SSC CGL Exam > SSC CGL Notes > General Awareness for SSC CGL > Organic Evolution
Organic Evolution | General Awareness for SSC CGL PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Evolution |

|
| Theories of Evolution |

|
| Evidences for Evolution |

|
| Mechanisms of Evolution |

|
| Human Evolution |

|
Evolution
- Evolution is the study of anatomical, biochemical, or behavioral changes over time resulting from gene-environment interactions in a population of organisms.
- Scientists hypothesize that the universe came into existence about 15 billion years ago with a colossal explosion often referred to as the Big Bang.
- About 3.8 billion years ago, Earth's atmosphere consisted of elements such as nitrogen, hydrogen, sodium, sulfur, and carbon.
- Some of these elements combined to form hydrogen sulfide, methane, water, and ammonia.
Theories of Evolution

- Lamarck (1809) proposed a theory that living organisms changed by inheriting acquired characteristics, e.g., giraffes stretched their necks to reach food, and their offspring inherited stretched necks. Although now known to be incorrect since many experiments and experiences have shown that acquired characteristics are not inherited, Lamarck's theory was the first to acknowledge that species change and attempt to explain how.
- Charles Darwin (1859) published the book "On the Origin of Species, by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life," recognized as one of the most important books ever written. A very similar theory was also proposed by Alfred Wallace, and they agreed to publish it simultaneously. In his book, Darwin presented evidence for his theory of descent with modification, which has come down to us as the theory of evolution, although Darwin avoided the term "evolution." Essentially, Darwin suggested that random variations occur in living things and that some external agents in the environment select individuals better able to survive. This method of selecting individuals is known as natural selection.
- Hugo de Vries' Mutation Theory suggests that sudden inheritable changes occur in an organism's genomes due to certain factors called mutations. These mutations lead to speciation (new species formation). Variation as the basis of evolution is the theme of Neo-Darwinism, supported by Hugo de Vries' Mutation Theory. Speciation is of the following types: sympatric, allopatric, and parapatric.
Question for Organic Evolution
Try yourself:
Which scientist proposed the theory that living organisms change by inheriting acquired characteristics?View Solution
Evidences for Evolution
In his book, Darwin offered several pieces of evidence supporting evolution. In a subdued manner, he attempted to convince the scientific community of the validity of his theory.

Mechanisms of Evolution
Evolution occurs in populations, not individuals. A population is an interbreeding group of individuals of one species in a given geographic area. A population evolves because it contains a collection of genes called the gene pool. As changes in the gene pool occur, the population evolves.
Human Evolution
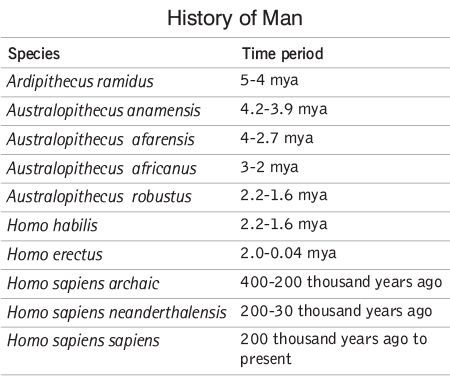
During the Miocene epoch, the family Hominoidea diverged into two sub-families: the Pongidae (apes) and the Hominidae (humans). The exact point of divergence between the ape and human lines is debatable. In general, Dryopithecus is considered the ancestor of both apes and humans.
- Dryopithecus: This genus lived in Africa, China, India, and Europe. The name Dryopithecus means oak wood apes.
- Ramapithecus: The first remains of Ramapithecus were discovered in the Shivalik hills of Punjab and later in Africa and Saudi Arabia. The region where Ramapithecines lived was not merely forest but open grassland. Fossil evidence indicates adaptations including robust jaws, thickened tooth enamel, and shorter canines. Extrapolation suggests an upright posture and the use of hands for food and defense.
- Australopithecus: This genus is the immediate forerunner of the genus Homo. The first Australopithecine find was made in 1924 at the Taung limestone quarry site in South Africa by Raymond Dart. They walked erect, lived on the ground, and probably used stones as weapons to hunt small animals. They weighed 60 to 90 pounds and were about 4 feet tall.
- Homo erectus: The first evidence of the Homo species was discovered in Java by Eugene Dubois in 1891, named Pithecanthropus erectus, meaning the erect ape man. Another find was made in China, southwest of Peking, called Peking man. These had a larger cranial capacity than Australopithecus, lived communally, and used fire.
- Homo sapiens neanderthalensis: Homo erectus gradually evolved into Homo sapiens. In this transitional event, two sub-species of Homo sapiens have been identified: the primitive man, labeled Homo sapiens Neanderthal, and the modern man, called Homo sapiens sapiens. Most evidence about the primitive man that has been unearthed is 75,000 years old.
- Homo sapiens sapiens: The first skeletal remains of Homo sapiens sapiens were found in Europe and were named Cro-Magnon. In Homo sapiens sapiens, there is a final reduction of the jaws, the appearance of the modern man's chin, and a rounded skull. The mean cranial capacity was about 1350 cc. Modern man is very closely related to Cro-Magnon. Their culture, dating back to 35,000 years, is also called the Upper Paleolithic culture.
- Kharai Camel:Kharai camels, or swimming camels, are found in Gujarat's Bhuj area. They are adapted to the extreme climate of the Rann, shallow seas, and high salinity. Kharai camels can live in both coastal and dry ecosystems. They graze on saline/mangrove trees and can swim up to three kilometers into the sea in search of mangroves, their primary food. They live in both wild and domestic settings.
The document Organic Evolution | General Awareness for SSC CGL is a part of the SSC CGL Course General Awareness for SSC CGL.
All you need of SSC CGL at this link: SSC CGL
|
448 videos|1497 docs|288 tests
|
FAQs on Organic Evolution - General Awareness for SSC CGL
| 1. What are some examples of evidences for evolution? |  |
Ans. Some examples of evidences for evolution include fossil records, comparative anatomy, molecular biology, and biogeography.
| 2. How does natural selection act as a mechanism of evolution? |  |
Ans. Natural selection is a process where organisms with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on those traits to their offspring. Over time, this leads to a gradual change in the population, resulting in evolution.
| 3. How does human evolution differ from other forms of evolution? |  |
Ans. Human evolution is a specific branch of organic evolution that focuses on the evolutionary history of the human species, Homo sapiens, and its ancestors. It involves studying the physical, behavioral, and genetic changes that have occurred in humans over time.
| 4. What are some theories of evolution that have been proposed? |  |
Ans. Some theories of evolution include Darwin's theory of natural selection, Lamarck's theory of acquired characteristics, and the modern synthetic theory of evolution which combines genetics with natural selection.
| 5. How does organic evolution relate to the concept of species diversity? |  |
Ans. Organic evolution is the process by which species change over time through genetic variation and natural selection. As species evolve and adapt to their environments, it leads to an increase in species diversity as new species emerge and existing species diverge into different forms.
Related Searches















