Grassroots Democracy — Part 3: Local Government in Urban Areas NCERT Solutions | Social Studies for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| The Big Questions |

|
| Let's Explore |

|
| Think About It |

|
| Questions, Activities and Projects |

|
| Page 181-182 |

|
The Big Questions
Q1: What are urban local bodies and what are their functions?
Ans: Urban local bodies are decentralized structures of governance in cities and towns. They include Municipal Corporations, Municipal Councils, and Nagar Panchayats. Their functions include infrastructure maintenance, garbage collection and disposal, health services, education, implementation of government schemes, and economic and social development planning.
Q2: Why are they important in governance and democracy?
Ans: Urban local bodies are important because they bring governance closer to the people in urban areas, allowing for more direct participation in decision-making. They ensure that local needs and issues are addressed efficiently and effectively, thereby promoting better quality of life and local development.
Let's Explore
Page 174
Q1: Why is a city like Kolkata, Chennai or Mumbai more complex and diverse than a village or a town?
Ans: Cities like Kolkata, Chennai, or Mumbai are more complex and diverse than villages or towns due to their larger populations, varied economic activities, and cultural diversity. These cities are hubs of commerce, industry, and education, attracting people from different regions, backgrounds, and cultures. This influx creates a multicultural environment with various languages, customs, and lifestyles coexisting. The complexity also arises from the need to manage more intricate infrastructure, services, and governance systems to cater to the diverse and dense population, making urban governance more challenging than in smaller, more homogenous rural areas.
Q2: With your classmates, make a list of diverse communities residing in any city that you are familiar with. How many were you able to list? What else do you observe in the list?
Ans: When making a list of diverse communities in a familiar city, we should observe communities based on ethnicity, religion, language or region of origin. For example, in a city like Mumbai, I might list communities such as Maharashtrians, Gujaratis, South Indians, North Indians, Parsis, and Muslims. Upon observing this list, it becomes evident that each community contributes to the city's cultural richness, bringing unique festivals, cuisines, and traditions. Additionally, I may notice that despite the diversity, these communities interact and coexist, reflecting the city's inclusive nature and the blend of modernity with traditional values.
Page 175
Q: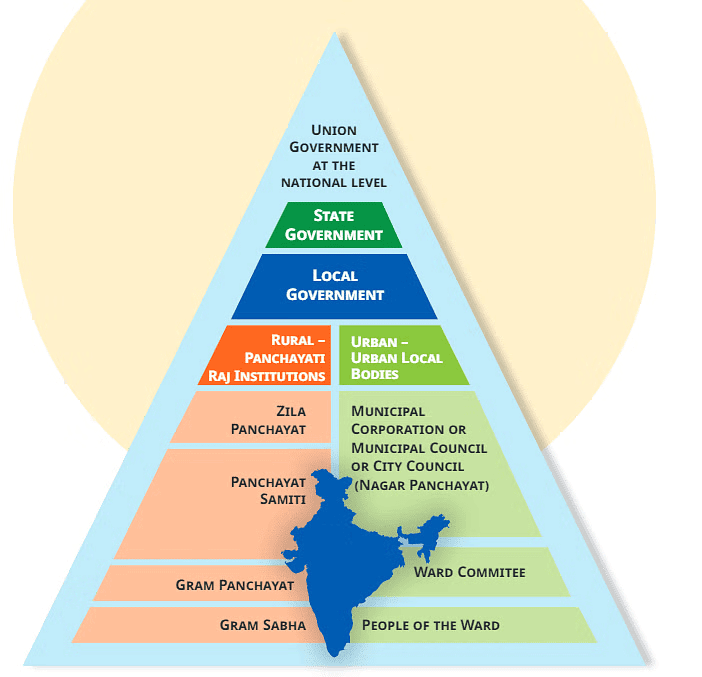 In Fig. 12.2 above, what similarities and differences do you notice between the Panchayati Raj system and the urban local government?
In Fig. 12.2 above, what similarities and differences do you notice between the Panchayati Raj system and the urban local government?
Ans:
Similarities:
- Three-tier Structure: Both the Panchayati Raj system and the urban local government have a hierarchical structure With three levels of governance—ranging from the local level closest to the people up to a higher level that coordinates larger areas.
- Local Participation: In both systems, governance begins at the grassroots level, with bodies such as the Gram Sabha or Ward Committees comprising local citizens who participate directly in decision-making processes.
- Decentralisation: Both systems emphasize decentralization, allowing local communities to have a significant say in governance and management of their immediate environment.
Differences:
- Geographic Focus: The Panchayati Raj system is designed for rural areas, whereas urban local governments serve cities and towns.
- Nomenclature and Structure: The Panchayati Raj system uses terms like Gram Panchayat, Panchayat Samiti, and Zila Panchayat, while urban local governments have structures such as Ward Committees, Municipal Councils, and Municipal Corporations.
- Functions and Challenges: Urban local bodies deal with more complex and diverse issues, such as urban infrastructure, sanitation, and traffic management, which are less prevalent in rural governance.
Page 177
Q: Can you think of four or five more actions that responsible citizens might take to help their area of the city?
Ans: Here are five simple ways responsible citizens can help their city:
- Report Safety Hazards: Let local authorities know about any safety issues, like broken streetlights or open manholes. This helps keep everyone safe and prevents accidents.
- Join Clean-up Drives: Participate in or organize neighborhood clean-up events. This helps keep the area clean and shows that you care about your community.
- Support Local Businesses: Buy from local shops and services. This helps the local economy and supports small businesses in your area.
- Volunteer for Local Projects: Offer your time and skills for community activities, like planting trees or helping with educational programs. This helps improve the community and brings people together.
- Promote Environmental Care: Practice and encourage habits that protect the environment, such as using less plastic and saving water. This helps keep the city healthy and sustainable.
These actions make the city a better place to live and strengthen the connections between people in the community.
Think About It
Page 179
Q: Indore in Madhya Pradesh has been awarded the cleanest city in India under the Swachh Survekshan government scheme for seven years in a row. What could have been the role of Indore citizens in this achievement?
Ans: Indore's success as India's cleanest city for seven years is largely due to the active role of its citizens. They likely segregate waste properly, making it easier for the city to manage garbage. Citizens also participate in community clean-up drives, helping keep public spaces clean. By promptly reporting sanitation issues, they ensure quick fixes. People avoid littering and encourage others to do the same, creating a cleaner environment. Additionally, they spread awareness about the importance of cleanliness, fostering a culture ofhygiene. These collective efforts, along with good municipal management, have made Indore a model for cleanliness.
Page 179
Q1: Select a few cities, from your State and from a few neighbouring States. These may include the city you live in or the city nearest to your town or village. How will you find out if they have a Nagar Panchayat, Municipal Council or Municipal Corporation? Draw a table with the names of the cities and the type of urban local body each of them has.
Ans: To find out if a city has a Nagar Panchayat, Municipal Council, or Municipal Corporation, you can:
- Check Government Websites: Look at the official websites for urban development or municipal affairs in your state. They usually have this information.
- Visit the City's Municipal Office: Go to or contact the local municipal office to ask about the type of urban body that manages the city.
- Look at Local Government Reports: Check annual reports or publications from local government bodies. They often include details about city classifications.
- Use Online Maps or Databases: Use tools like Google Maps or government portals. They sometimes show the type of urban body managing the city.
Here’s an example table: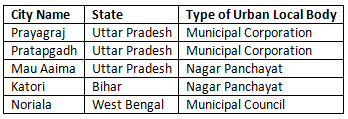
Q2: How do urban local bodies fund their activities? (Hint: Look carefully at the pictures of the functions performed by Indore Municipal Corporation in Figure 12.4 on page 178.) Are some of them paid services? Ans: Urban local bodies get their funds from several sources, including:
Ans: Urban local bodies get their funds from several sources, including:
- Local Taxes and Fees: They collect taxes like property tax and water charges from residents and businesses.
- Paid Services: Some services, such as issuing licenses or providing water tankers, come with fees. For example, the Indore Municipal Corporation charges for certain services.
- Government Grants: They receive money from state and central governments for specific projects or to improve infrastructure.
- Loans and Bonds: They may also borrow money or issue bonds to fund big projects, such as building roads or improving water supply systems.
These funding sources help urban local bodies provide and maintain essential services and infrastructure.
Questions, Activities and Projects
Page 181-182
Q1: On your way to school, you and your friends notice that a water pipe is leaking. A lot of water is being wasted on account of the leak. What would you and your friends do in such a situation?
Ans:
- If we notice a leaking water pipe, we would quickly report it to the local municipal office or the relevant urban local body.
- We could use a helpline number if available or ask a nearby adult to help contact the authorities.
- If it is safe, we might try to create a temporary barrier to reduce water wastage.
- Reporting the leak promptly helps ensure it is fixed, which conserves water and prevents damage to the area.
Q2: Invite a member of an urban local body near you to your class. Discuss with them their role and responsibilities. Prepare a set of questions to ask them so that the meeting is fruitful.
Ans: To prepare for the visit from a local urban body member, we would create a list of questions such as:
- What are your primary responsibilities as an urban local body member?
- How do you address citizens' concerns in your ward?
- What current projects or initiatives are underway in our area?
- How can students and young citizens contribute to improving our locality?
- What challenges do you face in your role, and how do you address them?
Q3: Discuss with adult members of your family and neighborhood, and make a list of their expectations from the urban local bodies.
Ans: From discussions with adults in our family and neighbourhood, we identified several expectations from urban local bodies, including:
- Regular maintenance of roads and public infrastructure.
- Efficient garbage collection and waste management.
- Access to clean and safe drinking water.
- Effective public health services and sanitation.
- Prompt responses to civic complaints and issues.
- Development of parks and recreational facilities.
- Ensuring safety and security in the community.
Q4: Make a list of characteristics of a good urban local body.
Ans: An effective urban local body should have the following characteristics:
- Transparency and accountability in its operations.
- Efficient and prompt service delivery.
- Active participation and engagement of citizens.
- Responsiveness to local needs and issues.
- Equitable distribution of resources and services.
- Effective planning and implementation of development projects.
- Strong leadership and management.
Q5: What are the similarities and differences between the Panchayati Raj system in rural areas and the urban local bodies?
Ans:
Similarities:
- Both systems have elected representatives managing local governance.
- They aim to bring governance closer to the people and encourage their participation in decision-making.
- Each has multiple levels of administration to effectively address local needs.
Differences:
- The Panchayati Raj system operates in rural areas, while urban local bodies are found in cities and towns.
- Panchayati Raj includes Gram Panchayats, Panchayat Samitis, and Zila Parishads; urban local bodies consist of Municipal Corporations, Municipal Councils, and Nagar Panchayats.
- Their functions differ based on local needs, focusing on agriculture and rural development in Panchayati Raj, and infrastructure and public services in urban local bodies.
|
46 videos|241 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Grassroots Democracy — Part 3: Local Government in Urban Areas NCERT Solutions - Social Studies for Class 6
| 1. What is the role of local government in urban areas? |  |
| 2. How are the members of urban local bodies elected? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of urban local bodies? |  |
| 4. What functions do municipal corporations perform? |  |
| 5. How do urban local governments contribute to grassroots democracy? |  |
















