Gujarat: Agriculture - GPSC (Gujarat) PDF Download
Main Highlights of Agriculture in Gujarat
- Gujarat's Agricultural Progress: Gujarat has made significant strides in agriculture, with more than 50% of its land dedicated to farming.
- Main Food Crops: The primary food crops in Gujarat include bajra, jowar, rice, and wheat.
- Commercial Cash Crops: Major cash crops like groundnut, tobacco, cotton, linseed, sugarcane, isabgul, cumin, mangoes, and bananas contribute significantly to the economy.
Modernization of Agriculture
- Utilization of High-Yielding Seeds: Farmers in Gujarat are adopting high-yielding seed varieties to boost productivity.
- Application of Chemical Fertilizers: The use of chemical fertilizers has become common practice to enhance soil fertility.
- Improved Irrigation Techniques: Gujarat leverages both groundwater and surface water resources effectively for irrigation.
- Diversified Cropping Pattern: The state's diverse cropping pattern is well-supported by efficient irrigation systems.
- Development of Infrastructure: Initiatives such as cold storage, logistics, and improved infrastructure are aiding in agricultural growth.
- Role of Research Institutes: Agricultural research institutions play a crucial role in advancing farming techniques and increasing output.
Enhanced Agricultural Outputs
- Steady Crop Production Increase: Due to modern practices, the production of various crops in Gujarat has been steadily rising.
- Impact of Cooperative Farming: Cooperative farming has significantly contributed to the agricultural and economic development of Gujarat.
Significance of Amul Dairy Program
- World's Largest Milk Dairy: Gujarat's Amul dairy program stands as the largest milk cooperative in the world, showcasing the state's dairy prowess.
 |  |
Agriculture in Gujarat
Overview:
- Gujarat's agriculture sector is experiencing a growth phase with the adoption of High Yielding Varieties (HYV) of seeds, use of chemical fertilizers, and enhanced irrigation methods.
- Between 2000 and 2010, Gujarat saw a remarkable agricultural growth rate of over 9%, a significant improvement from the 3% growth rate in the 1990s.
Agricultural Products
- Gujarat ranks first in groundnut production and second in tobacco production.
- Other cash crops grown in Gujarat include Isabgul, Cumin, Mangoes, and Bananas.
Tobacco Production:
- Gujarat ranks second in tobacco production, trailing Andhra Pradesh. Tobacco cultivation is concentrated in the alluvial soil of Kheda district.
- Additionally, crops like castor, sesamum, vegetables, and fruits thrive on the fertile goradu soil found in the plains.
Diversification of Agriculture
- In regions with limited rainfall like Kutch, north-west Kathiawar, and north Gujarat, animal husbandry plays a vital role with the rearing of goats, sheep, and cattle.
- Anand in Kheda district boasts a modern dairy industry operated on a cooperative basis.
Geographical Significance:
- Gujarat, a maritime state, is irrigated by rivers such as Narmada, Tapti, Mahe, and Sabarmati.
- The state's soil composition comprises a mix of Black soils, Sandy soil, and Alluvium soil, contributing to its agricultural diversity.
Visual Representations
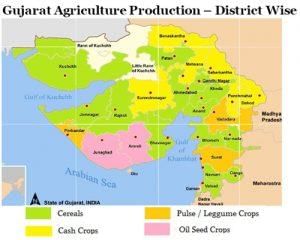
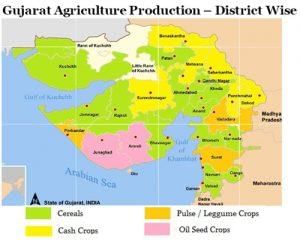
Agriculture in Gujarat
Main Agricultural Crops in Gujarat
- Bajra, jawar, rice, and wheat are the primary agricultural crops grown in Gujarat.
Major Commercial Crops
- Cotton, tobacco, groundnut, linseed, and sugar-cane are significant cash crops in the state.
- Groundnuts cover the largest acreage among all crops, followed by cotton.
Regional Crop Concentration
- Groundnuts are predominantly grown in peninsular Gujarat with light and gribble soil.
- Tobacco cultivation is concentrated in Kheda and Vadodra.
- Cotton thrives in the Gujarat Plain, where rainfall ranges from 60 to 100 cm.
Role of Cash Crops
- Cash crops play a pivotal role in Gujarat's economy.
Factors Contributing to Agricultural Success
- State-run institutions and the adoption of High Yielding Variety (HYV) seeds and improved irrigation techniques have significantly boosted agriculture.
- Introduction of new technologies by state-promoted agricultural universities has been instrumental.
Infrastructure Development
- Enhanced marketing, warehousing, and cold-storage facilities ensure the marketability, sustainability, and efficiency of food products.
Agro-Solar Policy in Gujarat
- Gujarat is the pioneer in implementing the Agro-Solar Policy.
- Under this policy, farmers harness solar energy to generate power, creating an additional income stream.
- The Gujarat Energy Research and Management Institute (GERMI) oversees projects under this initiative.
- By installing Solar Photovoltaic (SPV) panels, farmers can produce energy locally, reduce dependence on the grid, and even sell surplus energy to power generation companies.
Overview of Successful Solar Projects in Gujarat State
Several noteworthy solar projects have been implemented in Gujarat State, showcasing the region's commitment to sustainable energy solutions. Notably, Charanka village in Patan district hosts Asia's largest solar power plant, sprawling across a vast 2,000-hectare area. Another innovative initiative involved the inauguration of a 10 MW canal-top solar power plant on the Narmada canal in Vadodara, graced by UN Secretary General Ban-Ki Moon in January 2015.
Impact on Farmers and Energy Companies
These solar projects have had a positive impact on the local community and energy sector. Farmers benefit from a supplementary income stream, facilitated by revenue sharing agreements with power generation companies. Simultaneously, the companies gain access to ample space for efficient electricity production.
Key Points:
- Creation of Asia's largest solar power plant in Charanka village, covering 2,000 hectares.
- Inauguration of a 10 MW canal-top solar power plant on the Narmada canal in Vadodara by UN Secretary General Ban-Ki Moon in 2015.
- Facilitation of supplementary income for farmers through revenue sharing agreements.
- Provision of significant space for electricity generation, benefiting power companies.














