Evolution of Higher Learning and Research : Previous Years Questions | Higher Education System for UGC NET PDF Download
Q1: The policy on higher education during the eighth five-year plan was to encourage (December 2023)
(a) expansion of public sector.
(b) involvement of private sector.
(c) establishment of foreign campuses.
(d) entry of foreign universities.
Ans: (b)
Sol: After the LPG policy of 1991, the 8th five-year plan was introduced in 1992.
As many weaknesses were identified in the higher education system, this plan encouraged the involvement of the private sector in the education system to ensure quality education and standards. Many public sector schemes were launched, such as the MidDay Meals programme.
Educational goals of other five-year plans are as follows: 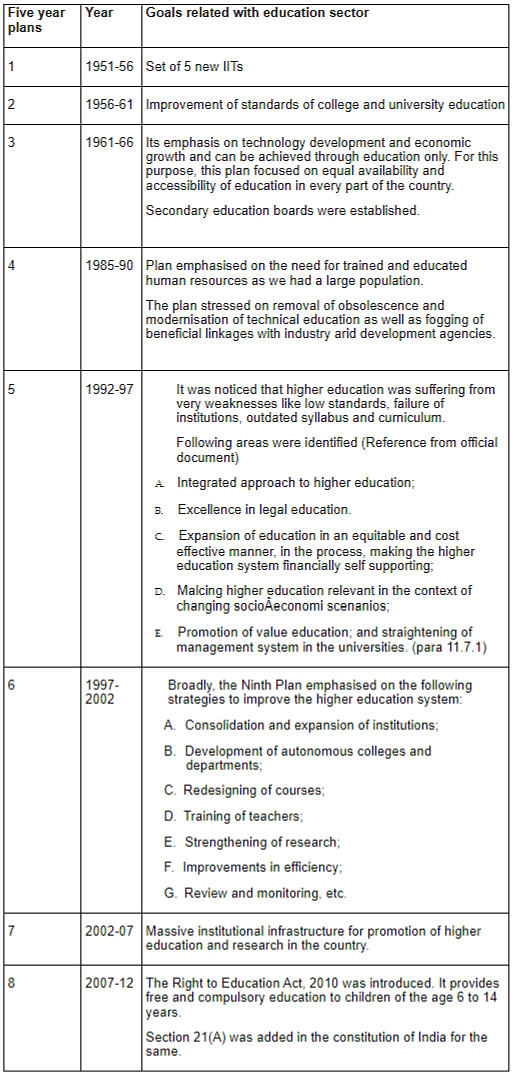
Q2: Which of the following recommendations were put forward by the University Education Commission appointed after independence by the Indian Government concerning medical education in India? Choose the correct answer from the options given below: (March 2023)
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, and 4
Ans: (d)
Sol: Institutions or related organizations like NCERT, NCET, etc., arrange in-service teacher training with adequate resources and at appropriate intervals.
All the given options are key ingredients for quality in-service training of teachers, which includes preparation, execution, evaluation, and assessment.
Q3: Given below are two statements Statement I: The recommendations of the Radhakrishnan Commission in 1949 resemble those of Calcutta University Commission in 1917. Statement II: The recommendations of the Mudaliar Commission in 1953 resemble those of John Sergent’s post-war Educational Development Plan in 1944. In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below (September 2022)
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: (a)
Sol:
- The recommendations of the Radhakrishnan Commission were similar to the Calcutta University commission of 1917.
- The commentation of the Mudaliar commission of 1953 resemble the recommendations of John surgeons post war educational development plan of 1994.
- Radhakrishnan Commission was set up in 1948 which is also known as University Education Commission.
- This is the first educational Commission after independence.
- It suggested various recommendations for Secondary And Higher Education. It was set up by UGC.
- Mudaliar Commission was set up in 1952.
It is also known as Secondary Education Commission.
- It suggested 3 years secondary and 4 years higher education system and multipurpose schools.
- Vocational training, demographic education with individual differences, home science study for girls, were some main recommendations of the commission.
The chairman of Vidyalaya Commission was Laxman Swami Mudaliar.
Q4: In order to transform the regulatory system of Higher Education, the NEP proposes to set up HECI (Higher Education Commission of India). Which of the following are verticals of HECI? Choose the correct answer from the options given below: (November 2021)
(a) A, B and C only
(b) A, C and E only
(c) B, C and E only
(d) C, D and E only
Ans: (b)
Sol:
The Higher Education Commission of India is a result of the New Education Policy of 2020. It is a regulatory body with four verticals:
- NHERC (National Higher Education Regulatory Council)
- GEC (General Education Council)
- HEGC (Higher Education Grant Council)
- NAC (National Accreditation Council)
Q5: CBCS is (November 2021)
(a) Choice Based Credit System
(b) Credit Based Choice Scores
(c) Criteria Based Choice System
(d) Criteria Based Creditable Scores
Ans: (a)
Sol: The Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) allows students to select subjects and fields of their choice, with the following characteristics:
- Choice among various courses and subjects
- Grading system
- Modern education system
- Semester system
- Various aspects for calculating credits
- Inclusion of various subjects in core, elective, and skill categories
Q6: Match List I with List II Choose the correct answer from the options given below: (November 2021)
(a) A - I, B - IV, C - II, D - III
(b) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: (a)
Sol: Indian Institute of Advanced Study (IIAS) - Shimla, Himachal Pradesh
Indian Biological Sciences and Research Institute - Noida, Uttar Pradesh
Indian Institute of Soil Science (IISS) - Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh
Indian Institute of Sugarcane Research - Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh
Q7: A special focus on the problems of the examination system of India formed a part of which one of the following reports? (June 2019)
(a) Report of the Calcutta university commission
(b) Report of the University Education Commission (1964–1966)
(c) Hartog committee report
(d) Report on standards of University education UGC (1965)
Ans: (d)
Sol: The report on standards of university education, published in 1965 by the UGC, aimed to promote and coordinate university education and ensure the standards of teaching, research, and evaluation in universities.
Q8: India has the largest Higher Education System in the World after: Select the correct answer from the code given below: (July 2018)
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 1, 3 and 4
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (d)
Sol: India has the third-largest higher education system in the world, after the US and China.
Q9: The South Asia University is situated in the city of: (December 2023)
(a) Colombo
(b) Dhaka
(c) New Delhi
(d) Kathmandu
Ans: (c)
Sol: South Asia University is situated in New Delhi and is sponsored by the eight member countries of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
Q10: The University Grants Commission was established with which of the following aims? Choose the correct answer from the codes given below: (December 2023)
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 4
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 2 and 4
Ans: (b)
Sol: The University Grants Commission (UGC), established in 1956 by an act, has the following objectives:
- Coordination
- Standardization in higher education institutes
- Providing recognition to universities in India
- Promotion of research and development in higher education in India
- Promotion of quality teachers in higher education institutes
- Capacity building of teachers with research, training, and standardization
- Identifying institutes with a potential learning environment
Q11: The total number of central universities in India in April 2015 was: (December 2023)
(a) 08
(b) 14
(c) 27
(d) 43
Ans: (d)
Sol: The number of central universities in India according to the list published by UGC on 31st March, 2021 is 54. In which Uttar Pradesh has a maximum number of central universities with 6 universities.
Q12: Which of the following institutions are empowered to confer or grant degrees under the UGC Act, 1956? Select the correct answer from the codes given below: (December 2014)
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Sol: A university/institution established by a linguistic minority is not empowered to grant degrees under UGC Act, 1956.
Q13: Which of the following are Central Universities? Select the correct answer from the code given below: (June 2014)
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 2 and 4
Ans: (a)
Sol: Kurukshetra university is a state university of Haryana.
Q14: Which of the following universities has adopted the meta university concept? (June 2014)
(a) Assam University
(b) Delhi University
(c) Hyderabad University
(d) Pondicherry University
Ans: (b)
Sol: Meta university is to create a common educational network among various universities. This concept was widely spread during COVID-19 period. Delhi university is the first university to adopt this concept of higher education.
Q15: Which of the following statements are correct about a Central University? Select the correct answer from the code given below: (June 2014)
(a) 1, 2 and 4
(b) 1, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Sol: Following statements are correct about central universities:
1. Central University is established under an Act of Parliament.
2. The President of India acts as the visitor and chancellor of the University.
3. The President has the power to nominate some members to the Executive Committee or the Board of Management of the University.
Q16: The first virtual university of India came up in (December 2013)
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Tamil Nadu
Ans: (d)
Sol:
- Tamil Virtual University or Tamil Virtual Academy, which was established in 2001, is the first virtual university of India.
- This university is located in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- This is a distance education based academy.
Q17: Which one of the following Councils has been disbanded in 2013? (December 2013)
(a) Distance Education Council (DEC)
(b) National Council for Teacher Education (NCTE)
(c) National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT)
(d) National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC)
Ans: (a)
Sol: The Distance Education council was established in 1985 as a part of UGC. In 2012-13, it was replaced by the Distance Education Bureau. It is based in New Delhi. The organisation was responsible for Open and Distance Education.
Q18: Which of the following is/are a minority institution(s)? Select the correct answer from the code given below: (September 2013)
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 4
(c) 2 only
(d) 4 only
Ans: (d)
Sol: St. Stephens college of Delhi University is a minority college. All others are state universities.
Q19: Which one of the following statements is not correct about the University Grants Commission (UGC)? (June 2013)
(a) It was established in 1956 by an Act of Parliament.
(b) It is tasked with promoting and coordinating higher education.
(c) It receives Plan and Non-Plan funds from the Central Government.
(d) It receives funds from State Governments in respect of State Universities.
Ans: (d)
Sol: The University Grant Commission (UGC) was established in 1956 by an act. This was established with the following objectives:
1. Coordination
2. Standardisation in higher education institutes.
3. Providing recognition to universities in India
4. Promotion of research and development in higher education in India.
5. Promotion of quality teachers in higher education institutes.
6. Capacity building of teachers with research, training and standardisation.
7. Identifying institutes with a potential learning environment.
Q20: India has the highest number of students in colleges after (December 2012)
(a) the U.K.
(b) the U.S.A.
(c) Australia
(d) Canada
Ans: (b)
Sol: India has the highest number of college students followed by China. The USA and Brazil with 37 million university students as per the reports of 2020.
Q21: MC National University of Journalism and Communication is located at (June 2012)
(a) Lucknow
(b) Bhopal
(c) Chennai
(d) Mumbai
Ans: (b)
Sol: MC National University of Journalism and Communication is located in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Is also known as Makhanlal University.
- MC stands for Makhanlal Chaturvedi
- Is named after Makhanlal Chaturvedi who was a freedom fighter, poet and journalist.
- Was established in 1992.
- Is the first university of India for Journalism and Mass communication.
Q22: Indian Institute of Advanced Study is located at (June 2012)
(a) Dharamshala
(b) Shimla
(c) Solan
(d) Chandigarh
Ans: (b)
Sol: Indian Institute of Advanced Study is located in Shimla. It is a research institute founded in 1964.
Q23: Indicate the number of Regional Offices of National Council of Teacher Education. (June 2012)
(a) 04
(b) 05
(c) 06
(d) 08
Ans: (a)
Sol: Teacher Education has four Regional Committees at Jaipur, Bengaluru, Bhubaneswar and Bhopal.
Q24: Indicate the number of Regional Offices of University Grants Commission of India. (December 2011)
(a) 10
(b) 07
(c) 08
(d) 09
Ans: (b)
Sol: There are seven regional offices of the UGC/ Universities Grant Commission. They are:
- Southern eastern regional office (SERO), Hyderabad
- Western regional Office (WRO), Puna
- Central Regional Office, Bhopal
- North eastern regional office, Guwahati.
- Northern Regional College Bureau, Delhi.
- South western regional office, Banglore
- Eastern regional office, kolkata
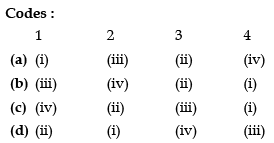
Q25: Match the List-I with the List-II and select the correct answer from the codes given below : (December 2011)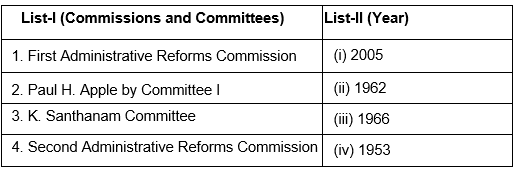
 (a) a
(a) a
(b) b
(c) c
(d) d
Ans: (b)
Sol: First Administrative Reforms Commission:
- Initially headed by Morarji Desai.
- Formed to review and to give suggestions on administration of the government.
- Formed in 1966
Second Administrative Reforms Commission:
- Formed in 2005.
- It submitted 15 reports on various topics such as e-governance, ethics in administration, Right to Information etc.
- Headed by V. Ramchandran K. Santhanam Committee:
- Formed by Lal Bahadur Sharsti
- Anti-corruption committee
- Formed in 1962.
Q26: The first Open University in India was set up in the State of (June 2011)
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Delhi
(c) Himachal Pradesh
(d) Tamil Nadu
Ans: (a)
Sol: First open university:
- Established in Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh.
- Established in 1982.
- Bheem Rao Ambedkar Open University, Hyderabad, A.P.
- Is a state open university. IGNOU is a central open university which was established in 1985 and is located in Delhi.
Q27: Most of the Universities in India are funded by (June 2011)
(a) the Central Government
(b) the State Governments
(c) the University Grants Commission
(d) Private bodies and Individuals
Ans: (c)
Sol: Universities in India are funded as follows:
- Central universities are funded by the central government and have The President of India as chancellor
- State universities are funded by the state government and have the Governor of the state as Chancellor.
- In the private sector, most of the universities get financial support from UGC.
Q28: Which of the following organisations looks after the quality of Technical and Management education in India? (June 2011)
(a) NCTE
(b) MCI
(c) AICTE
(d) CSIR
Ans: (c)
Sol: All India Council for Technical Education or AICTE has the Department of Higher Education as its parent institute. AICTE is responsible for planning and development of technical education in the country. NCTE or National Council for Teachers education is a statutory body for courses of teachers’ education. MCI stands for Medical Council of India.
CSIR stands for Council for Scientific and Industrial Research.
Q29: India’s first Defence University is in the State of (December 2010)
(a) Haryana
(b) Andhra Pradesh
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) Punjab
Ans: (a)
Sol: First defence university in India is in Haryana state at Binola village, Gurugram. The Ministry of Defense, Government of India is the parent institute for this university.
Q30: Most of the Universities in India (December 2010)
(a) conduct teaching and research only
(b) affiliate colleges and conduct examinations
(c) conduct teaching/research and examinations
(d) promote research only
Ans: (c)
Sol: Almost every University in India is engaged in teaching, research work and conducting examinations.
Q31: As per the NCTE norms, what should be the staff strength for a unit of 100 students at B.Ed. level? (June 2010)
(a) 1 + 7
(b) 1 + 9
(c) 1 + 10
(d) 1 + 5
Ans: (c)
Sol: National Council for Teachers’ education or NCTE has decided the staff strength for every teacher’s educational course. For a unit of 100 students at b.ed level, this strength of staff is 1+10 where 1 principal and 10 faculty members are included.
Q32: The accreditation process by National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) differs from that of National Board of Accreditation (NBA) in terms of: (June 2010)
(a) Disciplines covered by both being the same, there is duplication of efforts.
(b) One has institutional grading approach and the other has programme grading approach.
(c) Once get accredited by NBA or NAAC, the institution is free from renewal of grading, which is not a progressive decision.
(d) This accreditation amounts to approval of minimum standards in the quality of education in the institution concerned.
Ans: (c)
Sol: One has institutional grading approach whereas the other has programme grading approach.
NAAC or National Assessment and Accreditation Council has an approach of grading the institute engaged in higher education on the basis of administrative, educational, growth like aspects.
NBA or National Board of Accreditation grades the programmes in the institutes.
Q33: Which option is not correct? (June 2010)
(a) Most of the educational institutions of National repute in scientific and technical sphere fall under 64th entry of Union list.
(b) Education, in general, is the subject of concurrent list since 42nd Constitutional Amendment Act 1976.
(c) Central Advisory Board on Education (CABE) was first established in 1920.
(d) India had implemented the right to Free and Compulsory Primary Education in 2002 through 86th Constitutional Amendment.
Ans: (c)
Sol: India had implemented the right to free and compulsory education in 2002 through 86th amendment.
Right to education was added in fundamental rights under section 21-A in 2002 through 86th amendment but it was finally implemented in 2009 and enforced from the session of 2010.
Under this right, every child of age between 6 to 14 has a right to get free and compulsory education.
For this, a fundamental duty was also added that every parent who has child of this age should provide education to their child.
Q34: Who has signed an MOU for Accreditation of Teacher Education Institutions in India? (December 2009)
(a) NAAC and UGC
(b) NCTE and NAAC
(c) UGC and NCTE
(d) NCTE and IGNOU
Ans: (b)
Sol: NCTE (National Council for Teachers’ education) and NAAC (National Assessment and Accreditation Council) had signed a MOU (Memorandum of Understanding) for the assessment of institutes engaged in teachers’ education. This accreditation is for every five years.
Q35: The recommendation of National Knowledge Commission for the establishment of 1500 Universities is to: (December 2009)
(a) create more teaching jobs
(b) ensure increase in student enrolment in higher education
(c) replace or substitute the privately managed higher education institutions by public institutions
(d) enable increased movement of students from rural areas to urban areas
Ans: (b)
Sol: National Knowledge Commission was a think tank established by The Government of India to improve the education system of the country in 2005. It gave a recommendation to establish 1500 more universities by 2015 and to improve the enrollment ratio in higher education. Other facts about the commission were as follows:
- It submitted its recommendations in three years.
- The report of the commission had 27 focus areas.
- Chairman- Mr. Sam Pitroda
- This commission was established by Dr. Manmohan Singh.
- It had eight members including the chairman. All the members were part time occupied for the commission and were not getting any remuneration.
Q36: The enrolment in higher education in India is contributed both by Formal System of Education and by System of Distance Education. Distance education contributes: (December 2009)
(a) 50% of formal system
(b) 25% of formal system
(c) 10% of the formal system
(d) Distance education system’s contribution is not taken into account while considering the figures of enrolment in higher education
Ans: (b)
Sol: The contribution of distance education in enrollment in higher education of India is 25% of total enrollments whereas total enrollment ratio in higher education is 22%.
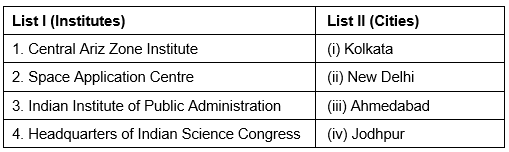
Q37: Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below
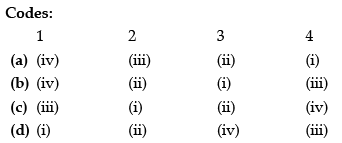
(a) a
(b) b
(c) c
(d) d
Ans: (a)
Sol: Central Arid Zone institute- Jodhpur, Space Application center - Ahmedabad, Indian Institute of Public Administration - New Delhi, Headquarters of Indian Science Congress- Kolkata.
Q38: The Kothari Commission’s report was entitled on :
(a) Education and National Development
(b) Learning to be adventure
(c) Diversification of Education
(d) Education and socialisation in democracy
Ans: (d)
Sol: The Kothari commission was formed in 1964 and it submitted its report in 1966 which was entitled as Shiksha Avam Rastriya Vikas or Education and National Development.
39. Which of the following is not a Dualmode University?
(a) Delhi University
(b) Bangalore University
(c) Madras University
(d) Indira Gandhi National Open University
Ans: (d)
Sol: IGNOU or Indira Gandhi National Open University is not a dual mode university. Dual mode university refers to the university which provides
|
33 videos|15 docs|6 tests
|
FAQs on Evolution of Higher Learning and Research : Previous Years Questions - Higher Education System for UGC NET
Ans. Higher learning and research play a crucial role in advancing knowledge, fostering innovation, and preparing individuals for specialized careers in various fields.
2. How has the evolution of higher learning and research impacted society?$#
Ans. The evolution of higher learning and research has led to significant advancements in technology, healthcare, and other industries, contributing to overall societal progress and development.
3. What are some key challenges faced by institutions involved in higher learning and research?$#
Ans. Some key challenges include securing funding for research projects, attracting and retaining top talent, and keeping up with rapidly changing technologies and methodologies.
4. How can individuals benefit from participating in higher learning and research programs?$#
Ans. Individuals can gain specialized knowledge and skills, enhance their career prospects, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields through participation in higher learning and research programs.
5. How can policymakers support and promote higher learning and research initiatives?$#
Ans. Policymakers can support higher learning and research by providing adequate funding, creating conducive research environments, and promoting collaboration between academia, industry, and government agencies.




















