000
Number of female students in passed students = total students passed - male students passed
= 2,40,000 – 1,80,000 = 60,000
Pass percentage of female students = (females passed the examination × 100) / total female students
= (60,000 × 100) / 2,40,000 = 25%
Q6: A businessman buys a house for ₹ 9.0 lakhs. He puts the house on rent and keeps 15% of each month’s rent separately for repairs. After paying ₹ 2106 as annual taxes on the rent, he realizes 10% annually on his investment. Find the monthly rent of the house. (March 2023)
(a) ₹ 10,000
(b) ₹ 9,080
(c) ₹ 9,030
(d) ₹ 9,500
Ans: (c)
Sol: Realisation over investment = 10%
Or 10% of 9 lakhs or 90,000 Rs.
Annual tax = 2,106 Rs.
Annual rent = 90,000 + 2,106 + 15% of the rent
If annual rent is 100%,
Here, it can be like - 90,000 + 2106 = 85% of rent
Annual rent = 92,106 × 100/85 = 1,08,360
Or monthly rent = 1,08,360/12 = 9,030
Q7: The selling price of 30 fans is equal to the purchase price of 25 fans. What is the profit or loss in percentage?
(a) 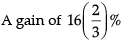
(b) A loss fo 15%
(c) 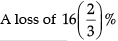
(d) No gain, no loss
Ans: (c)
Sol: Selling price of 30 fans = purchase price of 25 fans (given)
Let the purchase price of one fan = ₹1
Purchase price of 25 fans = ₹25
Purchase price of 30 fans = ₹30
Selling price of 30 fans = ₹25
Loss = CP – SP
= 30 – 25 = 5
Loss in per cent = (5 × 100) / 30 = 16.67% or 16 2/3%
Q8: Given below are two statements:
Statement I: The compound interest on 280 for 18 months at 10% per annum is 44.3.
Statement II: At 5.6% rate of simple interest, a certain sum will be doubled in 15 years
In light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below (November 2021)
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are false
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are true
(c) Statement I is false but Statement II is true
(d) Statement I is true but Statement II is false
Ans: (a)
Sol: Both statements are false.
Interest for principal 280 at the rate of 10% for 18 months:
(As calculating compound interest is quite complicated because of various aspects we can calculate it as follows:)
280 × 10% = 28
Amount after 1 year = 308
Interest for more 6 months 308 × 10 × 6 / (100 × 12) = 15.4
Total interest after 18 months = 28 + 15.4 = 43.4
Thus, statement 1 is incorrect.
For statement 2,
Let the principal 100
Interest for 15 years with 5.6%
100 × 15 × 5.6 / 100 = 84
Amount after 15 years = 100 + 84 = 184 (not doubled)
Thus, statement 2 is also incorrect.
Q9: 63% of employees in a company are female. If the number of male employees is 111, then the total number of employees is (November 2020)
(a) 270
(b) 290
(c) 300
(d) 310
Ans: (c)
Sol: 63% are female which means 37% is male. So, 37% is equal to 111. 100% will be 300.
(A × 37) / 100 = 111
(111 × 100) / 37 = 300
Q10: Average of two numbers a and b is 22 and 60% of a = 50% of b. What is the product of a and b? (December 2019)
(a) 160
(b) 384
(c) 480
(d) 484
Ans: (c)
Sol:
(a + b)/2 = 22
a + b = 22 × 2 = 44,
a = 44 – b, and
a × 60/100 = b × 50/100
3a/5 = b/2
a = b/2 × 5/3 = 5b/6
44 – b = 5b/6
5b/6 + b = 44
b = 24
a = 20
a × b = 480
Q11: Manoj’s commission is 10% of all sales upto ₹ 10,000 and 5% on all sales exceeding this. He remits ₹ 75,500 to his company after deducting his commission. The total sales will come out to be (June 2019)
(a) ₹ 78,000
(b) ₹ 80,000
(c) ₹ 85,000
(d) ₹ 90,000
Ans: (b)
Sol: Total sales = A
Manoj’s commission will be:
10,000 × 10 / 100 = 1,000, and,
(A – 10,000) × 5 / 100 = (A – 10,000) × 0.05 = 0.05A – 500
Hence,
A – 75,500 = 1,000 + 0.05A – 500
A – 0.05A = 1,000 – 500 + 75,500
A – 0.05A = 76,000
A (1 – 0.05) = 76,000
0.95A = 76,000
A = 76,000 / 0.95 = 80,000
Q12: The simple interest on a certain sum of money for 3 years at 4% per annum is half the compound interest on ₹ 2,000 for 2 years at 10% per annum. The sum invested on simple interest is (June 2019)
(a) ₹ 8,750
(b) ₹ 1,750
(c) ₹ 2,500
(d) ₹ 3,500
Ans: (b)
Sol: 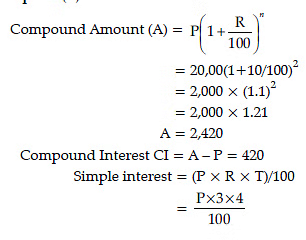
According to the problem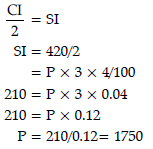
Q13: In a bag, there are coins of 5 ps, 10 ps and 25 ps in the ratio of 3:2:1. If there are ₹ 60 in all, how many 5 ps coins are there? (June 2019)
(a) 100
(b) 200
(c) 300
(d) 400
Ans: (c)
Sol: If total coins = 6A
5 ps coins = 3A × 5 / 100 = ₹ 0.05 × 3A
10 ps coins = 2A × 10 / 100 = ₹ 0.1 × 2A
25 ps coins = 1A × 25 / 100 = ₹ 0.25 × 1A
0.25A + 0.2A + 0.15A = 60
A = 100
Total coins = 600
5 ps coins = 300
Q14: Two numbers are in the ratio 2:5. If 16 is added to both the numbers, their ratio becomes 1:2. The numbers are: (July 2018)
(a) 16, 40
(b) 20, 50
(c) 28, 70
(d) 32, 80
Ans: (d)
Sol:
Q15: Ali buys a glass, a pencil box and a cup and pays ₹ 21 to the shopkeeper. Rakesh buys a cup, two pencil boxes and a glass and pays ₹ 28 to the shopkeeper. Preeti buys two glasses, a cup and two pencil boxes and pays ₹ 35 to the shopkeeper. The cost of 10 cups will be (January 2017)
(a) ₹ 40
(b) ₹ 60
(c) ₹ 80
(d) ₹ 70
Ans: (d)
Sol: Let assume, Price of glass = A
Price of box = B
Price of cup = C
Now putting it in equations,
Equation 1: A + B + C = 21
Equation 2: A + 2B + C = 28
By solving this equation, B = 7
Equation 3: 2A + 2B + C = 35
By putting values of B in Equation 3, we get
2A + C = 21
A = 21 – C/2
Now A and B in Equation 1, we get
21 – C/2 + 7 + C = 21
C (Price of cup) = 7
Hence, price of 10 cups = 70
Q16: A group of 210 students appeared in some test. The mean of 1/3rd of students is found to be 60. The mean of the remaining students is found to be 78. The mean of the whole group will be: (December 2015)
(a) 80
(b) 76
(c) 74
(d) 72
Ans: (d)
Sol: If the mean of all 210 students is A,
A = (1/3 × 210 – 60) + (2/3 × 210 – 78)
A = 72
Q17: At present a person is 4 times older than his son and is 3 years older than his wife. After 3 years the age of the son will be 15 years. The age of the person’s wife after 5 years will be: (June 2015)
(a) 42
(b) 48
(c) 45
(d) 50
Ans: (d)
Sol: Let the age of Son = X. Then as per the question age of his father will be = 4X Age of his mother = 4X – 3.
After 3 years the son will be of 15 years (given)
Current age of the son = 15 – 3 = 12 years
Current age of his father = 12 × 4 = 48 years.
Current age of his mother = 48 – 3 = 45 years.
Age of his mother after 5 years = 45 + 5 = 50 years.
Q18: Two numbers are in the ratio 3 : 5. If 9 is subtracted from the numbers, the ratio becomes 12 : 23. The numbers are (December 2014)
(a) 30, 50
(b) 36, 60
(c) 33, 55
(d) 42, 70
Ans: (c)
Sol: Given that two numbers are in the ratio of 3:5. So, let the numbers be 3x and 5x.
When 9 is subtracted from both the numbers then, numbers will be 3x – 9 and 5x – 9 respectively.
So, according to question,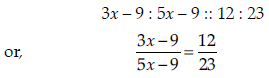
Cross multiplication will result in,
(3x – 9) 23 = (5x – 9)12
or, 69x – 207 = 60x – 108
or, 9x = 99
or, x = 11
So, the numbers will be, 3 × 11 = 33 and 5 × 11 = 55
i.e., option (c).
Q19: In a post-office, stamps of three different denominations of ₹ 7, ₹ 8, ₹ 10 are available. The exact amount for which one cannot buy stamps is (June 2014)
(a) 19
(b) 20
(c) 23
(d) 29
Ans: (a)
Sol: From 20 rs, he can buy two stamps of 10.
From 23 rs, two stamps of ₹7 and one of ₹8 stamps can be brought.
Three stamps of ₹ 8 and one of ₹7 can be bought with 29.
₹19 cannot be used exactly to buy stamps for the given denominations.
₹8 and one of ₹7 can be bought with ₹29.
Q20: The sum of the ages of two persons A and B is 50.5 years ago, the ratio of their ages was 5/3. The present age of A and B are (December 2012)
(a) 30, 20
(b) 35, 15
(c) 38, 12
(d) 40, 10
Ans: (a)
Sol: This answer can be done with the help of options which will be easy and quick in the examination.
Option A (30, 20) has fulfilled all the conditions of the questions.
1. Sum of their ages is 50 (30 + 20 = 50)
2. 5 years ago the ratio of their ages was 5/3 (25:15 or 5:3).
Q21: The price of petrol increases by 25%. By what percentage must a customer reduce the consumption so that the earlier bill on the petrol does not alter ? (June 2012)
(a) 20%
(b) 25%
(c) 30%
(d) 33.33%
Ans: (a)
Sol: Let the price of petrol = 100
Consumption = 100
Expenses = 100 × 100 = 10,000
After change in price
Price of petrol = 125
Consumption = x
Expenses = 10,000 (not changed)
Consumption = 10,000/125 = 80
Change = 20% (decrease)
Q22: The price of oil is increased by 25%. If the expenditure is not allowed to increase, the ratio between the reduction in consumption and the original consumption is (June 2011)
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 1 : 4
(c) 1 : 5
(d) 1 : 6
Ans: (c)
Sol: Let price = 100
Quantity = 100
Expenditure = 100 × 100 = 10,000
If price gets increase by 25%
New price will be = 125
Expenditure = 10,000 (same as before)
Consumption/quantity = 10,000/125 = 80
Reduction in consumption = 20
Original consumption = 100
Ratio = 20:100
Or 1:5
Q23: In an examination, 35% of the total students failed in Hindi, 45% failed in English and 20% in both. The percentage of those who passed in both subjects is (December 2010)
(a) 10
(b) 20
(c) 30
(d) 40
Ans: (d)
Sol: 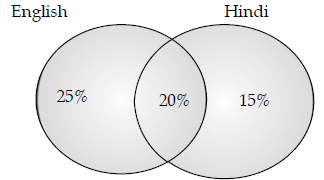
Failed in English = 45%
Failed in Hindi = 35%
Failed in both = 20%
Failed in English excluding common students = 45 – 20 = 25%
Failed in Hindi excluding common students = 35 – 20 = 15%
Total students failed = 15 + 20 + 25 = 60%
Total students passed in all subjects = 100 – 60 = 40%
Q24: When an error of 1% is made in the length of a square, the percentage error in the area of a square will be (June 2010)
(a) 0
(b) 1/2
(c) 1
(d) 2
Ans: (d)
Sol: Let the length of a square = 100
L and B are equal of a square hence, B = 100 Area of square = side × side
Area = 100 ×100 = 10,000
Length by error = 1%
L = 101
New area = 101 × 101 = 10,201
Percentage of error = 201 × 100/10,000
Approx. 2%.
Q25: In a large random data set following normal distribution, the ratio (%) of number of data points which are in the range of (mean ± standard deviation) to the total number of data points, is (December 2009)
(a) ~ 50%
(b) ~ 67%
(c) ~ 97%
(d) ~ 47%
Ans: (b)
Sol: In a normal distribution of a large set of random data, range points in percentage are 67%.
Q26: When an error of 1% is made in the length and breadth of a rectangle, the percentage error (%) in the area of a rectangle will be (December 2009)
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Ans: (c)
Sol: Area of a rectangle= L × B
Error in L and B = 1% each
Let the L= 100
B = 100
L (with error) = 101 (100 + 1) (Since 1% of 100 is 1)
B (with error) = 101
Area = 100 × 100 = 10,000
Area with error = 101 × 101= 10,201
Difference = 201
∴ Difference/error in %= 2 (200 × 100/10,000)
|
46 videos|53 docs|42 tests
|
FAQs on Percentage and its applications - Previous Year Questions - Mathematical Reasoning and Aptitude for UGC NET
| 1. What are some common applications of percentages in real life? |  |
| 2. How can percentages be used in financial planning? |  |
| 3. How are percentages utilized in academic grading systems? |  |
| 4. In what ways are percentages applied in business operations? |  |
| 5. How do percentages assist in understanding population demographics and trends? |  |





















