Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Notes > Engineering Hydrology > Infiltration - 1
Infiltration - 1 | Engineering Hydrology - Civil Engineering (CE) PDF Download
Introduction
Infiltration is the process by which water enters the soil from sources such as rainfall or irrigation. Soil water movement, or percolation, refers to the flow of water from one location to another within the soil. The infiltration rate is the speed at which water penetrates the soil during a storm, and it must be equal to the infiltration capacity or the rainfall rate, whichever is lower. Infiltration capacity is the maximum rate at which a soil can absorb water under given conditions.
Factors Influencing Infiltration Rates
- Land Surface Condition: Infiltration rates can vary significantly and are influenced by the condition of the land surface, such as whether it is cracked, crusted, or compacted. These conditions affect how easily water can enter the soil.
- Vegetation Cover: The presence of vegetation cover helps protect the soil surface. In contrast, bare soil can lead to the formation of a surface crust due to the impact of raindrops or other factors, which break down the soil structure and move soil fines into surface or near-surface pores. This crust formation impedes infiltration.
- Surface Soil Characteristics: Surface soil characteristics, including grain size and gradation, play a crucial role in determining the infiltration rate.
- Storm Characteristics: Storm characteristics, such as intensity, duration, and magnitude, significantly influence infiltration rates.
- Temperature: The temperature of the surface soil and water can also affect infiltration rates.
- Chemical Properties: The chemical properties of both the water and soil are important factors in determining infiltration rates.
Surface and Soil Factors
- Surface Factors: Surface factors affect the movement of water through the air-soil interface. Protective cover materials shield the soil surface, whereas bare soil can lead to the formation of a surface crust, which impedes infiltration. For example, removing surface cover (such as straw or burlap) can reduce the steady-state infiltration rate from approximately 3 to 4 cm/hr to less than 1 cm/hr.
- Soil Properties: Soil properties that affect water movement include hydraulic conductivity, which measures the soil’s ability to transmit water, and water-retention characteristics, which describe the soil's ability to store and release water. These properties are closely related to soil physical properties.
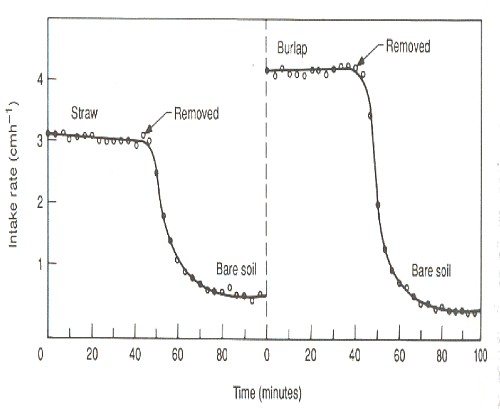 Effect of covered and bare soil on infiltration rates
Effect of covered and bare soil on infiltration rates
Soil Physical Properties
- Particle Size Properties: Particle size properties are determined by the size distribution of individual particles in a soil sample. Soil particles smaller than 2 mm are categorized into sand, silt, and clay texture groups.
- Morphological Properties: Morphological properties that most affect soil water properties include bulk density, organic matter, and clay type. Bulk density is defined as the ratio of the dry solid weight to the soil bulk volume, which includes both the volume of the solids and the pore space. These properties are closely related to soil structure and soil surface area.
- Impact of Natural and Human Activities: Natural processes like soil erosion and human activities such as tillage, overgrazing, and deforestation can alter soil surface configurations, impacting infiltration rates.
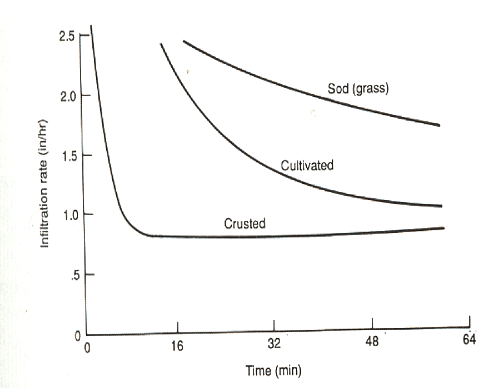 Effect of surface sealing and crusting on infiltration rates
Effect of surface sealing and crusting on infiltration rates
The document Infiltration - 1 | Engineering Hydrology - Civil Engineering (CE) is a part of the Civil Engineering (CE) Course Engineering Hydrology.
All you need of Civil Engineering (CE) at this link: Civil Engineering (CE)
|
20 videos|53 docs|30 tests
|
Related Searches
















