Biomolecules | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Lipids |

|
| Carbohydrates |

|
| Proteins |

|
| Nucleic Acids |

|
| Enzymes |

|
Introduction
Biomolecules are chemical compounds present in all living organisms, primarily composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. These molecules are essential building blocks of life, performing critical functions within living organisms. Despite the numerous types of molecules in a cell, only a few basic classes of biomolecules exist.
Lipids
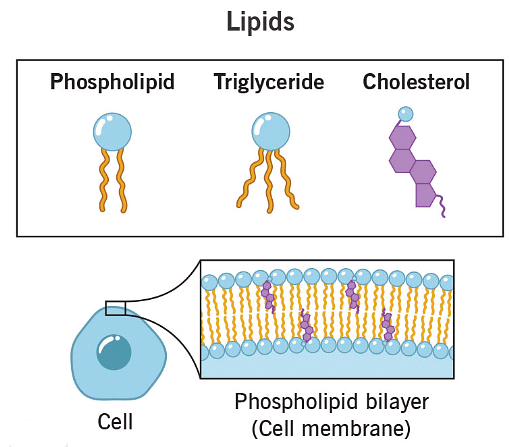
Lipids encompass various molecules such as neutral fats, oils, steroids, and waxes, all sharing a hydrophobic nature. Fats and oils typically form through the polymerization of two or three fatty acids with glycerol. However, other lipids, like steroids, do not form polymers. Diglycerides and triglycerides are produced via dehydration synthesis from smaller molecules, distinguishing them from typical polymerization. Lipids serve several vital functions in biological systems:
- Forming membranes that enclose cells and their compartments.
- Providing protection against desiccation.
- Storing concentrated energy.
- Offering insulation against cold.
- Absorbing shocks.
- Regulating cell activities through hormone actions.
Steroids
- Steroids function both as hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, and as structural materials, like cholesterol, which is integral to animal cell membranes.
- Unsaturated fats, currently popular due to marketing, are liquid at room/body temperature and beneficial for health.
- Trans fats, artificially produced unsaturated fats, contrast with these natural ones.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, hydrates of carbon, typically have the formula (CH2O)n, where n is an integer such as 5 (C5H10O5) or 6 (C6H12O6). Though this formula suggests carbon atoms joined to water, the actual molecules are more complex. Carbohydrates exist as both monomers and polymers, with small carbohydrates known as sugars, including monosaccharides and disaccharides, and larger ones called polysaccharides. Carbohydrates fulfill several functions:
- Acting as precursors for building many polymers.
- Storing short-term energy.
- Providing structural building materials.
- Serving as molecular tags for cell signaling and recognition.
Proteins
Proteins are polymers of specific amino acids, comprising about half the total weight of cellular biomolecules, excluding water. Protein deficiency can lead to serious disorders like Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM), such as Kwashiorkor and marasmus. Proteins have diverse functional roles, including:
- Acting as enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions, significantly speeding them up.
- Serving as structural materials, such as keratin in hair and nails and collagen in connective tissue.
- Binding specifically to foreign substances, as antibodies do.
- Functioning as specific carriers, such as membrane transport proteins and blood proteins like hemoglobin.
- Facilitating muscle contraction through actin and myosin fibers.
- Regulating sugar levels in blood through hormones like insulin.
Nucleic Acids
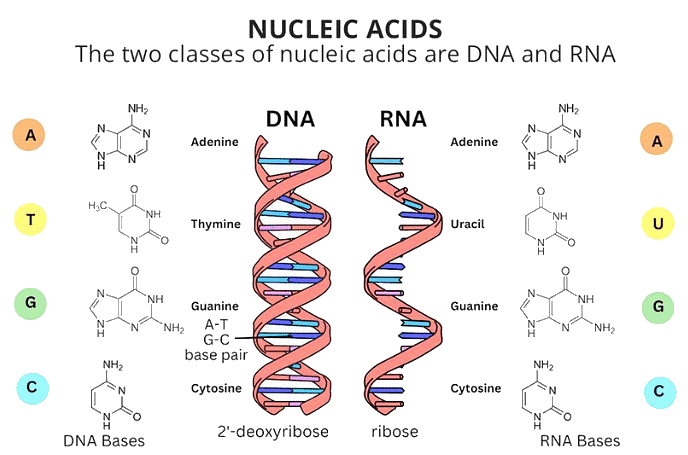
Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides, each composed of a nitrogenous base, a 5-carbon pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. There are two main types of nucleic acids:
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA): Serves as a cellular database, storing vast information about all proteins. There are five types of DNA: A-type, B-type (the major type found in humans), C-type, D-type, and Z-type (the most recent, with a zig-zag helix).
- Ribonucleic Acid (RNA): Occurs in various forms, converting DNA’s information into proteins. In some viruses, RNA is the primary genetic material. Certain RNAs, known as ribozymes, have catalytic abilities similar to protein enzymes. RNA can be divided into three types based on structure: t-RNA (transfer RNA), r-RNA (ribosomal RNA), and m-RNA (messenger RNA).
Enzymes
- Enzymes are biological catalysts, with about 40,000 different types present in human cells, each controlling a distinct chemical reaction.
- They increase reaction rates by a factor of 10-12 times, enabling reactions at normal temperatures.
- Discovered in fermenting yeast by Buchner in 1900, enzymes derive their name from "in yeast."
- Enzymes catalyze metabolic reactions such as respiration, photosynthesis, and digestion, and also function as promoters, membrane pumps, and receptors.
- The International Enzyme Commission (IEC) system classifies enzymes into six broad groups based on the type of reaction catalyzed.
- Enzymes, mostly proteins, have their function determined by their complex structure, with reactions occurring in a small part called the active site.
- The complete active enzyme with its cofactor is a holoenzyme, while the protein part alone is an apoenzyme.
- The catalytic action theory proposed by Savante Arrhenius in 1888 describes an enzyme-substrate complex formed during the reaction.
- The reaction can be represented as:

Factors Affecting Enzyme Reaction Rate
- Temperature: Enzymes work optimally between 35-40°C, with reaction rates increasing with temperature up to a certain point.
- pH: Enzymes have an optimal pH range (7-8) for proper functioning, with reaction rates increasing within this range.
- Enzyme Concentration: Reaction rates increase linearly with enzyme concentration until they plateau.
- Substrate Concentration: Reaction rates increase with substrate concentration.
Inhibitors
Inhibitors are substances that reduce enzyme activity by decreasing reaction rates. They occur naturally and are also used artificially as drugs, pesticides, and research tools.
Human Genome Project-Write
- The Human Genome Project-Write, announced on June 2, 2016, is a ten-year extension of the Human Genome Project, aimed at synthesizing the human genome.
- The human genome consists of three billion DNA nucleotides, described in the Human Genome Project-Read Program completed in 2003.
- Researchers expect that synthesizing large portions of the human genome will lead to significant scientific and medical advances.
|
468 videos|1404 docs|395 tests
|
FAQs on Biomolecules - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are the main types of biomolecules found in living organisms? |  |
| 2. How do lipids contribute to the structure and function of cells? |  |
| 3. What is the role of carbohydrates in the body? |  |
| 4. How do proteins function in living organisms? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of nucleic acids in genetics and inheritance? |  |




















