Temperature and its Measurement Chapter Notes | Science Olympiad Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Temperature and Thermometers |

|
| Hot or Cold? |

|
| Temperature |

|
| Measuring Temperature |

|
| Air Temperature |

|
| Key Notes |

|
Understanding Temperature and Thermometers
Have you ever touched an ice cube and felt the chill, or placed your hands near a flame and sensed the heat? Why do some things feel cold while others feel hot?
One evening, Shruti and her younger brother Amit returned home after playing outside. Amit looked pale and tired, and their parents noticed he seemed unwell. To check if he had a fever, they used a thermometer, which confirmed he had a fever. He was advised to rest and drink plenty of water.
Just like Amit’s parents used a thermometer to check his fever, scientists and doctors use thermometers to measure how hot or cold things are. In this chapter, we will learn all about temperature, thermometers, and how they work!
Hot or Cold?
Can We Always Trust Our Sense of Touch to Tell If Something Is Hot or Cold?
Not always! Sometimes, our skin gets tricked. For example, a metal spoon might feel colder than a wooden one, even if they are the same temperature. After being outside in the sun, normal water can feel super cold.
Our sense of touch is helpful, but it doesn’t always tell us the exact temperature. Things like the material and how hot or cold we already feel can change how we sense it.
Temperature
Temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is. It tells us the amount of heat energy present in an object. A higher temperature means more heat energy, while a lower temperature means less heat energy. The difference in temperature between two objects determines how heat moves—heat always flows from a hotter object to a colder one.
Understanding temperature and its measurement is important for various aspects of life, including health, cooking, and weather forecasting.
What is a Thermometer?
A thermometer is an instrument used to measure temperature accurately. It works by detecting changes in heat and displaying the temperature on a scale.
There are two main types of thermometers:
- Clinical Thermometers – Used to measure body temperature, usually in degrees Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit (°F).
- Laboratory Thermometers – Used in science experiments and research to measure the temperature of liquids, gases, or solids.
Measuring Temperature
Clinical Thermometers

A clinical thermometer is designed to measure human body temperatures. These are often called digital clinical thermometers and operate on batteries. They work by being placed in contact with a person's body.
How do Clinical Thermometers Work?
- They measure temperature using heat sensors.
- Temperature is shown digitally and powered by batteries.
- Temperature is measured in degrees Celsius, represented by the symbol °C.
- When placed against the skin, they quickly show the body's temperature.
Temperature Scales: Fahrenheit and Kelvin
- Fahrenheit Scale: Measures temperature in degrees Fahrenheit (°F). For instance, 37.0°C is equivalent to 98.6°F.
- Usage: The Fahrenheit scale is becoming less common in scientific studies.
- Kelvin Scale: Used in science, where temperature is measured in kelvins (K).
- SI Unit: Kelvin is the SI unit for temperature.
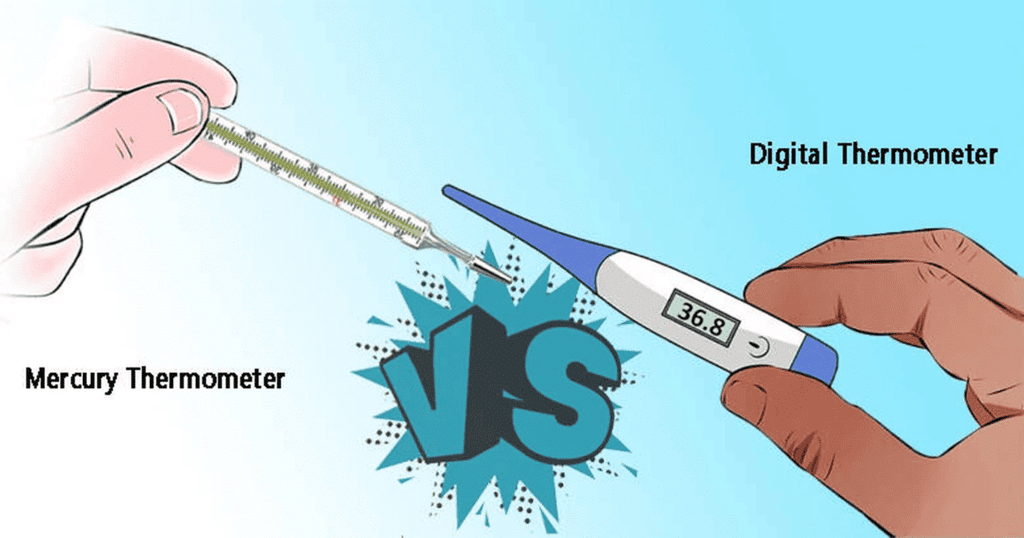
Differences between Digital and Mercury Thermometers
- Mercury thermometers were once popular but are hazardous due to the toxic nature of mercury and are challenging to dispose of properly.
- Digital thermometers are preferred now as they are safer and do not contain toxic materials. They also have clearer displays.
- Digital thermometers use heat sensors for accurate temperature readings, making them reliable and convenient.
Non-contact Thermometers
During the COVID-19 pandemic, non-contact thermometers, also known as infrared thermometers, became widely used. They measure temperature without needing to touch the person, which helps reduce the risk of spreading illness.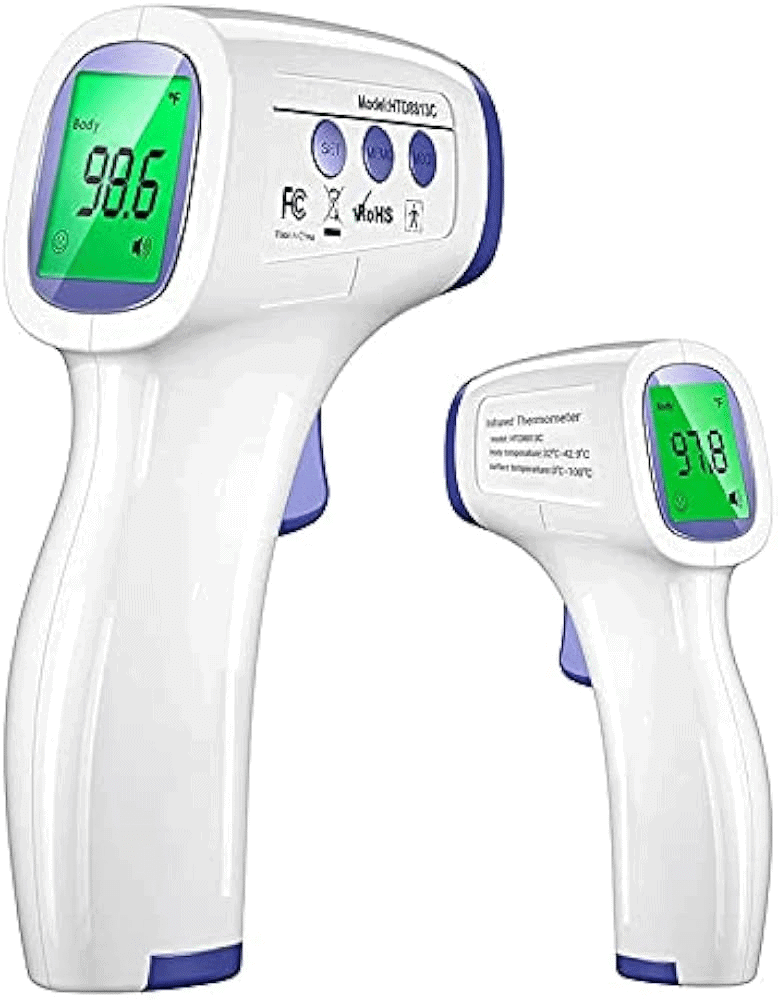
Converting Celsius to Kelvin Temperature Scale
To convert Celsius to Kelvin, use this formula:
Temperature in Kelvin = Temperature in Celsius + 273.15 (This indicates that you add 273.15 to Celsius to find Kelvin)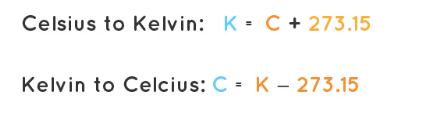
- Example: For a temperature of 25 degrees Celsius: Temperature in Kelvin = 25 + 273.15 = 298.15 K
Temperature Scales and Units
- Temperature scales are named after individuals: Celsius scale, Fahrenheit scale, and Kelvin scale. These names always start with a capital letter.
- When writing units like degree Celsius and degree Fahrenheit, the word degree starts with a small letter, while Celsius and Fahrenheit begin with a capital letter. The unit kelvin is always written with a small letter.
- Symbols for these units are written in capital letters: °C, °F, and K. Do not use the degree symbol (°) with K.
- When writing the symbols, do not place a full stop after them unless it is at the end of a sentence. Leave a space between the number and the unit, e.g., 30 °C, not 30°C.
- If the temperature is above one degree, use the plural form 'degrees', e.g., '20 degrees Celsius' is written as '20 °C'.
Fever Detection Before Thermometers
- Before thermometers were invented, people often checked pulse rates to detect fever, a method known in ancient India where an increased pulse was linked to fever.
- However, relying solely on pulse rates was not very accurate as other factors could also influence pulse rates.
- For example, physical activity, emotional stress, and other conditions can also raise pulse rates.
Laboratory Thermometers
A laboratory thermometer is used to measure temperatures in science experiments. It is different from a clinical thermometer, which is used to measure body temperature.
Main parts of a Laboratory Thermometer
- Capillary Tube– A long, thin tube made of glass, sealed at one end.
- Bulb – A small, round part at the bottom filled with liquid.
- Liquid Column – A thin line of liquid inside the tube that moves up and down.
- Celsius Scale – A marked scale along the tube, showing temperature readings.
- Stem- A narrow, long tube , usually made of glass and it contains the liquid.
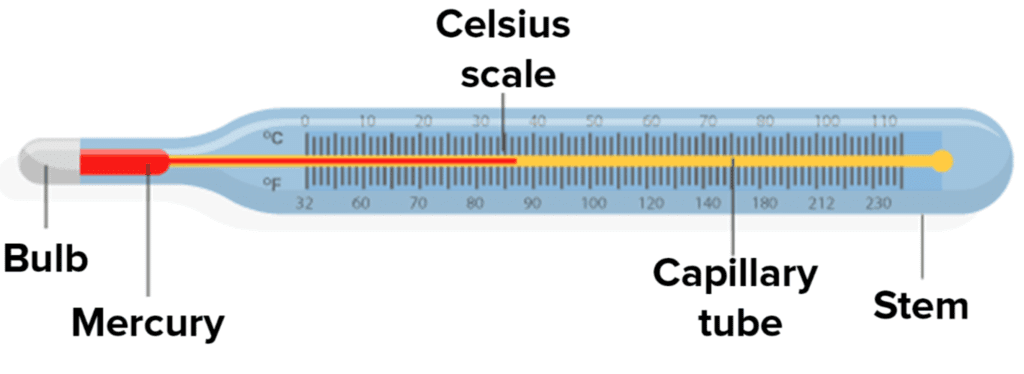
A laboratory thermometer can measure from -10°C to 110°C, which means it can measure very hot and very cold temperatures.
Laboratory thermometers usually contain either alcohol or mercury as the liquid.
- Alcohol: Often coloured red for better visibility.
- Mercury: Used as well, but it remains uncoloured.
Reading the Temperature
- Hold the thermometer upright.
- Look at the level of liquid inside the glass tube.
- Read the number on the Celsius scale that matches the top of the liquid column.
Precautions While Using a Laboratory Thermometer
- Be careful– It is made of glass and can break easily.
- Do not shake it – Unlike a clinical thermometer, it does not need shaking.
- Do not hold it by the bulb – This can affect the reading.
- Do not place it in direct sunlight – It can heat up and give incorrect readings.
Fun Fact!
A laboratory thermometer can measure boiling and freezing points of water! (Water boils at 100°C and freezes at 0°C).
Air Temperature
Have you noticed weather updates in newspapers, on TV, or online? These updates usually show the highest and lowest temperatures of the day.
The temperatures can change daily because many factors affect the weather. Typically, temperatures increase as summer approaches and decrease during winter.

Air Temperature and How We Measure It?
- Air temperature indicates how hot or cold the air is around us.
- Several methods are used to measure air temperature, which is a vital weather factor observed globally at weather stations.
- The information gathered on air temperature, along with other data, is crucial for accurate weather predictions.
Measuring Air Temperature: Techniques and Importance
- Weather stations worldwide monitor air temperature.
- The data collected on air temperature, along with other parameters, is used for weather forecasting.
Know a scientist: Anna Mani (1918-2001) was an Indian scientist, recognised as the 'Weather Woman of India'. She created and developed many weather measurement tools, which decreased the need for imported equipment.
Key Notes
- Temperature: This measures how hot or cold something is.
- Thermometers: Tools that measure temperature, including clinical types (both digital and mercury), laboratory thermometers, and non-contact (infrared) thermometers.
- Types of Thermometers: These are clinical thermometers (digital and mercury) and laboratory thermometers. Clinical thermometers usually use the Celsius scale, where temperature is measured in degrees Celsius (°C).
- Temperature Scales: Common scales include Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin. The standard unit for temperature is Kelvin (K).
- Measurement Techniques: For accurate readings, clinical thermometers must be placed in contact with the body.
- Body Temperature Variations: The typical temperature for a healthy adult is about 37.0 °C or 98.6 °F. Body temperature can change depending on age, activity, and the time of day.
- Laboratory Thermometers Range: These thermometers usually measure from -10 °C to 110 °C.
|
70 videos|150 docs|104 tests
|
FAQs on Temperature and its Measurement Chapter Notes - Science Olympiad Class 6
| 1. What is temperature and why is it important? |  |
| 2. How is air temperature measured? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of thermometers used to measure temperature? |  |
| 4. What factors can affect air temperature? |  |
| 5. Why do we use Celsius and Fahrenheit scales for temperature measurement? |  |





















