Notes: Earth and Its Environment | GK Olympiad for Class 3 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Earth's Features |

|
| Atmosphere and Composition of Air |

|
| Our Environment |

|
| Gemstones and Rocks |

|
| Pollution |

|
| Natural Disasters |

|
Earth's Features
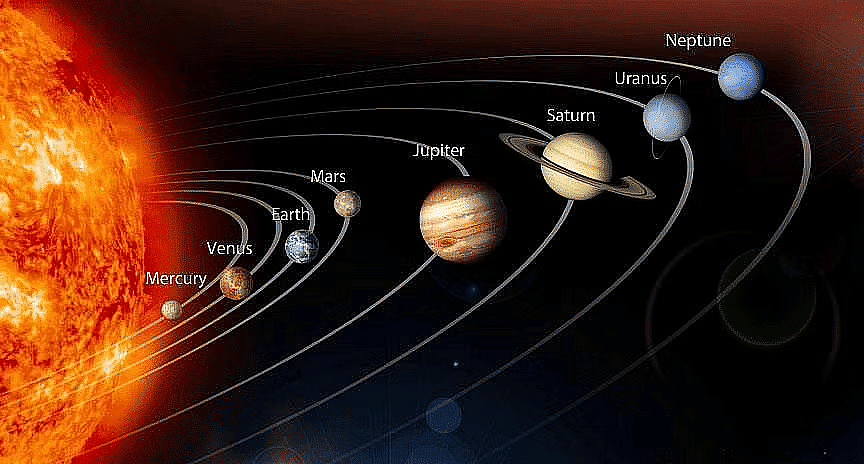
Solar System
- Our solar system consists of the sun, eight planets and their moon.
- The eight planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
- All eight planets revolve around the sun.
The Earth
- The earth was formed from a giant cloud of dust and gas.
- It is the third planet from the sun.
- It is the fifth largest of the eight planets in the solar system.

- Earth is the only planet that has life on it.
- It consists of land, water and air. Approximately two-third of the earth is covered with water and the rest is land.
- The earth is surrounded by a layer of air called the atmosphere.
- The earth has no light of its own.
Shape Of The Earth
The earth seems to be flat. However, the shape of the earth is spherical with flat poles and a slight bulge in the middle like an orange. Evidences which show that earth is spherical in shape are –
- When the shadow of the earth falls on the moon, it is called the eclipse of the moon. This shadow is round in shape. This shows that the earth is spherical in shape.
- When we observe a ship in the sea, we first see the top part of the ship and gradually the rest comes into view.
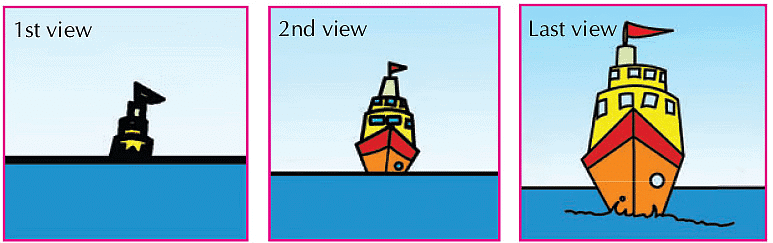 Viewing of ship
Viewing of ship
- Photographs of the earth taken by astronauts from space have also shown that the earth is spherical in shape.
Movement Of The Earth

1. Rotation of the earth
- The earth moves round and round just like a top.
- It spins about an imaginary line passing through its centre called its axis.
- The spinning of the earth on its own axis is called rotation.
- The earth rotates from West to East and completes one rotation in 24 hours.
- Rotation of the earth results in day and night.
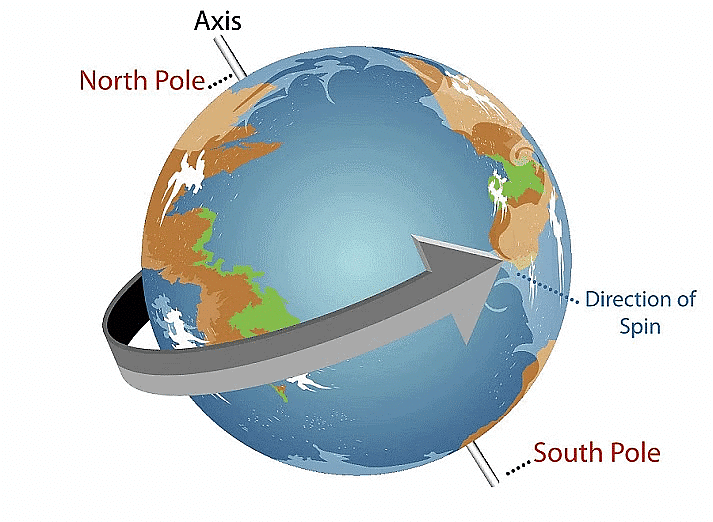
Formation of day and night
- The earth rotates from West to East.
- Half of the earth always faces the sun.
- The part of the earth which faces the sun experiences day.
- The other half which does not get light from the sun experiences night.
2. Revolution of the earth
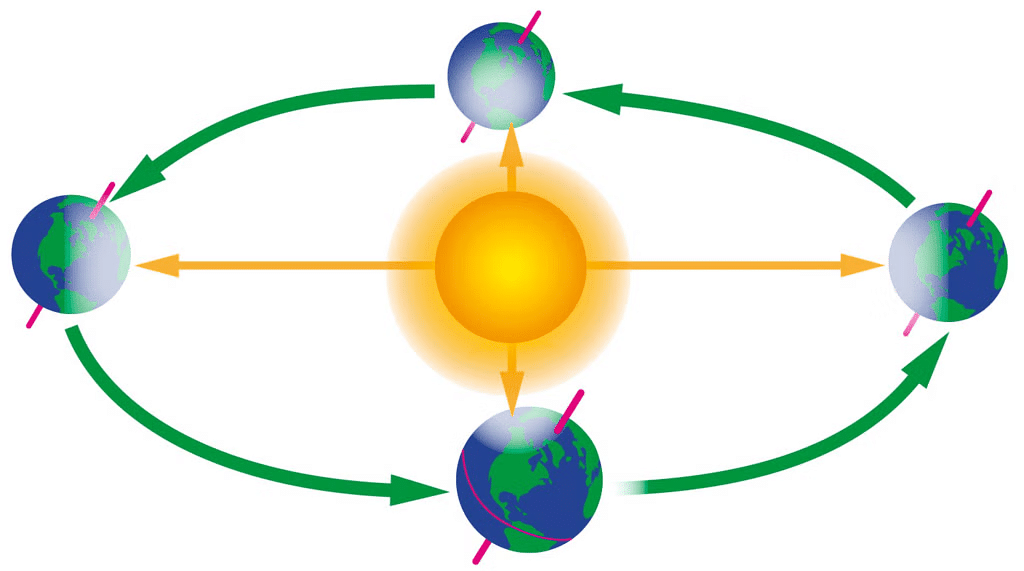
- The earth goes around the sun on a fixed path called an orbit.
- This movement of the earth around the sun is called revolution.
- The earth completes one revolution around the sun in 365¼ days (one year).
- The revolution of the earth causes the change in seasons.
Atmosphere and Composition of Air
Introduction
Imagine the atmosphere as a big, invisible blanket wrapped around our Earth. This blanket is made up of different gases that protect us and help life exist on our planet. Let's dive into the wonderful world of the atmosphere and learn what it's made of!
What is the Atmosphere?
The atmosphere is a thick layer of air that surrounds the Earth. It stretches from the ground up to the sky and is divided into different layers. These layers protect us from the sun's harmful rays, keep our planet warm, and provide the air we breathe.
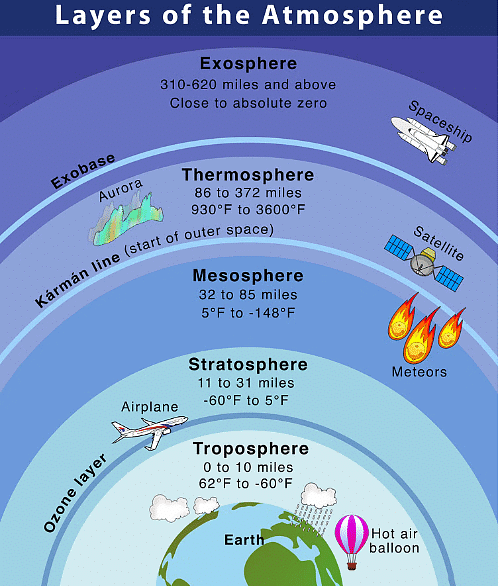
Layers of the Atmosphere
- Troposphere: This is the closest layer to the Earth's surface and where all weather happens. It’s where we live and breathe.
- Stratosphere: Above the troposphere, this layer contains the ozone layer, which protects us from the sun's harmful ultraviolet rays.
- Mesosphere: This layer is where meteors burn up when they enter the Earth's atmosphere.
- Thermosphere: In this layer, the temperature gets very high, and it contains the ionosphere, which helps in radio communication.
- Exosphere: This is the outermost layer, where the atmosphere merges into space.
Composition of Air
The air in the atmosphere is a mixture of different gases. Let’s see what makes up the air we breathe!
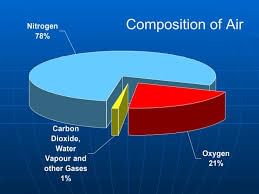
- Nitrogen (78%): Most of the air is made of nitrogen. It doesn’t support burning but is important for plant growth.
- Oxygen (21%): This gas is essential for breathing and burning. We need oxygen to live!
- Carbon Dioxide (0.04%): Plants use carbon dioxide to make their food through photosynthesis. It is also released when we breathe out.
- Water Vapor: This is water in the form of gas. It’s responsible for clouds, rain, and humidity.
- Other Gases: There are tiny amounts of other gases like argon, neon, helium, and methane.
Why the Atmosphere is Important
- Breathing: The atmosphere provides the oxygen we need to breathe.
- Weather: It holds water vapor, which forms clouds and brings rain.
- Protection: The atmosphere protects us from the sun's harmful rays and keeps our planet warm.
Fun Facts
- Bubbles in Water: When you boil water, bubbles form and rise. These bubbles are air that was dissolved in the water.
- Invisible Air: Air is colorless and invisible, which is why we can't see it but can feel it when the wind blows.
- Life Everywhere: Even soil and water have air in them, helping plants and animals live.
Our Environment
The natural surroundings in which living things live is called the environment.
The environment includes soil, water, air, plants, animals and other living things.
- Animals and plants are living. They are known as the living components or biotic components of the environment.
- Air, water, soil and sunshine are non-living. They are known as the non-living components or abiotic components of the environment.
- Both living and non-living things depend on each other in an environment. This kind of dependence is called interdependence.
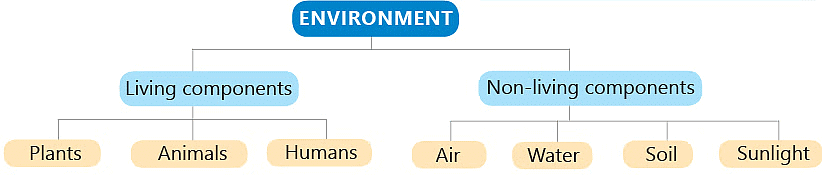
Dependence Of Living Components On Non-Living Component
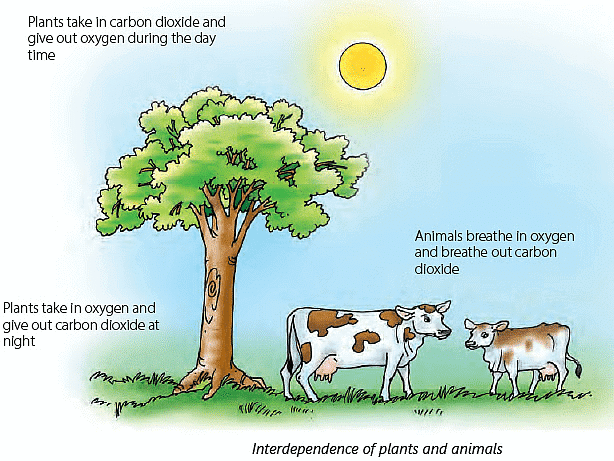
Air- All living organisms use oxygen present in the air to breathe.
- Plants also need carbon dioxide from air to make food.
Water
- Water is important for both plants and animals. Animals drink water. Plants absorb minerals dissolved in water through their roots. They also need water to prepare food.
- Our body is made up of 70% of water. Blood, a flowing liquid present in our body is also made up of nearly 90% of water.
Soil
- Plants need soil to grow. Fertile soil supports a rich variety of plants. Plants get water and minerals from the soil. Soil also provides them support.
- Soil provides shelter to animals such as rabbits, ants, earthworms and centipedes.
Heat and Light
- Plants need the energy of sun to make food. Sunlight also provides warmth for the survival of plants and animals.
- There would be no food or oxygen in the air if there was no sunlight. The heat from the sun keeps the Earth warm.
Interdependence Between Living Components Of Environment
Some ways in which living things depend on each other are as follows:
Animals (including humans) Depend on Plants
- Animals are dependent on plants for food, oxygen and shelter.
- Herbivorous animals such as goat, cow and deer directly depend on plants for food. Carnivorous animals get their food by eating other animals. Therefore, they also indirectly depend on plants for food.
- Many animals live in trees. Birds build nest on trees to lay their eggs.
Plants Depend on Animals
- Plants depend on animals for carbon dioxide that animals give out during breathing.
- Plants depend on animals for providing nutrients in the soil. Animal wastes as well as their dead bodies provide nutrients to the soil.
- Birds and animals like squirrels eat fruits and throw away seeds. This helps plants to reproduce.
- Insects and birds suck nectar (a sweet liquid) from flowers and helps in producing fruits by the plants.
Gemstones and Rocks
Imagine you are on a treasure hunt and you find shiny, colorful stones and big, strong rocks. These treasures are called gemstones and rocks. Let’s explore this exciting world and learn more about them!
What Are Rocks?
Rocks are solid pieces of the Earth. They are made up of minerals and come in many shapes, sizes, and colors. Rocks can be found everywhere - in mountains, rivers, and even in your backyard!
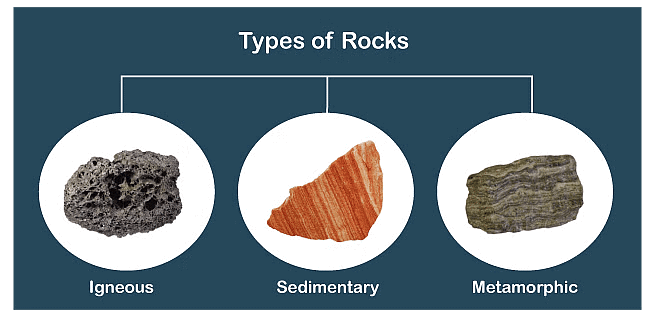
Types of Rocks
Igneous Rocks:
- How They Form: These rocks form when hot, melted rock from a volcano cools and hardens.
- Examples: Basalt, granite.
- Fun Fact: Granite is used to make kitchen countertops because it’s very strong!
Sedimentary Rocks:
- How They Form: These rocks form from tiny pieces of other rocks and plants that are pressed together over time.
- Examples: Sandstone, limestone.
- Fun Fact: Sandstone can feel like sandpaper because it’s made of tiny sand grains.
Metamorphic Rocks:
- How They Form: These rocks form when other rocks are changed by heat and pressure inside the Earth.
- Examples: Marble, slate.
- Fun Fact: Marble is often used in sculptures and buildings because it looks beautiful and can be polished.
What Are Gemstones?
Gemstones are special minerals that are rare, shiny, and beautiful. They are often cut and polished to make jewelry like rings and necklaces.
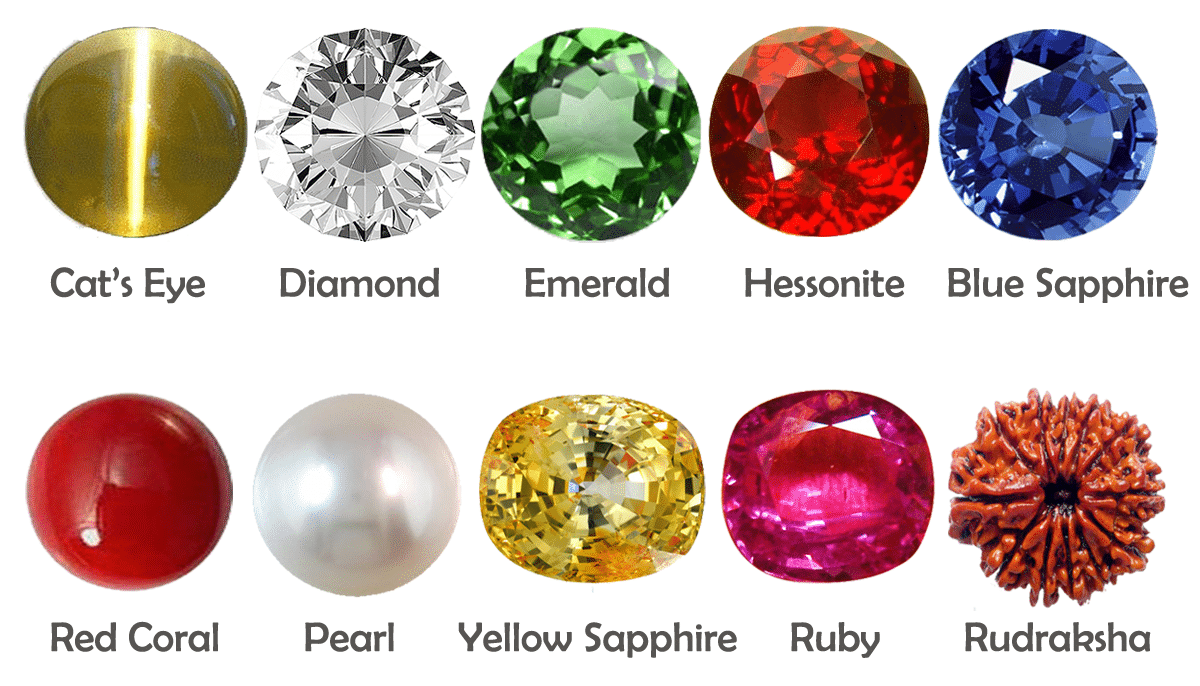

Types of Gemstones
Diamonds:
- Look: Clear and sparkly.
- Fun Fact: Diamonds are the hardest natural substance on Earth. They can cut through glass!
Rubies:
- Look: Bright red.
- Fun Fact: Rubies are very precious and symbolize love and passion.
Emeralds:
- Look: Deep green.
- Fun Fact: Emeralds are said to bring good luck and are often used in royal jewelry.
Sapphires:
- Look: Blue, but can also be other colors.
- Fun Fact: Sapphires are believed to protect wearers from harm and envy.
Amethysts:
- Look: Purple.
- Fun Fact: Amethysts were believed to keep people clear-headed and quick-witted in ancient times.
Why Are Rocks and Gemstones Important?
- Building: Rocks like granite and marble are used to build houses and buildings.
- Jewelry: Gemstones are used to make beautiful jewelry.
- Everyday Uses: Many rocks and minerals are used in everyday items like salt (from halite) and pencils (from graphite).
Pollution
What is Pollution?
Pollution is when harmful things are added to our environment, making it dirty and unsafe for living things. This can happen to the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the land we live on.
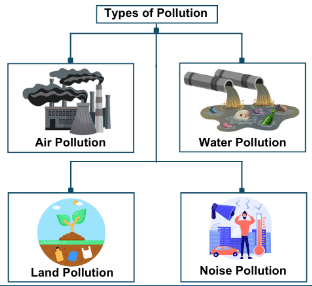
Types of Pollution
Air Pollution:
- Definition: Air pollution happens when harmful substances like smoke, dust, and gases mix with the air, making it dirty.
- Examples: Smoke from cars, factories, and burning trash. Also, dust and chemicals from construction sites.
- Why it's bad: It makes it hard to breathe and can cause health problems like coughing and asthma. It also harms animals and plants.
Water Pollution:
- Definition: Water pollution occurs when harmful substances like chemicals, trash, and waste get into rivers, lakes, and oceans.
- Examples: Oil spills, plastic bottles in rivers, and sewage from factories.
- Why it's bad: It harms fish and other animals that live in the water, and it makes the water unsafe to drink or swim in.
Land Pollution:
- Definition: Land pollution is the result of trash and harmful chemicals being dumped on the ground.
- Examples: Littering, dumping industrial waste, and using too many pesticides on crops.
- Why it's bad: It makes the land dirty and unsafe for plants, animals, and people. It can also contaminate the soil and water.
How We Can Help
- Recycle: Recycle paper, plastic, and glass to reduce waste.
- Plant Trees: Trees clean the air and provide oxygen.
- Pick Up Litter: Keep our surroundings clean by picking up trash.
Natural Disasters
What are Natural Disasters?
Natural disasters are sudden events caused by nature that can cause damage and harm to people, animals, and the environment.

Types of Natural Disasters
Earthquakes:
- Definition: Earthquakes happen when there is a sudden shaking of the ground caused by movements in the Earth's crust.
- Examples: Buildings shaking, roads cracking, and sometimes causing landslides.
- Fun Fact: Earthquakes can cause big cracks in the ground and sometimes trigger tsunamis.
Floods:
- Definition: Floods occur when there is too much water in places that are usually dry.
- Examples: Heavy rain causing rivers to overflow and cover roads and houses, and flash floods from sudden downpours.
- Fun Fact: While floods can be dangerous, they also bring nutrients to the soil, helping plants grow.
Tornadoes:
- Definition: Tornadoes are powerful, spinning columns of air that touch the ground.
- Examples: A tornado can pick up objects, uproot trees, and damage buildings.
- Fun Fact: Tornadoes look like giant funnels coming down from the sky and can spin at over 300 miles per hour.
Hurricanes:
- Definition: Hurricanes are huge storms with strong winds and heavy rain that form over the ocean.
- Examples: Hurricanes can cause big waves, heavy rain, and strong winds that damage buildings and trees.
- Fun Fact: Hurricanes have a calm center called the "eye," where the weather is peaceful.
Volcanoes:
- Definition: Volcanoes are mountains that erupt with lava, ash, and gases from inside the Earth.
- Examples: Hot lava flowing down the side of a volcano and ash clouds filling the sky.
- Fun Fact: Volcanoes can create new land when the lava cools and hardens, and volcanic soil is very fertile for growing plants.
How to Stay Safe
- Earthquakes: Drop, cover, and hold on to protect yourself from falling objects.
- Floods: Move to higher ground to avoid rising water.
- Tornadoes: Find a safe room or basement to stay safe from strong winds.
- Hurricanes: Stay indoors and away from windows; follow evacuation orders if needed.
- Volcanoes: Stay indoors to avoid ash and wear masks to protect your lungs.
|
44 videos|31 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Earth and Its Environment - GK Olympiad for Class 3
| 1. What is the composition of Earth's atmosphere? |  |
| 2. How do gemstones and rocks contribute to Earth's features? |  |
| 3. How does pollution impact Earth's environment? |  |
| 4. What are some examples of natural disasters that can occur on Earth? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to understand Earth's features and environment? |  |




















