Understanding AI, ML & DL | Artificial Intelligence for Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Machine Learning (ML)? |

|
| How Machine Learning works? |

|
| Artificial Intelligence vs Machine learning |

|
| What is Deep Learning? |

|
| Machine Learning vs Deep Learning |

|
Introduction
The terms Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are often used interchangeably, but they represent different concepts within the realm of technology.
Here's a breakdown of each:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Definition: AI is the broad field of creating machines or software that can perform tasks that would typically require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, learning, problem-solving, understanding natural language, and perception.
- Scope: AI encompasses a wide range of techniques and methods to achieve intelligent behavior. It includes both traditional rule-based systems and more advanced methods such as ML and DL.
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Definition: ML is a subset of AI focused on the idea that systems can learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for each specific task.
- Scope: ML algorithms use data to build models that can make predictions or decisions. It involves various techniques like supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- Deep Learning (DL)
- Definition: DL is a subset of ML that involves neural networks with many layers (deep neural networks). These networks are designed to automatically learn representations from data by processing it through multiple layers of abstraction.
- Scope: DL is particularly effective for handling large volumes of unstructured data, such as images, audio, and text. It excels in tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
This Flow chart will help us get an overview of Artificial Intelligence
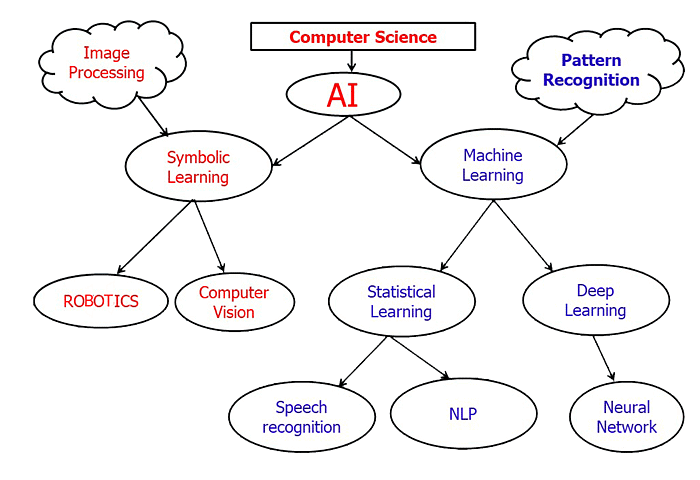
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
- Machine Learning (ML) is a key subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) focused on the ability of machines to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed for specific tasks.
- Here's a simple breakdown:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Encompasses all technologies that enable machines to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence, such as reasoning, learning, and problem-solving.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI, ML is specifically about training machines to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. It involves developing algorithms that allow machines to improve their performance on a task as they are exposed to more data.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of ML, DL uses neural networks with many layers (hence "deep") to analyze and learn from data. It's particularly powerful for tasks involving large amounts of unstructured data, such as image and speech recognition.
- In essence, ML enables machines to learn and adapt, while DL is a specific approach within ML that deals with complex data and tasks using deep neural networks.
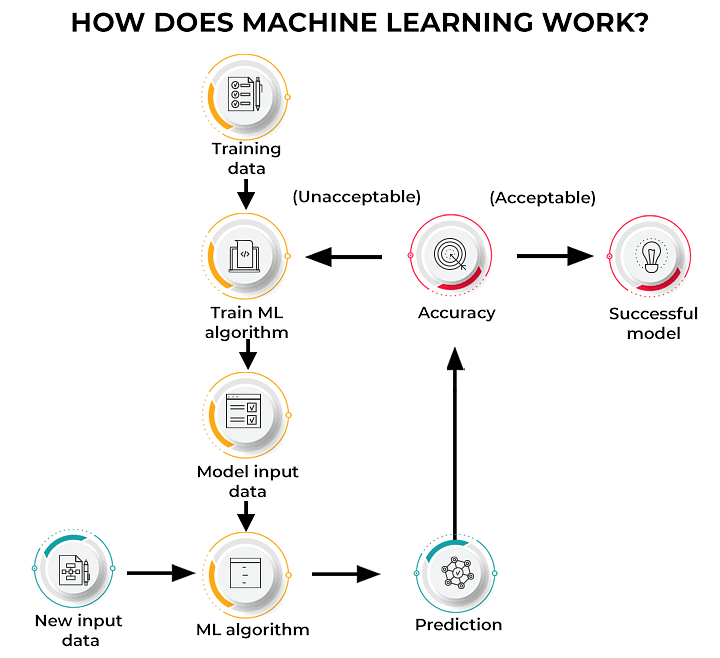
How Machine Learning works?
To grasp how humans learn, let’s look at a straightforward sequence of activities involved in the human learning process.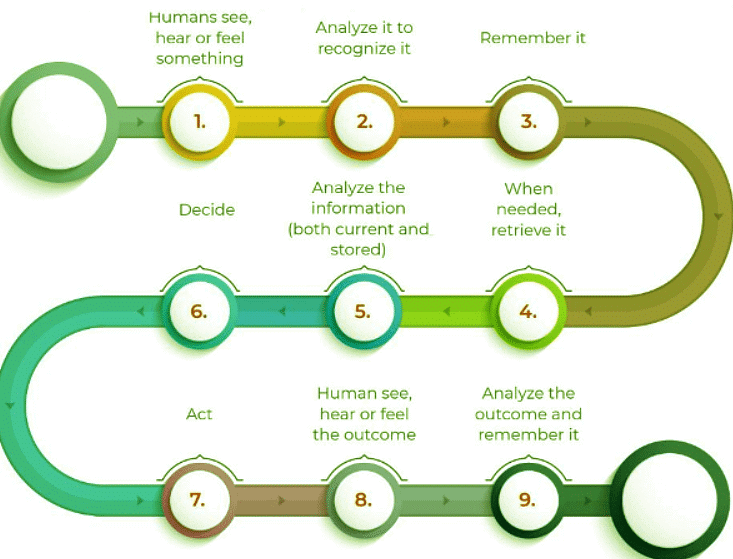
Machine Learning Process (ML)
- A computer learns in a way similar to humans but requires extensive data to ensure accurate recognition and decision-making. For example, to recognize a flame, a computer might use various features such as color, size, shape, origin, and temperature.
- Once the computer can identify the flame, it needs training to make decisions based on specific goals. For instance, if the goal is to extinguish the flame, the computer might act to touch it. Conversely, if the goal is to avoid harm, the computer might recognize the flame as a danger and refrain from touching it.
- Additionally, distinguishing between a real flame and an image of a flame poses a challenge. A poorly trained computer might mistakenly try to extinguish a photo of a flame or touch a real flame, leading to potential damage. Accurate differentiation might involve recognizing features like temperature and movement.
Capability of Machines
To enable a machine to learn, we first assess its capabilities.
These capabilities include:
- Cameras for capturing images.
- Receivers for capturing sound.
- Converters and speakers for producing sound.
- We can equip machines with sensing devices that mimic human senses, such as skin, eyes, ears, mouth, and nose. These devices are known as sensors.
- Sensors are artificial devices made from specific materials and connected through electronic signals. They detect and interpret various inputs like chemicals, waves, and light.
Artificial Intelligence vs Machine learning
But even though both AI and ML are based on statistics and mathematics, they are not the same thing.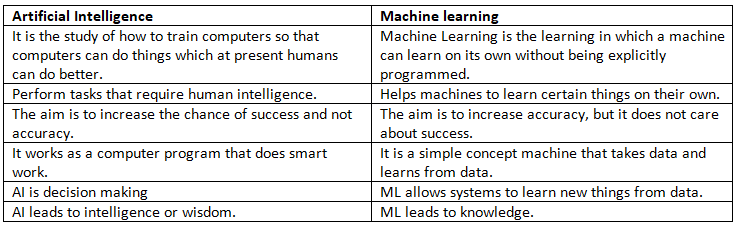
What is Deep Learning?
- Deep learning is a branch of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) that simulates how humans acquire certain types of knowledge. It is a key component of data science, involving complex algorithms and requiring extensive datasets.
- Deep learning works with both structured and unstructured data during training. Practical applications include virtual assistants, vision systems for driverless cars, fraud detection, and facial recognition.
- Essentially, deep learning mimics the human brain's processing of data to perform tasks such as object detection, speech recognition, language translation, and decision-making.
How Deep Learning works
- Deep learning, an advanced branch of machine learning (ML), excels in working with unstructured data.
- It learns autonomously by analyzing large datasets, known as Big Data, sourced from social media, internet search engines, e-commerce platforms, and more.
- These vast datasets are processed using complex ML algorithms to enable deep learning models to make sense of and learn from the data.
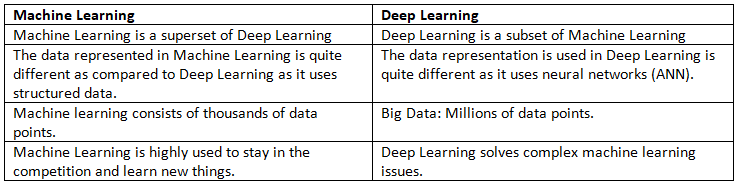
Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
|
24 videos|64 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Understanding AI, ML & DL - Artificial Intelligence for Class 10
| 1. What are the main differences between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning? |  |
| 2. How does Machine Learning work in practice? |  |
| 3. What are some common applications of Machine Learning? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of Deep Learning in the field of Machine Learning? |  |
| 5. Can Machine Learning and Deep Learning be used together? |  |




















