Microsoft Windows | Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Microsoft Windows (MS-Windows) |

|
| Windows NT (New Technology) |

|
| Key Components of the Desktop |

|
| Main Programs in Windows |

|
| Windows Library |

|
Microsoft Windows (MS-Windows)
Microsoft Windows, often abbreviated as MS-Windows, is a series of graphical user interface operating systems developed, marketed, and sold by Microsoft. It allows users to interact with programs and applications using a mouse or keyboard, making tasks more intuitive and efficient.
Windows NT (New Technology)
 Introduced in July 1993, Windows NT was designed specifically for businesses. It provides enhanced control over workstation capabilities, benefiting network administrators.
Introduced in July 1993, Windows NT was designed specifically for businesses. It provides enhanced control over workstation capabilities, benefiting network administrators.
Features:
- Based on a high-level language.
- Capable of running DOS, Windows 3, and Win32 applications.
- Supports 32-bit Windows applications.
- Offers improved stability and security.
Windows 95
Released on August 24, 1995, Windows 95 is a graphical user interface-based operating system aimed at consumers.
Features:
- Combines 16-bit and 32-bit architecture.
- Focused on consumer use.
- Supports FAT32 file system, multi-display setups, Web TV, and Internet Explorer.
Windows 98
Launched in 1998, Windows 98 was released in two main versions. The initial version had several programming issues, but the second edition, which followed, addressed many of these problems.
Features:
- Includes Internet Explorer 4.0.1.
- First operating system to use the Windows Driver Model (WDM).
- Provides a FAT32 converter utility to convert FAT16 drives to FAT32 without needing to format the partition.
- Supports various peripheral devices, including USB and DVD.
Windows ME
Released in June 2000, Windows ME (Millennium Edition) faced numerous programming errors, which often frustrated home users.
Features:
- Designed for single CPU use.
- Minimum internal storage of 64 MB and maximum of 4 GB.
- Introduced the Multilingual User Interface (MUI).
Windows XP
 Released on October 25, 2001, Windows XP was designed for personal computers with different versions tailored for various users.
Released on October 25, 2001, Windows XP was designed for personal computers with different versions tailored for various users.
Versions:
- Windows XP Home Edition: Intended for home users.
- Windows XP Professional: Aimed at business users.
Features:
- Supports multiple user profiles.
- Requires at least 64 MB of RAM, with a total disk space of 19.5 GB and 3.75 GB of free space.
- Provides 1.5 GB of available hard disk space.
- Compatible with Super VGA (Video Graphics Array) or higher resolution video adapters and monitors.
- Supports sound cards, CD-ROMs, DVD-ROM drives, speakers, or headphones.
Windows Vista
Released worldwide on January 30, 2007, Windows Vista was developed for personal computers, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and media center PCs.
Features:
- Can be installed on systems with Pentium 4 or higher processors, 512 MB of RAM, 32 MB video cards, and a 40 GB hard disk.
- Enhances visual style features.
Windows 7
Launched on October 22, 2009, Windows 7 is an upgrade from Windows XP and Vista, but it does not include some standard applications like Windows Movie Maker and Windows Mail.
Features:
- Supports 64-bit processors.
- Provides touch, speech, and handwriting recognition.
- Allows playback of media in MP4 format.
- Includes the Windows Biometric Framework.
- Offers multiple firewall options.
Windows 8
Released on October 26, 2012, Windows 8 was designed for personal computers and is based on Microsoft's Metro Design language.
Features:
- Compatible with 64-bit logical CPUs.
- Supports 3D graphics and Internet Explorer 10.
- Includes support for emerging technologies like USB 3.0 and cloud computing.
Windows 10
Released on July 29, 2015, Windows 10 is a personal computer operating system developed by Microsoft.
Features:
- Facilitates easy access to social media sites like Facebook and Twitter.
- Includes a ‘game DVR’ mode to record the last 30 seconds of gameplay for social sharing.
- Adapts its interface based on the hardware it is running on.
Desktop
When you turn on a computer, the first screen you see is called the desktop. The background image on this screen is known as the wallpaper. A small arrow or blinking symbol that moves around the desktop is called the cursor. The desktop includes components like the Start menu, Taskbar, icons, and gadgets.
Key Components of the Desktop
 Icon: An icon is a small image representing a program or file on the desktop. Icons represent files, folders, programs, and other items. Users can open programs by double-clicking on these icons. Moving an icon on the desktop is referred to as ‘dragging,’ and placing it in a new location is called ‘dropping.’
Icon: An icon is a small image representing a program or file on the desktop. Icons represent files, folders, programs, and other items. Users can open programs by double-clicking on these icons. Moving an icon on the desktop is referred to as ‘dragging,’ and placing it in a new location is called ‘dropping.’
Some common icons include:
Computer: This crucial icon shows document folders, hard disk partitions, and removable disk drives (e.g., floppy disks, CDs, DVDs). It allows users to access drives, printers, and other system applications.
- Recycle Bin: This icon holds deleted files, folders, or shortcuts. When files or folders are deleted, they are moved to the Recycle Bin, from where they can be restored to their original location. Once the Recycle Bin is emptied, the deleted items cannot be restored.
Taskbar: The taskbar is the long horizontal bar typically located at the bottom of the desktop. It displays buttons for open programs and windows. The taskbar generally consists of three parts:
- Start Button
- Middle Section
- Notification Area
Start Menu: The Start Menu is the main gateway to the computer's programs, files, folders, and settings. It also shows recently opened programs. Key options in the Start Menu include:
- All Programs: Lists all installed programs. New software appears here automatically after installation.
- Favorites: Contains bookmarked web pages.
- Documents: Displays a list of recently opened documents.
- Settings: Includes options for Control Panel, Printers, Taskbar, etc.
- Find: Allows users to search for specific files or folders.
- Log Off: Provides a way to protect the computer from unauthorized access by logging off.
- Turn Off (Shut Down): Provides options to shut down or restart the system.
Window: A window is a rectangular area on the screen that provides an environment for running programs. Key parts of a window include:
Title Bar: Located at the top of the window or dialog box, it displays the name of the window or program. The title bar usually contains three buttons:
- Close Button: A square button with an [×] symbol at the right edge of the title bar. It closes the current program.
- Minimize Button: Reduces the window to a button on the taskbar, allowing the window to be shrunk.
- Maximize Button: Expands the window to fill the entire desktop.
Scroll Bar:
- Appears on the right (or left) side or at the bottom of a window.
- It allows users to scroll through a document larger than the window area.
- There are two types of scroll bars: horizontal and vertical.
Menu Bar: Each window has its own menu bar, which includes several menus for performing specific actions:
- File Menu: Contains options like New, Open, Close, Save, Save As, Print, etc.
- Edit Menu: Includes options such as Undo, Cut, Copy, Paste, Clear, etc.
- View Menu: Offers options like Normal, Toolbar, Print Layout, etc.
- Insert Menu: Provides options like Header, Footer, etc.
- Help Menu: Provides information about the window and its features.
Dialog Box: When you attempt to close a document without saving it, a dialog box may appear. It typically contains a message and buttons such as Close, Yes, No, and Cancel, offering guidance on what action to take next.
Main Programs in Windows
Notepad
Notepad is a basic text editor used to view and edit text files. Files created with Notepad have a .txt (text document) extension.
To open: Click on Start → All Programs → Accessories → Notepad
WordPad
WordPad is a more advanced text editor that supports complex formatting and images. Files saved in WordPad have a .rtf (rich text format) extension.
To open: Click on Start → All Programs → Accessories → WordPad
Paint
Paint is a drawing program used for creating and editing images. Files created in Paint can have .png, .jpg, or .bmp extensions.
To open: Click on Start → All Programs → Accessories → Paint
Calculator
The Calculator application performs basic arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
To open: Click on Start → All Programs → Accessories → Calculator
Media Player
Windows Media Player is a tool for playing digital media files, organizing media collections, and burning CDs.
To open: Click on Start → All Programs → Windows Media Player
Files
- Files are collections of data stored on auxiliary storage media.
- In Windows, files are the fundamental units for data storage.
- Each file is given a specific name by the user, known as the filename, and has a file extension that indicates the file type.
- ZIP File: ZIP stands for Zone Information Protocol. This format compresses application files to reduce their size.
- Executable File: An executable file contains instructions that can be executed by the computer.
Some common file name extensions are as follows

Folders
Folders are containers used to organize and store files. They can also contain other folders, known as sub-folders. Users can create multiple sub-folders, each of which can hold files and additional sub-folders.
Windows Library
A Windows Library can include files and folders stored on the local computer, and is managed similarly to other folders. Types of Windows Libraries include:
- Documents Library: Organizes and arranges word processing documents, spreadsheets, presentations, and other text-related files.
- Pictures Library: Organizes and arranges digital pictures.
- Music Library: Organizes and arranges digital music files, such as songs.
- Video Library: Organizes and arranges video files, such as clips and recordings.
Tit-Bits
- To turn off the computer, we must click on the Start button and then choose the Shut down option.
- Windows Explorer is a program for managing files that comes with versions of the Microsoft Windows operating system.
- Clipboard is a temporary storage area in a computer's memory used for holding copied or cut data.
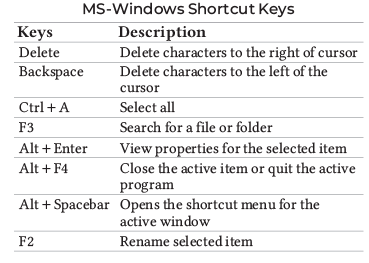

|
48 videos|43 docs|33 tests
|
FAQs on Microsoft Windows - Computer Awareness and Proficiency - SSC CGL
| 1. What are the key components of the desktop in Microsoft Windows? |  |
| 2. What is the main program in Windows NT? |  |
| 3. What is the Windows Library in Microsoft Windows? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the acronym "NT" in Windows NT? |  |
| 5. How does Microsoft Windows differ from other operating systems? |  |















