Methods of Separation in Everyday Life Chapter Notes | Chapter Notes For Class 6 PDF Download
Separation of Substances
In our daily lives, we often see substances being separated from mixtures. Below are some methods for separating substances.
- A mixture is made up of two or more substances, where each part keeps its own unique properties. For instance, air is a mixture of gases, and the water we drink contains pure water along with other substances.
- A pure substance is one where every particle has the same properties. For example, distilled water is pure because it contains only water.
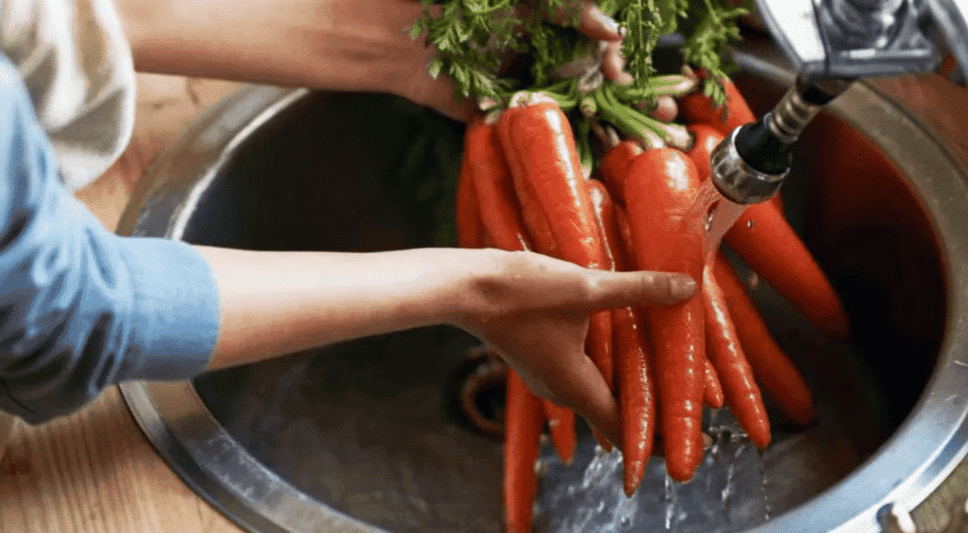

We separate substances mainly to extract useful components from mixtures. But why do we need to do this?
For Example, Ria and her brother Aryan visit their grandparents' farm. They notice their grandparents sorting vegetables. Curious, they ask why. Their Dadi explains, "We clean and sort them to make sure they’re fresh for cooking." Excited, Ria and Aryan help wash the vegetables, learning how to remove dirt before cooking. There are various methods for separation.
Different Methods of Separation
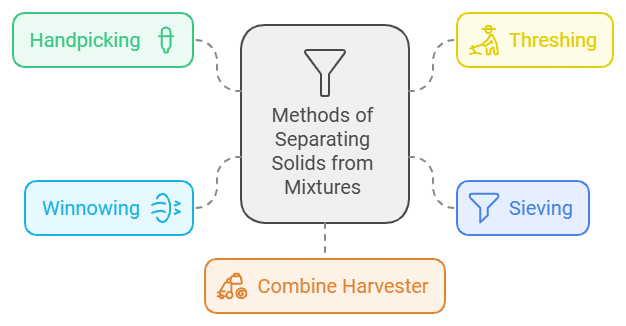 1. Handpicking
1. Handpicking
This is the easiest way to separate substances. It works best when the unwanted material is small in amount and has a different shape, size, or colour from the useful materials.
For instance, handpicking can remove larger impurities like dirt, stones, and husk from wheat, rice, or pulses. It is most effective when the impurities are not too many, such as when removing pebbles, broken grains, and insects from rice, wheat, and pulses.
Do you know what is handpicking?
Yes, a good example of handpicking is when Malli separates whole black peppers from the vegetable pulao using his hands. This shows how handpicking is used to remove unwanted substances from a mixture.

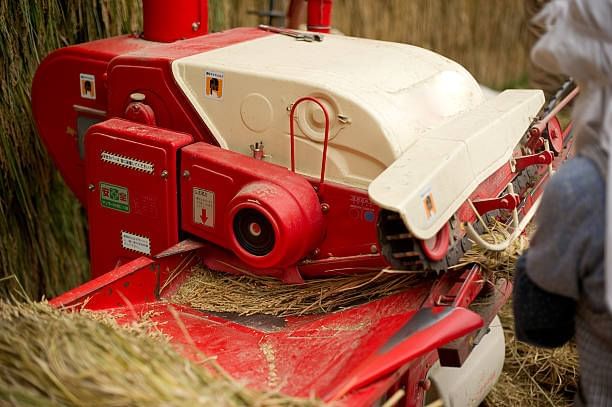
2. Threshing
This process separates grain from stalks. Before separating the grain, the stalks are dried in the sun. Each stalk has many seeds attached to it, and there can be hundreds of these in a field! Threshing involves beating the stalks to release the seeds.
- Manual Threshing: For small amounts, threshing is done by hand. Small bundles of stalks are thrashed on a hard surface to get the grains out.
- Threshing by Animals: For larger amounts, animals are used. Stalks are placed around a pole, and bullocks walk over them. Their hooves help separate the grains.
- Threshing Machine: Today, machines are often used. These can be powered by diesel engines or electric motors, making the process quicker and easier.
Threshing Machines: How They Work
- Threshing machines are made to separate grains from stalks and husk.
- These machines perform two tasks at once: threshing and winnowing.
- By using threshers, the process of separating grains becomes faster and more efficient.

3. Winnowing
Can you explain how winnowing helps farmers separate grains from chaff?
This process separates lighter particles from heavier ones using wind. It is often used to separate grain from husk.
Farmers drop a mixture of wheat and husk from a height. The wind carries the husk away, forming a heap nearby, while the heavier wheat grains fall straight down to form another heap.
Thus, winnowing uses wind or air to separate lighter particles from heavier ones.
4. Sieving
This method is used when the particles are too small to be picked by hand or when there are too many. A sieve with appropriately sized holes is used. Larger particles stay on the sieve, while smaller ones pass through. 
Sieving allows the small flour particles to go through the sieve's tiny holes. Example: Separating bran from wheat flour.
What happens if the holes in a sieve are larger than the particles being sieved?
If the holes are larger than the particles, both fine and larger particles will pass through. However, the process of separating solids from a mixture based on differences in particle size using a sieve is still called sieving.
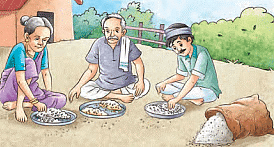
5. Evaporation
This process involves converting a liquid into vapour. It is useful for separating a solid that is dissolved in a liquid.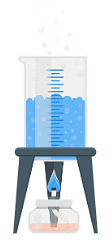
Example: Salt can be extracted from a salt solution by placing it in sunlight.
How is salt obtained from seawater?
Salt is separated from seawater by allowing it to sit in the sun. As the water evaporates, the salt is left behind.
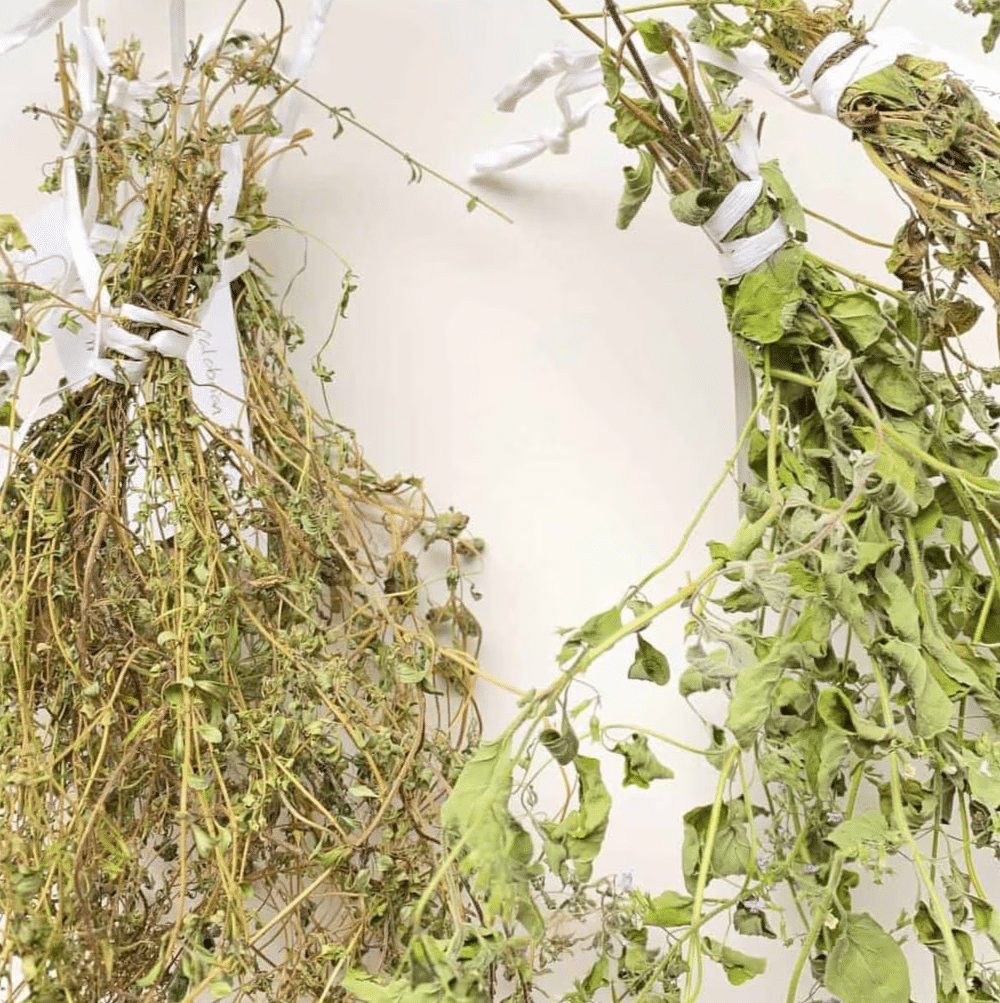
Ayurveda: The Ancient Indian Healing System
- Ayurveda is a traditional Indian system of health and medicine that focuses on overall well-being.
- In Ayurveda, herbs and plant parts such as roots, leaves, flowers, and seeds are used to treat various health issues.
- The plant materials are often dried in the shade . This process helps remove excess moisture while preserving the medicinal properties of the plants.

6. Sedimentation and Decantation
- Sedimentation: This is when insoluble particles settle at the bottom. For example, in muddy water, soil and sand are impurities that settle down after the water is left to stand.
- Decantation: Used after sedimentation, this method separates the heavier sand particles from water. The clear water is carefully poured off, leaving the sand behind.

7. Filtration
Filtration is a technique that separates fine, insoluble solid particles from liquids. The mixture is passed through a filter, which allows the liquid to flow through while trapping the solid particles.
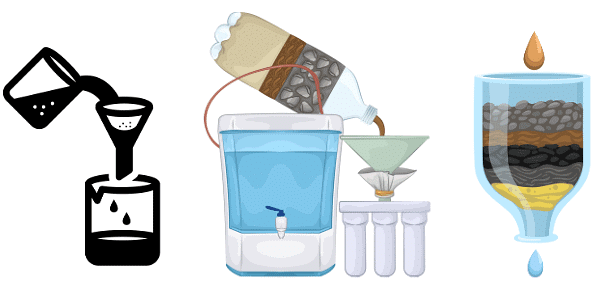
Example: Filtering tea leaves from tea using a strainer.
What do you observe when filtering muddy water using filter paper?
When filtering muddy water through filter paper, the mud particles are trapped in the filter paper, while clear water passes through and is collected.
Different Materials Used as Filters
- Other than filter paper, various materials like cotton, charcoal, and sand can also be used as filters.
The Evolution of Tea Bags
- Tea bags were first made from soft materials like silk as it could hold the tea leaves while allowing hot water to pass through.
- Silk was chosen because it was strong and didn't break apart when it came into contact with hot water.
- Later on, people began using gauze or muslin for making tea bags.
- Eventually, the use of filter paper became common, and today, most tea bags are made from this material.

8. Churning
- Churning is the process of mixing a liquid to separate lighter parts from heavier ones.

- Example: Separating butter from curd by churning.
9. Magnetic Separation
- The process of separating magnetic and non-magnetic materials using a magnet is known as magnetic separation.
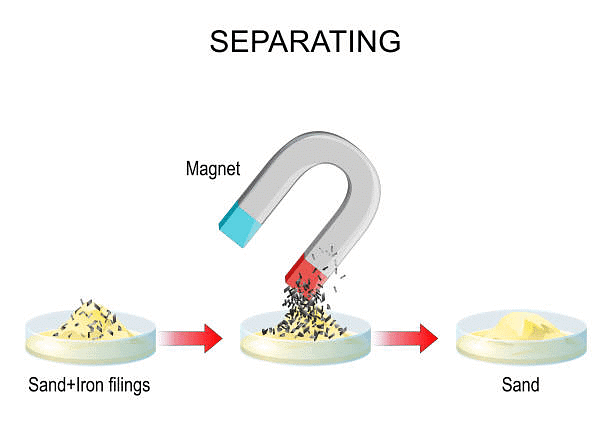
- Example: Using a magnet to separate iron nails from sawdust.
These days, recyclers use magnets to remove iron items from a pile of waste. In various industries, waste materials often include scrap iron, which is extracted using magnets attached to cranes. This scrap iron can be recycled and reused.
Separation of Scrap Iron from Waste
- In numerous industries, waste materials frequently include scrap iron. This scrap is removed from the waste pile using magnets attached to a crane.
- Materials that are drawn to a magnet are known as magnetic substances. Iron is a typical example of such a substance.
- The method of separating magnetic substances from non-magnetic ones using a magnet is referred to as magnetic separation.
- The scrap iron can be processed and reused.
Key Points
- Handpicking: Manual removal based on size, color, or shape.
- Threshing: Separating grains from stalks by beating.
- Winnowing: Using wind to separate lighter husk from heavier grains.
- Sieving: Using a sieve to separate particles of different sizes.
- Evaporation: Converting liquid to vapor to separate dissolved solids.
- Sedimentation and Decantation: Allowing heavy particles to settle and pouring off the liquid.
- Filtration: Using a filter medium to separate insoluble solids from liquids.
- Churning: Agitating a mixture to separate lighter components.
- Magnetic Separation: Using magnets to separate magnetic from non-magnetic substances.
Practical Applications
- Removing small stones from pulses.
- Churning curd to make butter.
- Taking out green chillies from cooked dalia (dish made of cracked wheat) or poha (dish made of flattened rice).
- Taking out seeds from watermelon.
- Separating pebbles from sand.
FAQs on Methods of Separation in Everyday Life Chapter Notes - Chapter Notes For Class 6
| 1. What are the common methods of separation used in everyday life? |  |
| 2. How does filtration work as a method of separation? |  |
| 3. What is the principle behind distillation? |  |
| 4. In what situations is centrifugation used for separation? |  |
| 5. What is chromatography and how is it applied in everyday life? |  |






















